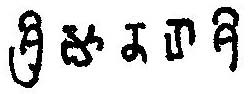Harappa is an archaeological site in Punjab, Pakistan, about 24 km (15 mi) west of Sahiwal. The site takes its name from a modern village located near the former course of the Ravi River which now runs 8 km (5.0 mi) to the north. The current village of Harappa is less than 1 km (0.62 mi) from the ancient site. Although modern Harappa has a legacy railway station from the British Raj period, it is a small crossroads town of 15,000 people today.

Telugu is a Dravidian language spoken by Telugu people predominantly living in the Indian states of Andhra Pradesh and Telangana, where it is also the official language. Telugu is also an official language in West Bengal, Yanam district of Puducherry and a linguistic minority in the states of Odisha, Karnataka, Tamil Nadu, Kerala, Punjab, Chhattisgarh, Maharashtra and Andaman and Nicobar Islands. It is one among the six languages designated as a classical language of India in the country. Telugu was also referred as Andhramu (ఆంధ్రము)

The Indus Valley Civilisation (IVC), also known as the Indus Civilisation, was a Bronze Age civilisation in the northwestern regions of South Asia, lasting from 3300 BCE to 1300 BCE, and in its mature form from 2600 BCE to 1900 BCE. Together with ancient Egypt and Mesopotamia, it was one of three early civilisations of the Near East and South Asia, and of the three, the most widespread, its sites spanning an area stretching from today's northeast Afghanistan, through much of Pakistan, and into western and northwestern India. It flourished in the basins of the Indus River, which flows through the length of Pakistan, and along a system of perennial, mostly monsoon-fed, rivers that once coursed in the vicinity of the seasonal Ghaggar-Hakra river in northwest India and eastern Pakistan.

Lothal was one of the southernmost cities of the ancient Indus Valley Civilization, located in the Bhāl region of the modern state of Gujarāt. Construction of the city began around 2200 BCE. Discovered in 1954, Lothal was excavated from 13 February 1955 to 19 May 1960 by the Archaeological Survey of India (ASI), the official Indian government agency for the preservation of ancient monuments. According to the ASI, Lothal had the world's earliest known dock, which connected the city to an ancient course of the Sabarmati river on the trade route between Harappan cities in Sindh and the peninsula of Saurashtra when the surrounding Kutch desert of today was a part of the Arabian Sea. However, this interpretation has been challenged by other archaeologists, who argue that Lothal was a comparatively small town, and that the "dock" was actually an irrigation tank. The controversy was finally settled when scientists from The National Institute of Oceanography, Goa discovered foraminifera and salt, gypsum crystals in the rectangular structure clearly indicating that sea water once filled the structure and it was definitely a dockyard. Lothal was a vital and thriving trade centre in ancient times, with its trade of beads, gems and valuable ornaments reaching the far corners of West Asia and Africa. The techniques and tools they pioneered for bead-making and in metallurgy have stood the test of time for over 4000 years.

Nandamuri Taraka Rama Rao, popularly known as Anna Garu, NTR was an Indian actor, producer, director, film editor and politician who served as Chief Minister of Andhra Pradesh for seven years over three terms. He starred in over 300 films, predominantly in Telugu cinema, and was referred to as Viswa Vikhyatha Nata Sarwa Bhouma. Rao received three National Film Awards for co-producing Thodu Dongalu (1954) and Seetharama Kalyanam (1960) under National Art Theater, Madras, and for directing Varakatnam (1970). He has received the erstwhile Rashtrapati Awards for his performance in the Raju Peda (1954) and the Lava Kusa (1963). He garnered the Nandi Award for Best Actor for Kodalu Diddina Kapuram in 1970, and the Inaugural Filmfare Award for Best Actor – Telugu in 1972 for Badi Panthulu.

Brahmi is a writing system of ancient South Asia. The Brahmi writing system, or script, appeared as a fully developed universal one in South Asia in the third century BCE, and is a forerunner of all writing systems that have found use in South Asia with the exception of the Indus script of the third millennium BCE, the Kharosthi script, which originated in what today is northwestern Pakistan in the fourth or possibly fifth century BCE, the Perso–Arabic scripts since the medieval period, and the Latin scripts of the modern period. Its descendants, the Brahmic scripts, continue to be in use today not only in South Asia, but also Southeast Asia.

The Indus script is a corpus of symbols produced by the Indus Valley Civilization. Most inscriptions containing these symbols are extremely short, making it difficult to judge whether or not these symbols constituted a script used to record a language, or even symbolise a writing system. In spite of many attempts, the 'script' has not yet been deciphered, but efforts are ongoing. There is no known bilingual inscription to help decipher the script, and the script shows no significant changes over time. However, some of the syntax varies depending upon location.

The Archaeological Survey of India (ASI) is an Indian government agency attached to the Ministry of Culture that is responsible for archaeological research and the conservation and preservation of cultural monuments in the country. It was founded in 1861 by Alexander Cunningham who also became its first Director-General.
Navaratna Srinivasa Rajaram was an Indian academic,notable for his publications from the Voice of India publishing house, propounding the "Indigenous Aryans" hypothesis and asserting that the Vedic period was extremely advanced from a scientific view-point. Rajaram also claimed to have deciphered the Indus script which was rejected by scholars.

Telugu literature is the body of works written in the Telugu language. It consists of poems, short stories, novels, plays, and song lyrics, among others. There is some indication that Telugu literature dates at least to the middle of the first millennium, the first extant works are from the 11th century when the Mahabharata was first translated to Telugu from Sanskrit by Nannaya. The language experienced a golden age under the patronage of the Vijayanagara king-poet Krishnadevaraya.

Asko Parpola is a Finnish Indologist and Sindhologist, current professor emeritus of Indology and South Asian Studies at the University of Helsinki. He specializes in the Indus script.

Shikaripura Ranganatha Rao, commonly known as Dr. S. R. Rao, was an Indian archaeologist who led teams credited with discoveries of a number of Harappan sites including the port city Lothal and Bet Dwarka in Gujarat.

Pendyala Varavara Rao is an Indian activist, poet, teacher, and writer from Telangana, India. He is an accused in the 2018 Bhima Koregaon violence and has been arrested under the Unlawful Activities (Prevention) Act. Rao was arrested on the charge of plotting to assassinate Indian prime minister.

Vundavalli Arun Kumar is a Public Speaker, Lawyer, Political Analyst and former Member of Parliament in India. He was elected to the 14th Lok Sabha and 15th Lok Sabha from Rajahmundry constituency of Andhra Pradesh. He was a member of the Indian National Congress party.
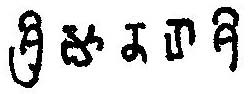
The Kadamba script is the first writing system devised specifically for writing Kannada and Telugu. It is a descendant of the Brahmi script. The Kadamba script is also known as Pre-Old-Kannada script. This script later became popular in what is today the state of Goa and was used to write Kannada and Sanskrit.

Dr. Burgula Ramakrishna Rao was the first elected Chief Minister of the erstwhile Hyderabad State. Prior to the independence of India and the political integration of the princely states into the Union, he was among the Telugu-speaking leaders to resist the Nizam in the princely state of Hyderabad.
Kanuru Lakshmana Rao was an Indian engineer and a Padma Bhushan awardee who served as the Union Minister of Irrigation & Power and Member of Parliament for Vijayawada from 1962 to 1977.
Pavani Parameswara Rao was a Senior Advocate practising in the Supreme Court of India. Widely considered a doyen of Constitutional Law, he had argued a number of landmark cases before the Supreme Court. He died on 13 September 2017 in a private hospital in South Delhi following a cardiac arrest, India.
Megalithic markings, Megalithic graffiti marks, Megalithic symbols or Non-Brahmi symbols are terms used to describe markings found on mostly potsherds found in Central India, South India and Sri Lanka during the Megalithic Iron Age period. They are usually found in burial sites but are also found in habitation sites as well. They are tentatively dated from 1000 BCE to 300 CE marking the transition of the proto-historic period into the historic period of South Asia. A number of scholars have tried to decipher the symbols since 1878, and currently there is no consensus as to whether they constitute undeciphered writing or graffiti or symbols without any syllabic or alphabetic meaning.

RX 100 is a 2018 Indian Telugu-language romantic action drama film written and directed by Ajay Bhupathi. The film features Kartikeya Gummakonda and Payal Rajput in the lead roles with Rao Ramesh and Ramki playing the supporting roles. This film was remade into Hindi as Tadap.