This article includes a list of references, related reading, or external links, but its sources remain unclear because it lacks inline citations .(March 2020) |

The Landenberg family was a noble family in medieval Switzerland.
This article includes a list of references, related reading, or external links, but its sources remain unclear because it lacks inline citations .(March 2020) |

The Landenberg family was a noble family in medieval Switzerland.
By the beginning 14th century, they were the most powerful family of eastern Switzerland, separating into four lines, Alt-Landenberg, Landenberg-Greifensee, Hohenlandenberg and Breitenlandenberg. The main line was extinct early, Rudolf I and his son Pantaleon both falling in the battle of Morgarten in 1315. The Landenberg-Greifensee line was the most successful during the 14th century but was outlived by the Hohenladenberg and Breitenlandenberg ones. Breitenlandenberg proved the most successful in the longer run, rising to significant power in the 15th century and lasting into the 19th.
The influence of the Landenberg-Greifensee line peaked in the 1350s with Hermann IV, whose sons came into financial difficulties and had to sell a number of castles, among them Alt-Landenberg and Greifensee. The reasons for this decline was their close ties with the house of Habsburg, which was itself struggling with difficulties and losing its hold over the territory due to both the rise of the city of Zürich and the growth of the Old Swiss Confederacy.
The Breitenlandenberg and Hohenlandenberg lines overcame this crisis by allying themselves with Zürich, adopting Zürich citizenship. Their territorial influence remained confined to the Zürcher Oberland due to the pressure of territorial expansion from both Zürich and the Swiss Confederacy, but by the end of the 14th century they became again very wealthy and gave out major credits to the cities of Winterthur and Constance.
The Hohenlandenberg line owned Andelfingen until 1434. The Breitenlandenberg line rose to great importance in Zürichgau in the 15th century. They had Zürich citizenship from the 14th century, and often intermarried with families of the Zürich patriciate like Schäfli. They also entered the Old Zürich War on the side of Zürich, and Wildhans von Breitenlandenberg was beheaded with his entire garrison at the siege of Greifensee in 1444. The knights of Breitenlandenberg also fought with Zürich, this time on the side of the Swiss, in the Burgundy Wars. They declined from the 16th century and sold the ancestral Breitenlandeberg castle in the 17th century, residing mostly in Zürich, although they retained jurisdiction in a number of communes, at Salenstein into the 18th century. The male line of Breitenlandenberg was extinct in the 1870s.


The House of Zähringen was a dynasty of Swabian nobility. The family's name derived from Zähringen Castle near Freiburg im Breisgau. The Zähringer in the 12th century used the title of Duke of Zähringen, in compensation for having conceded the title of Duke of Swabia to the Staufer in 1098. The Zähringer were granted the special title of Rector of Burgundy in 1127, and they continued to use both titles until the extinction of the ducal line in 1218.
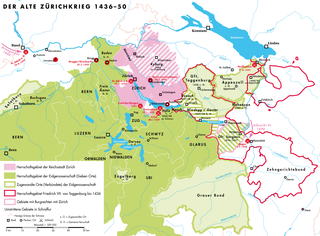
The Old Zurich War was a conflict between the canton of Zurich and the other seven cantons of the Old Swiss Confederacy over the succession to the Count of Toggenburg.

Greifensee is a municipality in the district of Uster in the Canton of Zurich in Switzerland.

Uster is a town and the capital of the Uster District in the Swiss canton of Zürich.

Grüningen is a town and municipality in the district of Hinwil in the canton of Zürich in Switzerland, notable for its well-preserved historic nucleus.
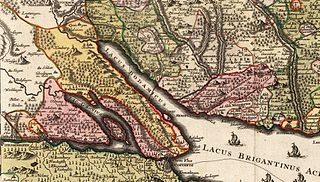
The Prince-Bishopric of Constance was a small ecclesiastical principality of the Holy Roman Empire from the mid-12th century until its secularisation in 1802–1803. In his dual capacity as prince and as bishop, the prince-bishop also administered the Diocese of Konstanz, which existed from about 585 until its dissolution in 1821, and whose territory extended over an area much larger than the principality. It belonged to the ecclesiastical province of Mainz since 780/782.

Hugo von Hohenlandenberg was Bishop of Konstanz from 1496 to 1529, and again in 1530 and 1531 until his death in 1532.

Reformierte Kirche Greifensee, is a church and a listed heritage building in the municipality of Greifensee, Canton of Zürich, Switzerland.

Werdenberg was a county of the Holy Roman Empire, within the Duchy of Swabia, situated on either side of the Alpine Rhine, including parts of what is now St. Gallen (Switzerland), Liechtenstein, and Vorarlberg (Austria). It was partitioned from Montfort in 1230. In 1260, it was divided into Werdenberg and Sargans.
The Kyburg family was a noble family of grafen (counts) in the Duchy of Swabia, a cadet line of the counts of Dillingen, who in the late 12th and early 13th centuries ruled the County of Kyburg, corresponding to much of what is now Northeastern Switzerland.

Rüti Monastery was a former Premonstratensian monastery, founded in 1206 and suppressed in 1525 on occasion of the Reformation in Zürich, situated in the municipality of Rüti in the canton of Zürich, Switzerland. The monastery's church was the final resting place of the Counts of Toggenburg, among them Count Friedrich VII and 13 other members of the Toggenburg family, and other noble families. Between 1206 and 1525, the monastery comprised 14 incorporated churches and the owner of extensive lands and estates at 185 localities.

Rietberg Castle is a castle in the municipality of Pratval of the Canton of Graubünden in Switzerland. It is a Swiss heritage site of national significance. It was the site of the murder of Pompeius Planta in 1621 by Jörg Jenatsch during the conflicts between Catholics and Protestants known as the Bündner Wirren.

The House of Rapperswil respectively Counts of Rapperswil ruled the upper Zürichsee and Seedamm region around Rapperswil and parts of, as of today, Swiss cantons of St. Gallen, Glarus, Zürich and Graubünden when their influence was most extensive around the 1200s until the 1290s. They acted also as Vogt of the most influential Einsiedeln Abbey in the 12th and 13th century, and at least three abbots of Einsiedeln were members of Rapperswil family.

Elisabeth von Rapperswil was the last countess of the House of Rapperswil, and secured by her second marriage the female line of the Counts of Rapperswil and the extensive possessions of Rapperswil in the former Zürichgau to the Laufenburg line. Her son by first marriage was Reichsvogt Wernher von Homberg, and her oldest son by second marriage was Count Johann von Habsburg-Laufenburg who passed over the title of the count of Rapperswil to his oldest son Johann II and his brothers Rudolf and Gotfried.
The Regensberg family was a family of counts from the Canton of Zürich in Switzerland. They had possessions in the medieval Zürichgau from the probably mid-11th century and became extinct in 1331 AD. With the extinction of the male line, the city republic of Zürich laid claim to the Regensberg lands and formed the Herrschaft Regensberg respectively Äussere Vogtei.

Alt-Regensberg Castle is a hill castle which was built about the mid-11th century AD by the House of Regensberg in the Swiss municipality of Regensdorf in the Canton of Zürich.

Uster Castle is a hill castle which was built probably around 1200 AD by the House of Rapperswil in the Swiss municipality of Uster in the Canton of Zürich. Since 1995 it houses a boarding school.
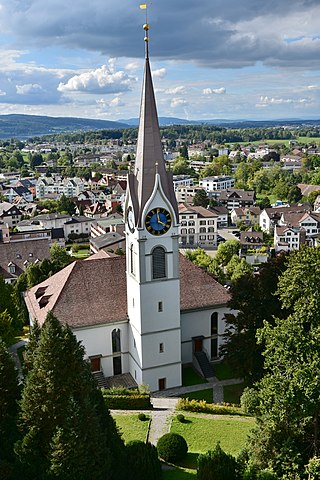
Reformierte Kirche Uster is an Evangelical Reformed church in the Swiss municipality of Uster in the Canton of Zürich that was built in 1824. The predecessor St. Andreas church, situated next to the Uster Castle, was given by the House of Rapperswil and first mentioned in 1099 AD.
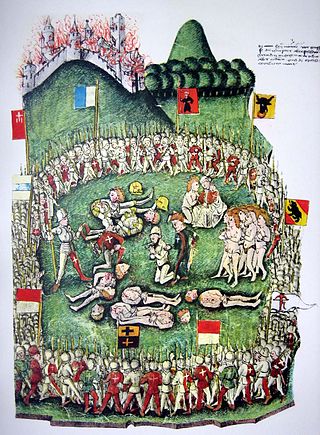
Ital Reding the Elder was Landammann of Schwyz and the leader of the forces of Schwyz during the Old Zürich War (1440–1450).