
Arabic is usually classified as a Central Semitic language, and linguists widely agree that the language first emerged in the 1st to 4th centuries CE.. It is now the lingua franca of the Arab world. It is named after the Arabs, a term initially used to describe peoples living in the area bounded by Mesopotamia in the east and the Anti-Lebanon mountains in the west, in northwestern Arabia, and in the Sinai Peninsula. Arabic is classified as a macrolanguage comprising 30 modern varieties, including its standard form, Modern Standard Arabic, which is derived from Classical Arabic.

Persian, also known by its endonym Farsi, is one of the Western Iranian languages within the Indo-Iranian branch of the Indo-European language family. It is a pluricentric language primarily spoken in Iran, Afghanistan, and Tajikistan, Uzbekistan and some other regions which historically were Persianate societies and considered part of Greater Iran. It is written right to left in the Persian alphabet, a modified variant of the Arabic script.

The Middle East is a transcontinental region centered on Western Asia, Turkey, and Egypt. Saudi Arabia is geographically the largest Middle Eastern nation while Bahrain is the smallest. The corresponding adjective is Middle Eastern and the derived noun is Middle Easterner. The term has come into wider usage as a replacement of the term Near East beginning in the early 20th century.

Tajik or Tajiki, also called Tajiki Persian, is the variety of Persian spoken in Tajikistan and Uzbekistan. It is closely related to Dari Persian. Since the beginning of the twentieth century and collapse of the Soviet Union, Tajik has been considered by a number of writers and researchers to be a variety of Persian. The popularity of this conception of Tajik as a variety of Persian was such that, during the period in which Tajik intellectuals were trying to establish Tajik as a language separate from Persian language, Sadriddin Ayni, who was a prominent intellectual and educator, made a statement that Tajik was not a bastardized dialect of Persian. The issue of whether Tajik and Persian are to be considered two dialects of a single language or two discrete languages has political sides to it.
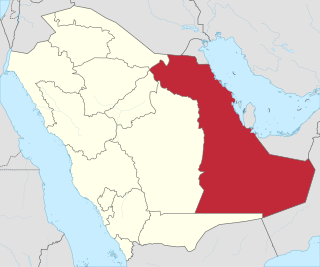
The Eastern Province is the largest province of Saudi Arabia by area. The province's capital is the city of Dammam, which hosts the majority of the region's population and its seat of government. The Eastern Province is the third most populous province in Saudi Arabia, after Makkah and Riyadh. Dammam is the province's most populous city, and the sixth most populous city in the country. The current governor of the Eastern Province is Prince Saud bin Nayef Al Saud.
A literary language is the form of a language used in its literary writing. It is typically a vernacular dialect or standardized variety of the language. It can sometimes differ noticeably from the various spoken lects, but difference between literary and non-literary forms is greater in some languages than in others. Where there is a strong divergence between a written form and the spoken vernacular, the language is said to exhibit diglossia.
Gulf Arabic is a variety of the Arabic language spoken in Eastern Arabia around the coasts of the Persian Gulf in Kuwait, Bahrain, Qatar, the United Arab Emirates, as well as parts of eastern Saudi Arabia, southern Iraq, and south Iran and northern Oman.
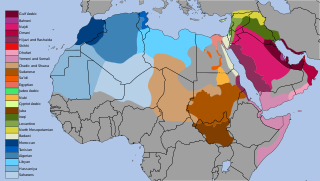
Mesopotamian Arabic, or Iraqi Arabic, is a continuum of mutually-intelligible varieties of Arabic native to the Mesopotamian basin of Iraq as well as spanning into Syria, Iran, southeastern Turkey, and spoken in Iraqi diaspora communities.

The Arab states of the Persian Gulf are the seven Arab states which border the Persian Gulf, namely Bahrain, Iraq, Kuwait, Oman, Qatar, Saudi Arabia and the United Arab Emirates (UAE). This excludes the non-Arab state of Iran. All of these nations except Iraq are part of the Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC), and prefer to use the term "Arabian Gulf" rather than the official and historical name of the Persian Gulf.
The Baharna are a Shia Muslim ethnoreligious group who mainly inhabit the historical region of Eastern Arabia. They are generally regarded by scholars to be the original inhabitants of the Bahrain archipelago. Most Shi'i Bahraini citizens are ethnic Baharna. Regions with most of the population are in Eastern Arabia, with historical diaspora populations in Kuwait,, Qatar, United Arab Emirates, Oman, Iran, and Iraq. Some Bahrainis are from other parts of the world too.
Bahrani Arabic is a variety of Arabic spoken in Eastern Arabia and Oman. In Bahrain, the dialect is primarily spoken in Shia villages and some parts of Manama.

Lar is a city and capital of Larestan County, Fars Province, Iran. At the 2006 census, its population was 55,265, in 6,891 families. Lar's inhabitants are Larestani people.
Arabic is the official language of Syria and is the most widely spoken language in the country. Several modern Arabic dialects are used in everyday life, most notably Levantine in the west and Mesopotamian in the northeast.
Hadhrami Arabic, or Ḥaḍrami Arabic, is a variety of Arabic spoken by the Hadhrami people (Ḥaḍārima) living in the Hadhramaut. It is also spoken by many emigrants, who migrated from the Hadhramaut to the Horn of Africa, East Africa, Southeast Asia and, recently, to the other Arab states of the Persian Gulf.

The official and de facto national language of Bangladesh is Modern Standard Bengali. It serves as the lingua franca of the nation, with 98% of Bangladeshis fluent in Bengali as their first language. English, having no official status, is prevalent across government, law, business, media and education and can be regarded as the de facto co-official language of Bangladesh.

There are many varieties of Arabic in existence. Arabic is a Semitic language within the Afroasiatic family that originated on the Arabian Peninsula. It is classified as a macrolanguage comprising 30 modern varieties, including its standard form. The largest divisions occur between the spoken languages of different regions. Some varieties of Arabic in North Africa, for example, are not easily comprehensible to an Arabic speaker from the Levant or the Persian Gulf. Within these broad regions further and considerable geographic distinctions exist, within countries, across country borders, even between cities and villages.
Peninsular Arabic, or Southern Arabic, are the varieties of Arabic spoken throughout the Arabian Peninsula. This includes the countries of Saudi Arabia, Yemen, Oman, United Arab Emirates, Kuwait, Bahrain, Qatar, Southern Iraq and the tribal people of Jordan.
Mashriqi Arabic, or Mashriqi ʿAmmiya, is the varieties of Arabic spoken in the Mashriq, including the countries of Egypt, Lebanon, Palestine, Israel, Kuwait, Jordan, Syria, Cyprus, Turkey, Iraq, Sudan, Saudi Arabia, UAE, Oman, Bahrain and Qatar. The variety is sometimes referred to as Eastern Arabic, as opposed to Western Arabic and includes Mesopotamian Arabic and Gulf Arabic, along with Egyptian Arabic, Sudanese Arabic, and Levantine Arabic. Speakers of Mashriqi call their language ʿAmmiya, which means "dialect" in Modern Standard Arabic.
Kuwaiti Persian, known in Kuwait as ʿīmi and spelled Eimi in some works is a dying (endangered) combination of different varieties of the Persian language and Achomi language that has been spoken in Kuwait for more than two centuries. Persian was spoken since the foundation of Kuwait, especially in the Sharg district of the historical Kuwait City, where families that emigrated from Persia had settled.










