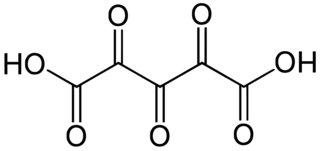
Ketoglutaric acid or oxoglutaric acid, or its conjugate base, the carboxylate ketoglutarate or oxoglutarate, may refer to the following chemical compounds:
- α-Ketoglutaric acid, an intermediate in the citric acid cycle
- β-Ketoglutaric acid (acetonedicarboxylic acid or 3-oxoglutaric acid)