These are lists of incumbents, including heads of states or of subnational entities.

Togo, officially the Togolese Republic, is a country in West Africa. It is bordered by Ghana to the west, Benin to the east and Burkina Faso to the north. It is one of the least developed countries and extends south to the Gulf of Guinea, where its capital, Lomé, is located. It is a small, tropical country, which covers 57,000 square kilometres and has a population of approximately 8 million, and has a width of less than 115 km (71 mi) between Ghana and its eastern neighbor Benin.
The history of Togo can be traced to archaeological finds which indicate that ancient local tribes were able to produce pottery and process tin. During the period from the 11th century to the 16th century, the Ewé, the Mina, the Gun, and various other tribes entered the region. Most of them settled in coastal areas. The Portuguese arrived in the late 15th century, followed by other European powers. Until the 19th century, the coastal region was a major slave trade centre, earning Togo and the surrounding region the name "The Slave Coast".

British Togoland, officially the Mandate Territory of Togoland and later officially the Trust Territory of Togoland, was a territory in West Africa under the administration of the United Kingdom, which subsequently entered a union with Ghana, part of which became its Volta Region. The territory was effectively formed in 1916 by the splitting of the German protectorate of Togoland into two territories, French Togoland and British Togoland, during the First World War. Initially, it was a League of Nations Class B mandate. In 1922, British Togoland was formally placed under British rule, and French Togoland, now Togo, was placed under French rule.

The music of Togo has produced a number of internationally known popular entertainers including Bella Bellow, Akofah Akussah, Afia Mala, Itadi Bonney, Wellborn, King Mensah and Jimi Hope.
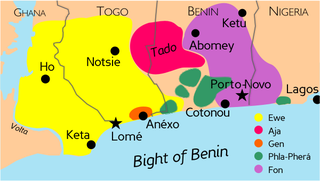
Ewe is a language spoken by approximately 20 million people in West Africa, mainly in Ghana, Togo and Benin, and also in some other countries like Liberia and southwestern Nigeria. Ewe is part of a cluster of related languages commonly called the Gbe languages. The other major Gbe language is Fon, which is mainly spoken in Benin. Like many African languages, Ewe is tonal as well as a possible member of the Niger-Congo family.
The Aja also spelled Adja are an ethnic group native to south-western Benin and south-eastern Togo. According to oral tradition, the Aja migrated to southern Benin in the 12th or 13th century from Tado on the Mono River, and c. 1600, three brothers, Kokpon, Do-Aklin, and Te-Agbanlin, split the ruling of the region then occupied by the Aja amongst themselves: Kokpon took the capital city of Great Ardra, reigning over the Allada kingdom; Do-Aklin founded Abomey, which would become capital of the Kingdom of Dahomey; and Te-Agbanlin founded Little Ardra, also known as Ajatche, later called Porto Novo by Portuguese traders and the current capital city of Benin.

The Gbe languages form a cluster of about twenty related languages stretching across the area between eastern Ghana and western Nigeria. The total number of speakers of Gbe languages is between four and eight million. The most widely spoken Gbe language is Ewe, followed by Fon. The Gbe languages were traditionally placed in the Kwa branch of the Niger–Congo languages, but more recently have been classified as Volta–Niger languages. They include five major dialect clusters: Ewe, Fon, Aja, Gen (Mina), Gun and Phla–Pherá.

The Anlo Ewe are a sub-group of the Ewe people of approximately 6 million people, inhabiting southern Togo, southern Benin, southwest Nigeria, and south-eastern parts of the Volta Region of Ghana; meanwhile, a majority of Ewe are located in the entire southern half of Togo and southwest Benin. They are a patrilineal society governed by a hierarchal, centralized authority. Their language is a dialect of the Ewe language, itself part of the Gbe language cluster. The Ewe religion is centered on the Supreme God, Mawu and several intermediate divinities. Christianity has been accepted in every part of Anlo Ewe land, with a minority of people still practicing traditional Vodun beliefs. The Vodu religion is slowly becoming a previous religion among the Anlo Ewes, with the youth of the community today practicing Christianity much more. However, those who still practice the Vodu religion also believe their tradition is a factor that keeps integrity and probit, while Christianity stands to pave way for integrity, honesty and probity to be washed away as years go by. It is for this reason that some Anlo Ewe people do away with Christianity when it comes to issues of accountability.

The Ewe people are a Gbe-speaking ethnic group. The largest population of Ewe people is in Ghana, and the second largest population is in Togo. They speak the Ewe language which belongs to the Gbe family of languages. They are related to other speakers of Gbe languages such as the Fon, Gen, Phla Phera, Gun, Maxi, and the Aja people of Togo, Benin and southwestern Nigeria.

Aflao is a town in Ketu South District in the Volta Region on Ghana's border with Togo. Aflao is the twenty-eighth most populous settlement in Ghana, in terms of population, with a population of 96,550 people.
Notsé is a town in the Plateaux Region of Togo. It is the capital of Haho Prefecture and is situated 95 km north of the capital Lomé. The town was formed around 1600 by the Ewe people, after they were displaced westward by the expansion of the Yoruba.
The Lambas are an ethnic and linguistic group of people living in the Kéran and Doufelgou Districts (Préfecture) of the Kara Region in Northern Togo and in the Atakora and Donga Departments of Bénin, West Africa. The capital of the Kéran District is Kanté and the capital of the Doufelgou District is Niamtougou.

King Mensah, also known as "The Golden Voice of Togo", is a Togolese singer from West Africa. Though based in Lomé, he regularly records and promotes his albums in Paris, and has embarked on several world tours since 2005. Singing in Mina, Ewe, and French, King Mensah's sound fuses elements of traditional Ewe music, and Kabye dance-drum music, with funk, reggae and West African Afropop. King Mensah's lyrical themes are steeped in religion and hopeful encouragement for the orphaned, oppressed and downtrodden.

Rail transport in Togo began in 1905.

The Ewe Unification Movement was a series of west African ethno-nationalist efforts which sought the unification of the Ewe peoples spread across what are now modern Ghana and Togo. It emerged as a direct political goal around 1945 under the colonial mandate of French Togoland, however the ideal of unifying the group has been an identifiable sentiment present amongst the ethnicity's leadership and wider population ever since their initial colonial partitions by the British and German Empires from 1874 to 1884. While there have been many efforts to bring about unification, none have ultimately been successful due to both the platform itself often being a secondary concern for political leadership, or inter/intrastate conflicts overshadowing them.

The Benin–Togo border is 651 km in length and runs from the tripoint with Burkina Faso in the north down to the Bight of Benin in the south.
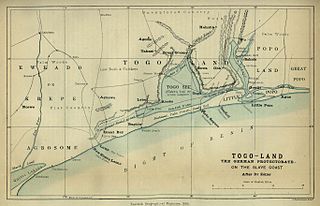
The kingdom of Togo-Bè was a precolonial state located in the south of modern day Togo, founded by Ewe people. It was situated around the Togo lake and has possibly encompassed an area of 600 km². The foundation of the kingdom remains unclear and its history is widely disputed. Togo-Bè lost its independence when it became a protectorate of the German Empire on 5 July, 1884. A treaty was signed by its last ruling king Mlapa III and German explorer Gustav Nachtigal. The treaty declared a German protectorate over a stretch of territory along the Slave Coast on the Bight of Benin. With the small gunboat SMS Möwe at anchor, the imperial flag was raised for the first time on the African continent. Consul Heinrich Ludwig Randad Jr., resident agent of the firm C. Goedelts at Ouidah, was appointed as the first commissioner for the territory. The most important exports were slaves, until local slavery was declared illegal and was abolished by the French in 1848, but cotton, sisal fibre, cacao beans and different textiles were also traded. Because of the slave trade ban, its economy was ravaged and its kings lost most of the power, so it was easily colonized. Traditionally the kingdom was animist, but by 1884 had moved towards Christianity due to the influence of German missionaries operating in the region since 1847.









