Kurt Linck (born 1889), was a German writer of the Religiongeschichteschule . He wrote in Latin, about the non-Biblical references to Jesus. His works are cited as a reliable source (e.g. for the usualness of the name Chrestus in the Roman Empire) in books written in the 1920s (Judentum und Heidentum zur Zeit Christi und der Apostel by Dr. Joseph Felten [1851 - 1929], 1925, Jesus the Nazarene: Myth or History by Maurice Goguel, 1926) and in modern works (e.g. The Jesus of the Early Christians by G. A. Wells, 1971, Jesus Outside the New Testament: An Introduction to the Ancient Evidence, Robert E. Van Voorst, 2000, Den Jesus som aldrig funnits, Roger Viklund, 2005).

The terms anno Domini (AD) and before Christ (BC) are used to label or number years in the Julian and Gregorian calendars. The term anno Domini is Medieval Latin and means "in the year of the Lord" but is often presented using "our Lord" instead of "the Lord", taken from the full original phrase "anno Domini nostri Jesu Christi", which translates to "in the year of our Lord Jesus Christ". The form "BC" is specific to English, and equivalent abbreviations are used in other languages: the Latin form, rarely used in English, is Ante Christum natum (ACN) or Ante Christum (AC).

The extant manuscripts of the book Antiquities of the Jews, written by the first-century Jewish historian Flavius Josephus around AD 93–94, contain two references to Jesus of Nazareth and one reference to John the Baptist.

Flavius Josephus was a Roman–Jewish historian and military leader. Best known for writing The Jewish War, he was born in Jerusalem—then part of the Roman province of Judea—to a father of priestly descent and a mother who claimed royal ancestry.

The Roman historian and senator Tacitus referred to Jesus, his execution by Pontius Pilate, and the existence of early Christians in Rome in his final work, Annals, book 15, chapter 44.

Bruno Bauer was a German philosopher and theologian. As a student of G. W. F. Hegel, Bauer was a radical Rationalist in philosophy, politics and Biblical criticism. Bauer investigated the sources of the New Testament and, beginning with Hegel's Hellenophile orientation, concluded that early Christianity owed more to ancient Greek philosophy (Stoicism) than to Judaism.

Abgar V, called Ukkāmā, was the King of Osroene with his capital at Edessa.

Jakob Balde, a German poet who wrote primarily in Neo-Latin rather than in his native German language, was born at Ensisheim in Alsace.

Noli me tangere is the Latin version of a phrase spoken, according to John 20:17, by Jesus to Mary Magdalene when she recognized him after his resurrection. The biblical scene has been portrayed in numerous works of Christian art from Late Antiquity to the present. The phrase has also been used in literature, and later in a variation by military units since the late 18th century.

Joseph ben Caiaphas, known simply as Caiaphas in the New Testament, was the Jewish high priest during the years of Jesus' ministry, according to Josephus. The Gospels of Matthew, Luke and John indicate he was an organizer of the plot to kill Jesus. He famously presided over the Sanhedrin trial of Jesus. The primary sources for Caiaphas' life are the New Testament, and the writings of Josephus. The latter records he was made high priest by the Roman procurator Valerius Gratus after Simon ben Camithus had been deposed.
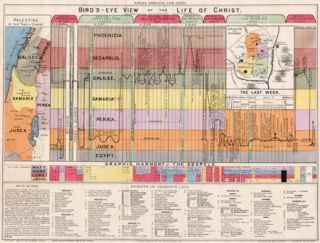
A chronology of Jesus aims to establish a timeline for the events of the life of Jesus. Scholars have correlated Jewish and Greco-Roman documents and astronomical calendars with the New Testament accounts to estimate dates for the major events in Jesus's life.
Clement Schrader was a German Jesuit theologian.

Johann Heinrich Linck was a German pharmacist and naturalist. He was born in Leipzig and ran the family pharmacy known as "The Golden Lion". He wrote a treatise on sea stars, De stellis marinis liber singularis (1733). The genus Linckia of sea stars is named after him.

The Quest of the Historical Jesus is a 1906 work of Biblical historical criticism written by Albert Schweitzer during the previous year, before he began to study for a medical degree.

Saint Peter, also known as Peter the Apostle, Simon Peter, Simeon, Simon, or Cephas, was one of the Twelve Apostles of Jesus Christ and one of the first leaders of the early Christian Church. He appears repeatedly and prominently in all four New Testament gospels as well as the Acts of the Apostles. Catholic and Orthodox tradition accredits Peter as the first bishop of Rome—or pope—and also as the first bishop of Antioch.
Ernest Joseph Burrus (1907–1991) was a Jesuit and a leading historian of northwestern New Spain, particularly the Baja California peninsula and Sonora. He made notable contributions in editing many accounts of the Jesuit period in documents from European archives.

Friedrich Loofs was a German theologian and church historian best remembered for his studies involving the history of dogma.
Advent songs are songs and hymns intended for Advent, the four weeks of preparation for Christmas. Topics of the time of expectation are the hope for a Messiah, prophecies, and the symbolism of light, among others. Several of the songs are part of hymnals such as the German Catholic Gotteslob (GL) and the Protestant Evangelisches Gesangbuch (EG).

"Meinen Jesum laß ich nicht" is a German Lutheran hymn, with lyrics by Christian Keimann written in 1658. The theme of the hymn is trust in Jesus, based on memorial sermons for John George I, Elector of Saxony recalling conversations of the elector with his minister on his deathbed.

"Liebster Jesu, wir sind hier" is a Lutheran hymn with text written by Tobias Clausnitzer in 1663, and a hymn tune, Zahn No. 3498b, based on a 1664 melody by Johann Rudolph Ahle. A prayer for illumination, it is suitable for the opening of a church service and to be sung before a sermon. The song is part of the Protestant hymnal Evangelisches Gesangbuch as EG 161. It is also part of the Catholic hymnal Gotteslob as GL 149. It is popular also in English translations such as "Blessed Jesus, at your word" by Catherine Winkworth.















