Overview
Knowledge environments departing from constructivist epistemology assume that domain knowledge is built in and results from cognitive and/or social practices. From this perspective the primary purpose of knowledge environments is to host and support activities of knowledge building, the means including cognitive ergonomics, social software, immediate information access exploiting means of multimedia and hypertext, content contribution functionalities and structured ontologies. Wikipedia itself is a prototypical example of a knowledge environment in this sense.
From another perspective, the purpose of a knowledge environment can be defined as a method to facilitate consistent knowledge outcomes. Knowledge outcomes reveal themselves as learning, communication, goals, decisions, etc. Consistent knowledge outcomes imply predictable learning results or replicable communication results and predictable quality of decisions. The design of knowledge environments is both commonplace activity and specialised expert work. At a simplistic level every teacher, every author, every librarian and every database manager is a creator of a knowledge environment. At a specialized level, knowledge environments need sophisticated architecture and modeling capabilities. This approach is necessary when the creator of the knowledge environment wants to deliver replicable results in hundreds of specific instances of the same knowledge environment. On the other hand, the strengthening trend of public authorship leads to open-ended ontologies by means of, say, tagging or folksonomies. In a significant sense, knowledge environments are in such cases created not only by their authors or owners but also by the contributors of their ontologies.
Educational psychology is the branch of psychology concerned with the scientific study of human learning. The study of learning processes, from both cognitive and behavioral perspectives, allows researchers to understand individual differences in intelligence, cognitive development, affect, motivation, self-regulation, and self-concept, as well as their role in learning. The field of educational psychology relies heavily on quantitative methods, including testing and measurement, to enhance educational activities related to instructional design, classroom management, and assessment, which serve to facilitate learning processes in various educational settings across the lifespan.
Educational games are games explicitly designed with educational purposes, or which have incidental or secondary educational value. All types of games may be used in an educational environment, however Educational games are games that are designed to help people learn about certain subjects, expand concepts, reinforce development, understand a historical event or culture, or assist them in learning a skill as they play. Game types include board, card, and video games. As educators, governments, and parents realize the psychological need and benefits that gaming has on learning, this educational tool has become mainstream. Games are interactive play that teach us goals, rules, adaptation, problem solving, interaction, all represented as a story. They satisfy our fundamental need to learn by providing enjoyment, passionate involvement, structure, motivation, ego gratification, adrenaline, creativity, social interaction and emotion in the game itself while the learning takes place.

Problem-based learning (PBL) is a student-centered pedagogy in which students learn about a subject through the experience of solving an open-ended problem found in trigger material. The PBL process does not focus on problem solving with a defined solution, but it allows for the development of other desirable skills and attributes. This includes knowledge acquisition, enhanced group collaboration and communication. The PBL process was developed for medical education and has since been broadened in applications for other programs of learning. The process allows for learners to develop skills used for their future practice. It enhances critical appraisal, literature retrieval and encourages ongoing learning within a team environment.

IDEF, initially an abbreviation of ICAM Definition and renamed in 1999 as Integration Definition, is a family of modeling languages in the field of systems and software engineering. They cover a wide range of uses from functional modeling to data, simulation, object-oriented analysis and design, and knowledge acquisition. These definition languages were developed under funding from U.S. Air Force and, although still most commonly used by them and other military and United States Department of Defense (DoD) agencies, are in the public domain.
Situated cognition is a theory that posits that knowing is inseparable from doing by arguing that all knowledge is situated in activity bound to social, cultural and physical contexts.
Distributed cognition is an approach to cognitive science research that deploys models of the extended mind by taking as the fundamental unit of analysis "a collection of individuals and artifacts and their relations to each other in a particular work practice". "DCog" is a specific approach to distributed cognition which takes a computational perspective towards goal-based activity systems.
Human-centered computing (HCC) studies the design, development, and deployment of mixed-initiative human-computer systems. It is emerged from the convergence of multiple disciplines that are concerned both with understanding human beings and with the design of computational artifacts. Human-centered computing is closely related to human-computer interaction and information science. Human-centered computing is usually concerned with systems and practices of technology use while human-computer interaction is more focused on ergonomics and the usability of computing artifacts and information science is focused on practices surrounding the collection, manipulation, and use of information.
A collaboratory, as defined by William Wulf in 1989, is a “center without walls, in which the nation’s researchers can perform their research without regard to physical location, interacting with colleagues, accessing instrumentation, sharing data and computational resources, [and] accessing information in digital libraries”.
Educational technology is the combined use of computer hardware, software, and educational theory and practice to facilitate learning. When referred to with its abbreviation, EdTech, it is often referring to the industry of companies that create educational technology.
Situational awareness or situation awareness (SA) is the perception of environmental elements and events with respect to time or space, the comprehension of their meaning, and the projection of their future status.
Computer-supported collaborative learning (CSCL) is a pedagogical approach wherein learning takes place via social interaction using a computer or through the Internet. This kind of learning is characterized by the sharing and construction of knowledge among participants using technology as their primary means of communication or as a common resource. CSCL can be implemented in online and classroom learning environments and can take place synchronously or asynchronously.
Evolutionary educational psychology is the study of the relation between inherent folk knowledge and abilities and accompanying inferential and attributional biases as these influence academic learning in evolutionarily novel cultural contexts, such as schools and the industrial workplace. The fundamental premises and principles of this discipline are presented below.

Enterprise modelling is the abstract representation, description and definition of the structure, processes, information and resources of an identifiable business, government body, or other large organization.
Social cognitive theory (SCT), used in psychology, education, and communication, holds that portions of an individual's knowledge acquisition can be directly related to observing others within the context of social interactions, experiences, and outside media influences. This theory was advanced by Albert Bandura as an extension of his social learning theory. The theory states that when people observe a model performing a behavior and the consequences of that behavior, they remember the sequence of events and use this information to guide subsequent behaviors. Observing a model can also prompt the viewer to engage in behavior they already learned. In other words, people do not learn new behaviors solely by trying them and either succeeding or failing, but rather, the survival of humanity is dependent upon the replication of the actions of others. Depending on whether people are rewarded or punished for their behavior and the outcome of the behavior, the observer may choose to replicate behavior modeled. Media provides models for a vast array of people in many different environmental settings.
Narrative-based learning is a learning model grounded in the theory that humans define their experiences within the context of narratives – which serve as cognitive structures and a means of communication, as well as aiding people in framing and understanding their perceptions of the world. Narrative contextualises abstract concepts and provides a scaffold for the transfer of knowledge within specific contexts and environments. This model aligns with the constructivist ideals of situated learning—which theorises that active learning takes place within the context in which the knowledge must be applied. Anchored Instruction is a type of situated learning that presents students with a realistic narrative within a specific context. At the narrative's core is a problem that must be solved by constructing and applying the knowledge within the targeted learning domain.
Goal orientation is an "individual disposition towards developing or validating one's ability in achievement settings."
Embodied cognition is the theory that many features of cognition, whether human or otherwise, are shaped by aspects of the entire body of the organism. The features of cognition include high level mental constructs and performance on various cognitive tasks. The aspects of the body include the motor system, the perceptual system, bodily interactions with the environment (situatedness), and the assumptions about the world that are built into the structure of the organism.
Positive interdependence is an element of cooperative and collaborative learning where members of a group who share common goals perceive that working together is individually and collectively beneficial, and success depends on the participation of all the members.
In education, authentic learning is an instructional approach that allows students to explore, discuss, and meaningfully construct concepts and relationships in contexts that involve real-world problems and projects that are relevant to the learner. It refers to a "wide variety of educational and instructional techniques focused on connecting what students are taught in school to real-world issues, problems, and applications. The basic idea is that students are more likely to be interested in what they are learning, more motivated to learn new concepts and skills, and better prepared to succeed in college, careers, and adulthood if what they are learning mirrors real-life contexts, equips them with practical and useful skills, and addresses topics that are relevant and applicable to their lives outside of school."
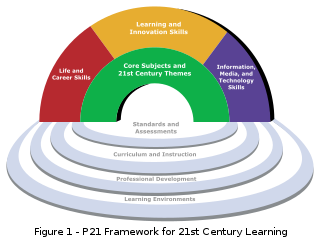
21st century skills comprise skills, abilities, and learning dispositions that have been identified as being required for success in 21st century society and workplaces by educators, business leaders, academics, and governmental agencies. This is part of a growing international movement focusing on the skills required for students to master in preparation for success in a rapidly changing, digital society. Many of these skills are also associated with deeper learning, which is based on mastering skills such as analytic reasoning, complex problem solving, and teamwork. These skills differ from traditional academic skills in that they are not primarily content knowledge-based.




