
Berlin Hauptbahnhof is the main railway station in Berlin, Germany. It came into full operation two days after a ceremonial opening on 26 May 2006. It is located on the site of the historic Lehrter Bahnhof, and on the Berlin S-Bahn suburban railway. The station is owned by DB InfraGO, a subsidiary of Deutsche Bahn AG, and is classified as a Category 1 station, one of 21 in Germany and four in Berlin, the others being Berlin Gesundbrunnen, Berlin Südkreuz and Berlin Ostbahnhof.
The Hanover Fairground is an exhibition area in the Mittelfeld district of Hanover, Germany. Featuring 392,453 m² of covered indoor space, 58,000 m² of open-air space, 24 halls and pavilions, and a convention center with 35 function rooms, it is the largest exhibition ground in the world.

Frankfurt (Main) Hauptbahnhof, also called Frankfurt Central Station and Frankfurt Main Station, is the busiest train station in the German state of Hesse. Due to its location near the middle of Germany and usage as a transport hub for long and short distance travelling, Deutsche Bahn refers to it as the most important station in Germany.

Hannover Hauptbahnhof is the main railway station for the city of Hanover in Lower Saxony, Germany. The railway junction is one of the 21 stations listed as a railway Category 1 station by DB Station&Service. It is also the most important public transport hub of the region of Hanover and it is served regional and S-Bahn services. The station has six platforms with twelve platform tracks, and two through tracks without platforms. Every day it is used by 250,000 passengers and 622 trains stop at the platforms. About 2,000 people work here.

The Hanover Stadtbahn is a Stadtbahn system in the city of Hanover, Lower Saxony, Germany. The Stadtbahn opened on 29 September 1975, gradually replacing the city's tramway network over the course of the following 25 years. Currently, the Hanover Stadtbahn system consists of 12 main lines, serving 201 stations, and operating on 121 kilometres (75 mi) of route. The system is run by üstra, which was originally an abbreviation for Überlandwerke und Straßenbahnen Hannover AG. As of 2007, it transported 125 million passengers per year.

The Hanover S-Bahn is an S-Bahn network operated by DB Regio and Transdev Hannover in the area of Hanover in the German state capital of Lower Saxony. It went operational shortly before Expo 2000 and is focused on the Hanover region, and also connects with adjacent districts, and into the state of North Rhine-Westphalia. The S-Bahn is an evolution of a suburban railway.

Hamburg Hauptbahnhof, or Hamburg Central Railway Station in English, is the main railway station of the city of Hamburg, Germany. Opened in 1906 to replace four separate terminal stations, today Hamburg Hauptbahnhof is operated by DB Station&Service AG. With an average of 550,000 passengers a day, it is Germany's busiest railway station and the second-busiest in Europe after the Gare du Nord in Paris. It is classed by Deutsche Bahn as a category 1 railway station.

Köln Hauptbahnhof is the central railway station of Cologne, Germany. The station is an important local, national and international transport hub, with many ICE, Eurostar and Intercity trains calling there, as well as regional Regional-Express, RegionalBahn and local S-Bahn trains. EuroNight and Nightjet night services also call at the station. It has frequent connections to Frankfurt by way of the Cologne–Frankfurt high-speed rail line, which starts in southern Cologne. On an average day, about 280,000 travellers frequent the station, making it the fifth busiest station in Germany.

Essen Hauptbahnhof is a railway station in the city of Essen in western Germany. It is situated south of the old town centre, next to the A 40 motorway. It was opened in 1862 by the Bergisch-Märkische Eisenbahn. However, the station was not the first in Essen: as the station called Essen on the Köln-Mindener Eisenbahn was opened in 1847.

Bochum Hauptbahnhof is a railway station for the city of Bochum in western Germany. In its current incarnation, it was built from 1955 to 1957 and is one of the most notable 1950s railway stations in Germany. The station underwent extensive remodeling and modernisation from 2004 to 2006 and was officially reopened on 29 May 2006.

The Berlin Stadtbahn is the historic east-west elevated railway of Berlin. It runs from Friedrichshain in the east to Charlottenburg in the west, connecting several of the most major sights of the German capital. The line is protected cultural heritage since 1995. It is often defined more simply as the slightly longer route between Ostkreuz and Westkreuz, although this is not technically correct.

Braunschweig Hauptbahnhof is a railway station in the German city of Braunschweig (Brunswick). It is about 1.5 km (0.93 mi) southeast of the city centre and was opened on 1 October 1960, replacing the old passenger station on the southern edge of the old town. The train services are operated by Deutsche Bahn, Erixx, Metronom and WestfalenBahn.

The Karlsruhe Stadtbahn is a German tram-train system combining tram lines in the city of Karlsruhe with railway lines in the surrounding countryside, serving the entire region of the middle upper Rhine valley and creating connections to neighbouring regions. The Stadtbahn combines an efficient urban railway in the city with an S-Bahn, overcoming the boundary between trams and trains. Its logo does not include the green and white S-Bahn symbol used in other German suburban rail systems and the symbol is only used at stops and stations outside the inner-city tram-operation area.

The Hanover–Brunswick Railway is a German main line railway in Lower Saxony and is one of the oldest lines in Germany, opened in 1843 and 1844. It was the first railway line linking to the city of Hanover and the first operating line of the Royal Hanoverian State Railways. It is now one of the main routes for east-west traffic. The main intermediate station is Peine.
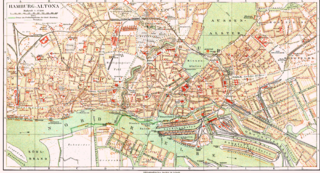
The Hamburg-Altona link line is a railway line in Hamburg, Germany. Nowadays, it connects the lines from the north and northwest of Hamburg and Altona station with Hamburg Hauptbahnhof and the lines to the southwest, south and east. Initially designed as a freight line only, it is now one of the busiest lines in Germany. It includes the suburban tracks of the Hamburg Stadtbahn, originally the core of the Hamburg S-Bahn.

Hannover Messe/Laatzen station is a Category 4 station in the German town of Laatzen near the Hanover fairground. It is normally served only by the Hanover S-Bahn. During major events such as CeBIT and Hanover Messe, all passing regional and long distance trains stop at the station. The station opened in 2000, replacing the old Messe station, which was located on a spur line in the fairgrounds.

The Red Thread is a 4.2-kilometre (2.6 mi) urban walking trail in Hanover, Germany, to 36 significant points of interest about architecture and the history of the city centre.
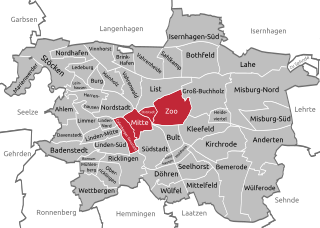
Mitte is the first borough of Hanover, the state capital of Lower Saxony. As of 2020, it has 36,645 inhabitants and consists of the quarters Mitte, Calenberger Neustadt, Oststadt and Zoo. The district mayor is Cornelia Kupsch (CDU).

Hannover-Linden/Fischerhof is a railway station located in Hannover, Germany. The station opened in 1872 and is located on the Hanover–Altenbeken line and the Hanover freight bypass. The train services are operated by Deutsche Bahn as part of the Hanover S-Bahn.

Aegidien Gate Square is a busy square known colloquially as Aegi in Hanover, Germany. Located above a subway station of the same name, the square was named for the Aegidien Gate, one of the city gates of medieval Hanover. While the gate was removed in 1780, the square is still named after it.





















