
Euler's formula, named after Leonhard Euler, is a mathematical formula in complex analysis that establishes the fundamental relationship between the trigonometric functions and the complex exponential function. Euler's formula states that for any real number x:
In probability theory, the expected value of a random variable, intuitively, is the long-run average value of repetitions of the same experiment it represents. For example, the expected value in rolling a six-sided die is 3.5, because the average of all the numbers that come up is 3.5 as the number of rolls approaches infinity. In other words, the law of large numbers states that the arithmetic mean of the values almost surely converges to the expected value as the number of repetitions approaches infinity. The expected value is also known as the expectation, mathematical expectation, EV, average, mean value, mean, or first moment.
In mathematics, the factorial of a positive integer n, denoted by n!, is the product of all positive integers less than or equal to n. For example,

The median is the value separating the higher half from the lower half of a data sample. For a data set, it may be thought of as the "middle" value. For example, in the data set {1, 3, 3, 6, 7, 8, 9}, the median is 6, the fourth largest, and also the fifth smallest, number in the sample. For a continuous probability distribution, the median is the value such that a number is equally likely to fall above or below it.
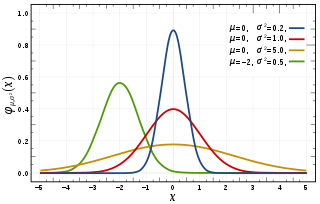
In probability theory, the normal distribution is a very common continuous probability distribution. Normal distributions are important in statistics and are often used in the natural and social sciences to represent real-valued random variables whose distributions are not known. A random variable with a Gaussian distribution is said to be normally distributed and is called a normal deviate.
The number π is a mathematical constant. Originally defined as the ratio of a circle's circumference to its diameter, it now has various equivalent definitions and appears in many formulas in all areas of mathematics and physics. It is approximately equal to 3.14159. It has been represented by the Greek letter "π" since the mid-18th century, though it is also sometimes spelled out as "pi". It is also called Archimedes' constant.
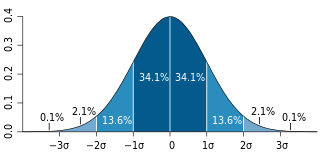
In statistics, the standard deviation is a measure that is used to quantify the amount of variation or dispersion of a set of data values. A low standard deviation indicates that the data points tend to be close to the mean of the set, while a high standard deviation indicates that the data points are spread out over a wider range of values.

In mathematics, the trigonometric functions are real functions which relate an angle of a right-angled triangle to ratios of two side lengths. They are widely used in all sciences that are related to geometry, such as navigation, solid mechanics, celestial mechanics, geodesy, and many others. They are among the simplest periodic functions, and as such are also widely used for studying periodic phenomena, through Fourier analysis.

In mathematics, a Taylor series is a representation of a function as an infinite sum of terms that are calculated from the values of the function's derivatives at a single point.

In probability theory and statistics, variance is the expectation of the squared deviation of a random variable from its mean. Informally, it measures how far a set of (random) numbers are spread out from their average value. Variance has a central role in statistics, where some ideas that use it include descriptive statistics, statistical inference, hypothesis testing, goodness of fit, and Monte Carlo sampling. Variance is an important tool in the sciences, where statistical analysis of data is common. The variance is the square of the standard deviation, the second central moment of a distribution, and the covariance of the random variable with itself, and it is often represented by
,
, or
.
The gas constant is also known as the molar, universal, or ideal gas constant, denoted by the symbol R or R and is equivalent to the Boltzmann constant, but expressed in units of energy per temperature increment per mole, i.e. the pressure–volume product, rather than energy per temperature increment per particle. The constant is also a combination of the constants from Boyle's law, Charles's law, Avogadro's law, and Gay-Lussac's law. It is a physical constant that is featured in many fundamental equations in the physical sciences, such as the ideal gas law and the Nernst equation.
2 (two) is a number, numeral, and glyph. It is the natural number following 1 and preceding 3.

Exponentiation is a mathematical operation, written as bn, involving two numbers, the base b and the exponent or power n. When n is a positive integer, exponentiation corresponds to repeated multiplication of the base: that is, bn is the product of multiplying n bases:

In statistics, the Pearson correlation coefficient, also referred to as Pearson's r, the Pearson product-moment correlation coefficient (PPMCC) or the bivariate correlation, is a measure of the linear correlation between two variables X and Y. According to the Cauchy–Schwarz inequality it has a value between +1 and −1, where 1 is total positive linear correlation, 0 is no linear correlation, and −1 is total negative linear correlation. It is widely used in the sciences. It was developed by Karl Pearson from a related idea introduced by Francis Galton in the 1880s and for which the mathematical formula was derived and published by Auguste Bravais in 1844.. The naming of the coefficient is thus an example of Stigler's Law.

In geology, the places known as hotspots or hot spots are volcanic regions thought to be fed by underlying mantle that is anomalously hot compared with the surrounding mantle. Their position on the Earth's surface is independent of tectonic plate boundaries. There are two hypotheses that attempt to explain their origins. One suggests that hotspots are due to mantle plumes that rise as thermal diapirs from the core–mantle boundary. The other hypothesis is that lithospheric extension permits the passive rising of melt from shallow depths. This hypothesis considers the term "hotspot" to be a misnomer, asserting that the mantle source beneath them is, in fact, not anomalously hot at all. Well-known examples include the Hawaii, Iceland and Yellowstone hotspots.

In probability theory and statistics, the continuous uniform distribution or rectangular distribution is a family of symmetric probability distributions such that for each member of the family, all intervals of the same length on the distribution's support are equally probable. The support is defined by the two parameters, a and b, which are its minimum and maximum values. The distribution is often abbreviated U(a,b). It is the maximum entropy probability distribution for a random variable X under no constraint other than that it is contained in the distribution's support.
In statistics, the bias of an estimator is the difference between this estimator's expected value and the true value of the parameter being estimated. An estimator or decision rule with zero bias is called unbiased. Otherwise the estimator is said to be biased. In statistics, "bias" is an objective property of an estimator, and while not a desired property, it is not pejorative, unlike the ordinary English use of the term "bias".

In probability theory and statistics, the Poisson distribution, named after French mathematician Siméon Denis Poisson, is a discrete probability distribution that expresses the probability of a given number of events occurring in a fixed interval of time or space if these events occur with a known constant rate and independently of the time since the last event. The Poisson distribution can also be used for the number of events in other specified intervals such as distance, area or volume.
Francisco G. Granfil is a retired Philippine Army enlisted trooper and a recipient the Philippines' highest military award for courage, the Medal of Valor.














