
Arabic is a Semitic language that first emerged in the 1st to 4th centuries CE. It is now the lingua franca of the Arab world. It is named after the Arabs, a term initially used to describe peoples living in the area bounded by Mesopotamia in the east and the Anti-Lebanon mountains in the west, in Northwestern Arabia and in the Sinai Peninsula. The ISO assigns language codes to thirty varieties of Arabic, including its standard form, Modern Standard Arabic, also referred to as Literary Arabic, which is modernized Classical Arabic. This distinction exists primarily among Western linguists; Arabic speakers themselves generally do not distinguish between Modern Standard Arabic and Classical Arabic, but rather refer to both as al-ʿarabiyyatu l-fuṣḥā or simply al-fuṣḥā (اَلْفُصْحَىٰ).

French is a Romance language of the Indo-European family. It descended from the Vulgar Latin of the Roman Empire, as did all Romance languages. French evolved from Gallo-Romance, the Latin spoken in Gaul, and more specifically in Northern Gaul. Its closest relatives are the other langues d'oïl—languages historically spoken in northern France and in southern Belgium, which French (Francien) largely supplanted. French was also influenced by native Celtic languages of Northern Roman Gaul like Gallia Belgica and by the (Germanic) Frankish language of the post-Roman Frankish invaders. Today, owing to France's past overseas expansion, there are numerous French-based creole languages, most notably Haitian Creole. A French-speaking person or nation may be referred to as Francophone in both English and French.
Baja California, officially the Free and Sovereign State of Baja California, is a state in Mexico. It is the northernmost and westernmost of the 32 Federal Entities of Mexico. Before becoming a state in 1952, the area was known as the North Territory of Baja California. It has an area of 70,113 km2 (27,071 sq mi), or 3.57% of the land mass of Mexico and comprises the northern half of the Baja California Peninsula, north of the 28th parallel, plus oceanic Guadalupe Island. The mainland portion of the state is bordered on the west by the Pacific Ocean, on the east by Sonora, the U.S. state of Arizona, and the Gulf of California, and on the south by Baja California Sur. Its northern limit is the U.S. state of California.

Amerind is a hypothetical higher-level language family proposed by Joseph Greenberg in 1960 and elaborated by his student Merritt Ruhlen. Greenberg proposed that all of the indigenous languages of the Americas belong to one of three language families, the previously established Eskimo–Aleut and Na–Dene, and with everything else—otherwise classified by specialists as belonging to dozens of independent families—as Amerind. Due to a large number of methodological flaws in the 1987 book Language in the Americas, the relationships he proposed between these languages have been rejected by the majority of historical linguists as spurious.

The Kumeyaay, also known as Tipai-Ipai, formerly Kamia or Diegueño, are Native American people of the extreme southwestern United States and northwest Mexico. They live in the states of California in the US and Baja California in Mexico. In Spanish, the name is commonly spelled Kumiai.
Yuman music is the music of Yumans, a group of Native American tribes from what is now Southern California and Baja California. They include Paipai, Havasupai, Yavapai, Walapai, Mohave, Quechan. Maricopa, Tipai-Ipai, Cocopa, and Kiliwa people. Folk songs in Yuma culture are said to be given to a person while dreaming. Many individuals who are in emotional distress go to a secluded area for a few weeks, there to receive new songs.

Mission Santo Domingo was founded among the Kiliwa Indians of Baja California, Mexico, by the Dominicans Miguel Hidalgo and Manuel García in 1775. It is located near Colonia Vicente Guerrero and northeast of San Quintín Bay.

The Yuman–Cochimí languages are a family of languages spoken in Baja California, northern Sonora, southern California, and western Arizona. Cochimí is no longer spoken as of the late 18th century, and most other Yuman languages are threatened.

Mission Santa Catarina was founded on November 12, 1797 in the present-day Valle of El Álamo in the municipio of Ensenada, Baja California, México, by the Dominican missionary José Loriente. The ruins of the Mission are located at 31°49′38″N115°49′16″W.

Many different languages are spoken in Mexico, though Spanish is the most widespread. The indigenous languages are from eleven distinct language families, including four isolates and one that immigrated from the United States. The Mexican government recognizes 68 national languages, 63 of which are indigenous, including around 350 dialects of those languages. The large majority of the population is monolingual in Spanish. Some immigrant and indigenous populations are bilingual, while some indigenous people are monolingual in their languages. Mexican Sign Language is spoken by much of the deaf population, and there are one or two indigenous sign languages as well.

Mission San Pedro Mártir was established by the Dominican missionary José Loriente on 27 April 1794, in the Sierra San Pedro mountain range in northern Baja California, Mexico.

Sierra de San Pedro Mártir National Park is a national park in the Mexican state of Baja California. The Park is part of the municipality of Ensenada, Baja California. The area was first explored by Europeans in 1701 by Eusebio Francisco Kino by Dominican orders.
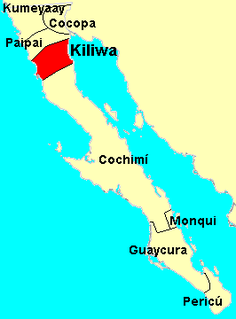
The Kiliwa are an indigenous people of Mexico living in northern Baja California. Historically they occupied a territory lying between the Cochimí on the south and the Paipai on the north, and extending from San Felipe on the Gulf of California to San Quintín on the Pacific coast. Their traditional language is the Kiliwa language.

The Paipai are an indigenous people of Mexico living in northern Baja California. Their traditional territory lies between the Kiliwa on the south and the Kumeyaay and Cocopa on the north, and extending from San Vicente near the Pacific coast nearly to the Colorado River's delta in the east. Today they are concentrated primarily at the multi-ethnic community of Santa Catarina in Baja California's Sierra de Juárez.
Peveril Meigs, III, was an American geographer, notable for his studies of arid lands on several continents and in particular for his work on the native peoples and early missions of northern Baja California, Mexico.

English is a West Germanic language that was first spoken in early medieval England and eventually became a global lingua franca. It is named after the Angles, one of the Germanic tribes that migrated to the area of Great Britain that later took their name, England. Both names derive from Anglia, a peninsula on the Baltic Sea. English is most closely related to Frisian and Low Saxon, while its vocabulary has been significantly influenced by other Germanic languages, particularly Norse, as well as Latin, Norman and French.
The Inaja Band of Diegueño Mission Indians of the Inaja and Cosmit Reservation is a federally recognized tribe of Kumeyaay Indians, who are sometimes known as Mission Indians.
Kiliwa, alternate Names: Kiliwi, Ko’lew or Quiligua is a Yuman language spoken in Baja California, in the far northwest of Mexico, by the Kiliwa people.

El Vallecito is an archaeological site located in the city of La Rumorosa, in the Tecate Municipality, Baja California, Mexico.
The Master-Apprentice Language Learning Program is a program to help younger community members learn their language of heritage with fluent elders in the community, typically in the form of a summer program.














