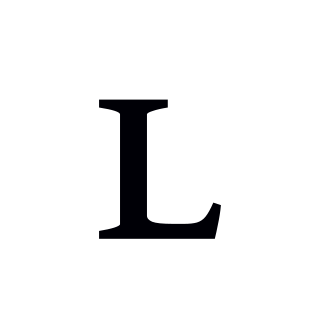A lateral is a consonant in which the airstream proceeds along one or both of the sides of the tongue, but it is blocked by the tongue from going through the middle of the mouth. An example of a lateral consonant is the English L, as in Larry. Lateral consonants contrast with central consonants, in which the airstream flows through the center of the mouth.
Postalveolar (post-alveolar) consonants are consonants articulated with the tongue near or touching the back of the alveolar ridge. Articulation is farther back in the mouth than the alveolar consonants, which are at the ridge itself, but not as far back as the hard palate, the place of articulation for palatal consonants. Examples of postalveolar consonants are the English palato-alveolar consonants, as in the words "ship", "'chill", "vision", and "jump", respectively.

A retroflex, apico-domal, or cacuminalconsonant is a coronal consonant where the tongue has a flat, concave, or even curled shape, and is articulated between the alveolar ridge and the hard palate. They are sometimes referred to as cerebral consonants—especially in Indology.
The voiced alveolar tap or flap is a type of consonantal sound, used in some spoken languages. The symbol in the International Phonetic Alphabet that represents a dental, alveolar, or postalveolar tap or flap is ⟨ɾ⟩.
The voiced alveolar lateral approximant is a type of consonantal sound used in many spoken languages. The symbol in the International Phonetic Alphabet that represents dental, alveolar, and postalveolar lateral approximants is ⟨l⟩, and the equivalent X-SAMPA symbol is l.

The voiced alveolar lateral flap is a type of consonantal sound, used in some spoken languages. The symbol in the International Phonetic Alphabet that represents this sound is ⟨ɺ⟩, a fusion of a rotated lowercase letter ⟨r⟩ with a letter ⟨l⟩. Approved in 1928, the symbol represented a sound intermediate between and or between and until 1979 when its value was redefined as an alveolar lateral flap.
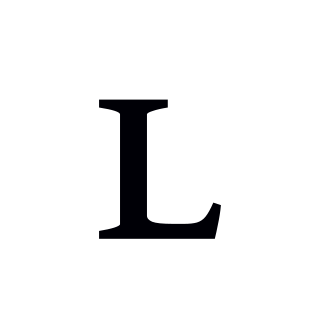
The voiced velar lateral approximant is a type of consonantal sound, used as a distinct consonant in a very small number of spoken languages in the world. The symbol in the International Phonetic Alphabet that represents this sound is ⟨ʟ⟩ a small capital version of the Latin letter l, and the equivalent X-SAMPA symbol is L\.

The voiced alveolar lateral fricative is a type of consonantal sound, used in some spoken languages. The symbol in the International Phonetic Alphabet that represents voiced dental, alveolar, and postalveolar lateral fricatives is ⟨ɮ⟩, and the equivalent X-SAMPA symbol is K\.
The voiced alveolar fricatives are consonantal sounds. The symbol in the International Phonetic Alphabet that represents these sounds depends on whether a sibilant or non-sibilant fricative is being described.
In phonetics, a trill is a consonantal sound produced by vibrations between the active articulator and passive articulator. Standard Spanish ⟨rr⟩ as in perro, for example, is an alveolar trill.
In phonetics, a flap or tap is a type of consonantal sound, which is produced with a single contraction of the muscles so that one articulator is thrown against another.
A central consonant, also known as a median consonant, is a consonant sound that is produced when air flows across the center of the mouth over the tongue. The class contrasts with lateral consonants, in which air flows over the sides of the tongue rather than down its center.

The voiced retroflex lateral flap is a type of consonantal sound, used in some spoken languages. The 'implicit' symbol in the International Phonetic Alphabet is ⟨𝼈 ⟩. The sound may also be transcribed as a short ⟨ɭ̆ ⟩, or with the retired IPA dot diacritic, ⟨ɺ̣⟩.
The voiced palatal lateral flap is a rare type of consonantal sound, used in some spoken languages. There is no dedicated symbol in the International Phonetic Alphabet that represents this sound. However, the symbol for a palatal lateral approximant with a breve denoting extra-short ⟨ʎ̆⟩ may be used.
The voiced alveolar lateral affricate is a type of consonantal sound, used in some spoken languages. The symbol in the International Phonetic Alphabet is ⟨d͡ɮ⟩, and in Americanist phonetic notation it is ⟨λ⟩ (lambda). It is usually in free variation or an allophone of /ɮ/, /t͡ɬ/ or /l/; no known language contrasts [dɮ] and [ɮ].
The alveolar lateral ejective fricative is a type of consonantal sound, reported in the Northwest Caucasian languages and in Modern South Arabian languages. The symbol in the International Phonetic Alphabet that represents this sound is ⟨ɬʼ⟩.
The voiceless alveolar tap or flap is rare as a phoneme. The symbol in the International Phonetic Alphabet that represents this sound is ⟨ɾ̥⟩, a combination of the letter for the voiced alveolar tap/flap and a diacritic indicating voicelessness. The equivalent X-SAMPA symbol is 4_0.
The voiceless retroflex trill is a sound that has been reported to occur as a diaphoneme of in the Maldivian language. Although the tongue starts out in a sub-apical retroflex position, trilling involves the tip of the tongue and causes it to move forward to the alveolar ridge; this means that the retroflex trill gives a preceding vowel retroflex coloration the way other retroflex consonants do, but the vibration itself is not much different from an alveolar trill.
The voiceless alveolar lateral flap is a type of consonantal sound, used in some spoken languages. The symbol in the International Phonetic Alphabet that represents this sound is ⟨ɺ̥⟩, a fusion of a rotated lowercase letter ⟨r⟩ with a letter ⟨l⟩ and a voiceless diacritic.
The voiceless retroflex lateral flap is a type of consonantal sound, used in some spoken languages. The implicit symbol for this sound in the International Phonetic Alphabet is ⟨𝼈̊⟩.