
Spirit, also known as MER-A or MER-2, is a Mars robotic rover, active from 2004 to 2010. Spirit was operational on Mars for 2208 sols or 3.3 Martian years. It was one of two rovers of NASA's Mars Exploration Rover Mission managed by the Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL). Spirit landed successfully within the impact crater Gusev on Mars at 04:35 Ground UTC on January 4, 2004, three weeks before its twin, Opportunity (MER-B), which landed on the other side of the planet. Its name was chosen through a NASA-sponsored student essay competition. The rover got stuck in a "sand trap" in late 2009 at an angle that hampered recharging of its batteries; its last communication with Earth was on March 22, 2010.

Opportunity, also known as MER-B or MER-1, and nicknamed Oppy, is a robotic rover that was active on Mars from 2004 until mid-2018. Opportunity was operational on Mars for 5110 sols. Launched on July 7, 2003, as part of NASA's Mars Exploration Rover program, it landed in Meridiani Planum on January 25, 2004, three weeks after its twin Spirit (MER-A) touched down on the other side of the planet. With a planned 90-sol duration of activity, Spirit functioned until it got stuck in 2009 and ceased communications in 2010, while Opportunity was able to stay operational for 5111 sols after landing, maintaining its power and key systems through continual recharging of its batteries using solar power, and hibernating during events such as dust storms to save power. This careful operation allowed Opportunity to operate for 57 times its designed lifespan, exceeding the initial plan by 14 years, 46 days. By June 10, 2018, when it last contacted NASA, the rover had traveled a distance of 45.16 kilometers.

Fram is an impact crater located within the Meridiani Planum extraterrestrial plain, situated within the Margaritifer Sinus quadrangle (MC-19) region of the planet Mars. It was visited by the rover Opportunity (MER-B) on Sol 84, April 24, 2004.
Argo is a crater in the Meridiani Planum on Mars, which was visited by the Opportunity rover on approximately its 365th Martian sol. The crater is about 300 meters (980 ft) south of the heat shield and Heat Shield Rock.

Vostok is a crater lying situated within the Margaritifer Sinus quadrangle (MC-19) region of the planet Mars that was reached by the rover Opportunity on sol 399. Vostok is located roughly 1,200 metres (3,900 ft) south of Endurance in Meridiani Planum. The crater appears to have been covered up with sand by the winds on the red planet, but many rock outcrops are still visible from the surface.

Victoria is an impact crater on Mars located at 2.05°S, 5.50°W in the Meridiani Planum extraterrestrial plain, lying situated within the Margaritifer Sinus quadrangle (MC-19) region of the planet Mars. This crater was first visited by the Mars Exploration Rover Opportunity. It is roughly 800 metres (2,600 ft) wide, nearly eight times the size of the crater Endurance, visited by Opportunity from sols 951 to 1630. It is informally named after Victoria – one of the five Spanish ships of Ferdinand Magellan and the first ship to circumnavigate the globe – and formally named after Victoria, Seychelles. Along the edges of the crater are many outcrops within recessed alcoves and promontories, named for bays and capes that Magellan discovered.
Larry Crumpler is a geologist and volcanologist. He is Research Curator for Volcanology & Space Science at the New Mexico Museum of Natural History and Science, and a member of the Mars Exploration Rover science team. Larry's Lookout on Mars is named after him.
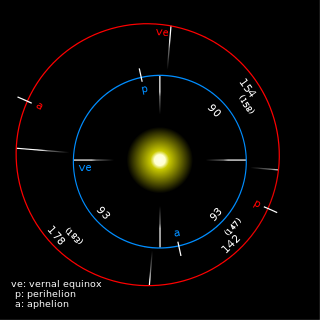
Though no standard exists, numerous calendars and other timekeeping approaches have been proposed for the planet Mars. The most commonly seen in the scientific literature denotes the time of year as the number of degrees from the northern vernal equinox, and increasingly there is use of numbering the Martian years beginning at the equinox that occurred April 11, 1955.

Home Plate is a plateau roughly 90 m across within the Columbia Hills, Mars. It is informally named for its similarity in shape to a baseball home plate. Home Plate is a rocky outcrop that appears to show layered features.
McCool Hill is the tallest of the Columbia Hills in Gusev crater, Mars. It was named in honor of William C. McCool, an astronaut of the Space Shuttle Columbia during its final mission where it disintegrated during atmospheric reentry.

Beagle is a crater lying within the Margaritifer Sinus quadrangle (MC-19) portion of the planet Mars, the crater is one of multiple topographical depressions within the Meridiani Planum extraterrestrial plain, which was explored by the Opportunity rover. It was located by the rover in images taken on sol 855, 310 metres (1,107 ft) away. It is on the edge of the much larger ejecta blanket surrounding the crater Victoria, named the Victoria Annulus. This impact crater was named in honor of HMA Beagle of the Royal Navy, ordered in February 1817, which carried Charles Darwin on his voyage round the world.

Cape Verde is a large promontory and extremity on the rim of Victoria Crater in Meridiani Planum, an extraterrestrial plain within the Margaritifer Sinus quadrangle (MC-19) region of the planet Mars. The Mars Exploration Rover Opportunity perched atop this feature in 2006 to take a true-color mosaic of the crater below. Sols 958 to 991 were spent on this cape, including the period of solar conjunction which spanned from sol 970 to sol 984.
The embedded computer systems on board the Mars rovers sent by NASA must withstand the high radiation levels and large temperature changes in space. For this reason their computational resources are limited compared to systems commonly used on Earth.

Bathurst Inlet is a rock on the surface of Aeolis Palus, between Peace Vallis and Aeolis Mons, in Gale crater on the planet Mars. The rock was encountered by the Curiosity rover on the way from Bradbury Landing to Glenelg Intrigue on September 30, 2012 and was named after Bathurst Inlet, a deep inlet located along the northern coast of the Canadian mainland. The "approximate" site coordinates are: 4.59°S 137.44°E.

Goulburn, also known as Goulburn Scour, is a rock outcrop on the surface of Aeolis Palus, between Peace Vallis and Aeolis Mons, in Gale crater on the planet Mars. The outcrop was encountered by the Curiosity rover on landing at the Bradbury Landing on August 6, 2012 and is named after a two-billion year-old sequence of rocks in Northern Canada. The "approximate" site coordinates are: 4.59°S 137.44°E.

Matijevic Hill, named after American NASA engineer Jacob "Jake" Matijevic, is a hill located on "Cape York", itself on the western rim of Endeavour Crater lying within the Margaritifer Sinus quadrangle (MC-19) region of the planet Mars. It was discovered by the Opportunity rover, and named by NASA on September 28, 2012. The "approximate" site coordinates are: 2.22923°S 5.35068°W.

Opportunity is a robotic rover that was active on the planet Mars from 2004 to 2018. Launched on July 7, 2003, Opportunity landed on Mars' Meridiani Planum on January 25, 2004 at 05:05 Ground UTC, three weeks after its twin Spirit (MER-A), also part of NASA's Mars Exploration Rover Mission, touched down on the other side of the planet. While Spirit became immobile in 2009 and ceased communications in 2010, Opportunity exceeded its planned 90 sol duration of activity by 17 years, 275 days. Opportunity continued to move, gather scientific observations, and report back to Earth until 2018. What follows is a summary of events during its continuing mission.

Sol is a solar day on Mars; that is, a Mars-day. A sol is the apparent interval between two successive returns of the Sun to the same meridian as seen by an observer on Mars. It is one of several units for timekeeping on Mars.














