The Lake Superior Sounder was a newspaper published in Ashland, WI, with its inaugural issue released in January 2003. Unlike the other Ashland newspaper (The Ashland Daily Press), The Sounder focused less on hard news, and more on the leisure aspects of life in northern Wisconsin. It served the counties of Sawyer, Bayfield, Ashland and Iron for five years, published every other Thursday and available throughout Wisconsin's Lake Superior region.
The Sounder discontinued publication in January 2008.

Bayfield County is a county located in the U.S. state of Wisconsin. As of the 2020 census, its population is 16,220. Its county seat is Washburn. The county was created in 1845 and organized in 1850. The Red Cliff Band of Lake Superior Chippewa has a reservation in Bayfield County and is the county's largest employer.

Ashland County is a county located in the U.S. state of Wisconsin. As of the 2020 census, the population was 16,027. Its county seat is Ashland. The county was formed on March 27, 1860, from La Pointe County. The county partly overlaps with the reservation of the Bad River Band of the Lake Superior Tribe of Chippewa Indians.

Sanborn is a town in Ashland County in the U.S. state of Wisconsin. The population was 1,331 at the 2010 census. The unincorporated communities of Bayfront, Birch, Birch Hill, Diaperville, Franks Field, New Odanah, Odanah, and Sedgwick are located in the town. Long Island, one of the Apostle Islands, is also a part of the town. The entire town is part of the Bad River Reservation of the Bad River Band of the Lake Superior Tribe of Chippewa Indians.
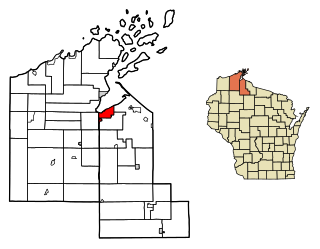
Ashland is a city in Ashland and Bayfield counties in the U.S. state of Wisconsin. It is the county seat of Ashland County. The city is a port on Lake Superior, near the head of Chequamegon Bay. The population was 7,908 at the 2020 census, all of whom resided in the Ashland County portion of the city. The unpopulated Bayfield County portion is in the city's southwest, bordered by the easternmost part of the Town of Eileen.
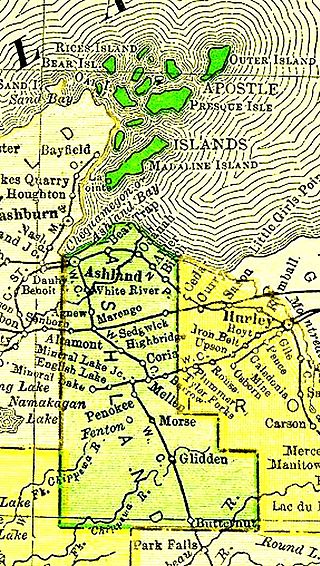
The Apostle Islands are a group of 22 islands in Lake Superior, off the Bayfield Peninsula in northern Wisconsin. The majority of the islands are located in Ashland County—only Sand, York, Eagle, and Raspberry Islands are located in Bayfield County. All the islands except for Madeline Island are part of the Apostle Islands National Lakeshore. The islands in Ashland County are all in the Town of La Pointe, except for Long Island, which is in the Town of Sanborn, while those in Bayfield County are in the Towns of Russell and Bayfield.

In the U.S. state of Wisconsin, the Lake Superior Lowland, also known as the Superior Coastal Plain, is a geographical region located in the far northern part of the state bordering Lake Superior. It covers about 1,250 square miles (3,200 km2), and does not extend beyond 20 miles (32 km) from the Lake Superior shore.

The Bad River LaPointe Band of the Lake Superior Tribe of Chippewa Indians or Bad River Tribe for short are a federally recognized tribe of Ojibwe people. The tribe had 6,945 members as of 2010. The Bad River Reservation is located on the south shore of Lake Superior and has a land area of about 193.11 square miles (500.15 km2) in northern Wisconsin, straddling Ashland and Iron counties. Odanah, the administrative and cultural center, is located five miles (8.0 km) east of the town of Ashland on U.S. Highway 2. The reservation population was 1,545 in 2020. Most of the reservation is managed as undeveloped forest and wetland, providing a habitat for wild rice and other natural resources.

The Bad River is a river flowing to Lake Superior in northern Wisconsin in the United States. It flows for 119.6 kilometres (74.3 mi) in Ashland County, draining an area of 1,061 square miles (2,750 km2) in portions of Ashland, Bayfield and Iron counties. The Bad River sloughs were designated a Ramsar Wetland of International Importance on February 2, 2012.

Lake Duluth was a proglacial lake that formed in the Lake Superior drainage basin as the Laurentide Ice Sheet retreated. The oldest existing shorelines were formed after retreat from the Greatlakean advance, sometime around 11,000 years B.P. Lake Duluth formed at the western end of the Lake Superior basin. Lake Duluth overflowed south through outlets in Minnesota and Wisconsin at an elevation of around 331 m above sea level.

There are several historic lighthouses on Lake Superior on or near the Apostle Islands in Wisconsin. Six of these lighthouses, all in the Apostle Islands National Lakeshore, were listed as a group on the National Register of Historic Places in 1977 under the name Apostle Islands Lighthouses.

State Trunk Highway 13 is a state highway running north–south across northwest and central Wisconsin. WIS 13 serves as a major north–south route connecting the communities of Wisconsin Dells, Wisconsin Rapids, Marshfield and Ashland. WIS 13 is part of the Lake Superior Circle Tour from its northern/western terminus to Ashland at is eastern junction with U.S. Highway 2 (US 2). The road also provides access to the Apostle Islands National Lakeshore off the Lake Superior shoreline at Bayfield. The highway is two-lane surface road with the exception of various urban multilane road sections.

US Highway 2 (US 2) is a part of the United States Numbered Highway System that runs from Everett, Washington, to St. Ignace, Michigan. In Wisconsin, the highway enters runs east–west across the northwestern part of the state and re-enters the state in the northeast part. It runs from the Richard I. Bong Memorial Bridge over the Saint Louis Bay at Superior, where it enters from Minnesota, east to the Michigan state line near Hurley. Further east, US 2 re-enters Wisconsin from Michigan in Florence County and briefly traverses that county before re-entering Michigan. US 2 is a Wisconsin Corridors 2020 Connecting route east of its concurrency with US 53. The section concurrent with US 53 is a Wisconsin Corridors 2020 Backbone route.

Samuel S. Fifield was a Wisconsin politician and influential businessperson. The Town of Fifield in Price County, Wisconsin is named after him.

The Minneapolis, St. Paul and Sault Ste. Marie Railroad (MStP&SSM) was a Class I railroad subsidiary of the Canadian Pacific Railway in the Midwestern United States. Commonly known since its opening in 1884 as the Soo Line after the phonetic spelling of Sault, it was merged with several other major CP subsidiaries on January 1, 1961, to form the Soo Line Railroad.

The original Wisconsin Central Railroad Company was a major early railroad that operated throughout northern Wisconsin. It built lines up through the forested wilderness, and opened large tracts to logging and settlement. It established stations which would grow into a string of cities and towns between Stevens Point and Ashland, including Marshfield and Medford, and it connected these places to Chicago and St. Paul. It also played a major role in building Chicago's Grand Central Station.
The 25th Senate District of Wisconsin is one of 33 districts in the Wisconsin Senate. Located in northwest Wisconsin, where Wisconsin meets Lake Superior, the district comprises all of Ashland, Bayfield, Burnett, Douglas, Iron, Polk, Sawyer, and Washburn counties. It contains the cities of Superior, Ashland, Bayfield, Hayward, Spooner, and Washburn. The district also includes the Bad River Indian reservation and the Chequamegon–Nicolet National Forest.

Asaph Whittlesey was the first Wisconsin state legislator from the Lake Superior region. In 1854, he settled the city of Ashland, Wisconsin.

The Moonlight was a schooner that sank in Lake Superior off the coast of Michigan Island. The wreckage site was added to the National Register of Historic Places in 2008.

City of Ashland was a sidewheel paddle steamer that sank in Chequamegon Bay, Lake Superior, off Ashland, Wisconsin. The ship was named for Ashland, a port community. The wreckage remains at the bottom of the bay, close to the ship's namesake city.

SS Robert Wallace was a wooden-hulled American bulk freighter that served on the Great Lakes of North America from her construction in 1882 to her sinking in 1902 on Lake Superior near the town of Palmers, St. Louis County, Minnesota, United States. On November 17, 1902 shortly after leaving Superior, Wisconsin with a cargo of iron ore, Robert Wallace sprang a leak and sank. Her wreck was found in 2006, and on October 14, 2009, the wreck of Robert Wallace was listed in the National Register of Historic Places.