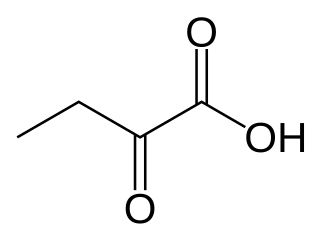
See also
Index of chemical compounds with the same name
This set index article lists chemical compounds articles associated with the same name.If an internal link led you here, you may wish to change the link to point directly to the intended article.