This page is based on this
Wikipedia article Text is available under the
CC BY-SA 4.0 license; additional terms may apply.
Images, videos and audio are available under their respective licenses.

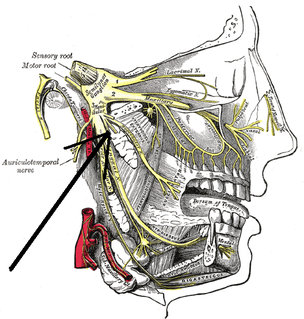
The mandibular nerve (V3) is the largest of the three divisions of the trigeminal nerve, the fifth cranial nerve (CN V).

The sphenoid bone is an unpaired bone of the neurocranium. It is situated in the middle of the skull towards the front, in front of the temporal bone and the basilar part of the occipital bone. The sphenoid bone is one of the seven bones that articulate to form the orbit. Its shape somewhat resembles that of a butterfly or bat with its wings extended.

There are four classical muscles of mastication. During mastication, three muscles of mastication are responsible for adduction of the jaw, and one helps to abduct it. All four move the jaw laterally. Other muscles, usually associated with the hyoid, such as the mylohyoid muscle, are responsible for opening the jaw in addition to the lateral pterygoid.

The medial pterygoid, is a thick, quadrilateral muscle of mastication.
Pterygoid, from the Greek for 'winglike', may refer to:
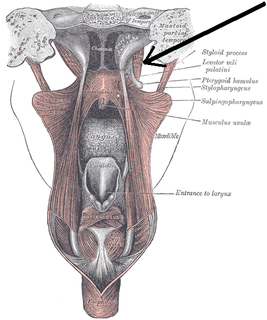
The tensor veli palatini muscle is a broad, thin, ribbon-like muscle in the head that tenses the soft palate.

The sphenomandibular ligament is a flat, thin band which is attached superiorly to the spina angularis (spine) of the sphenoid bone, and, becoming broader as it descends, is fixed to the lingula of the mandibular foramen. The function of the sphenomandibular ligament is to limit distension of the mandible in an inferior direction. It is slack when the temporomandibular joint (TMJ) is in closed position. It is taut as the condyle of the mandible is in front of the temporomandibular ligament.

The pterygoid processes of the sphenoid, one on either side, descend perpendicularly from the regions where the body and the greater wings of the sphenoid bone unite.

The greater wing of the sphenoid bone, or alisphenoid, is a bony process of the sphenoid bone; there is one on each side, extending from the side of the body of the sphenoid and curving upward, laterally, and backward.
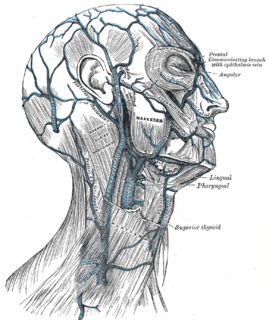
The pterygoid plexus is a venous plexus of considerable size, and is situated between the temporalis muscle and lateral pterygoid muscle, and partly between the two pterygoid muscles.

The maxillary artery supplies deep structures of the face. It branches from the external carotid artery just deep to the neck of the mandible.
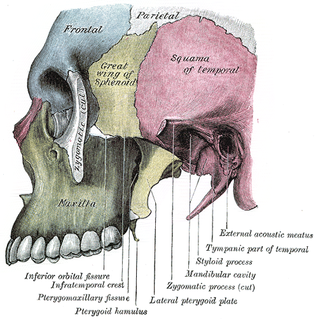
The infratemporal fossa is an irregularly shaped cavity, situated below and medial to the zygomatic arch. It is not fully enclosed by bone in all directions, and it contains superficial muscles that are visible during dissection after removing skin and fascia: namely, the lower part of the temporalis muscle, the lateral pterygoid, and the medial pterygoid.
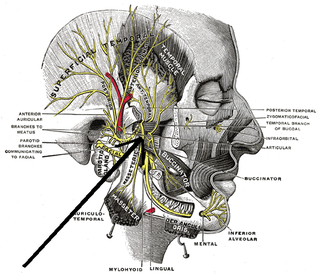
The medial pterygoid nerve is a branch of the mandibular nerve that innervates the medial pterygoid muscle, tensor veli palatini and tensor tympani.

The sphenoidal process of the palatine bone is a thin, compressed plate, much smaller than the orbital, and directed upward and medialward.
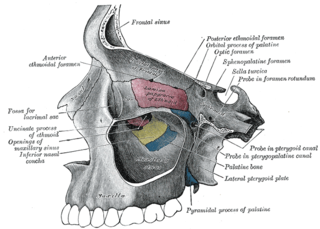
The pyramidal process of the palatine bone projects backward and lateralward from the junction of the horizontal and vertical parts, and is received into the angular interval between the lower extremities of the pterygoid plates.
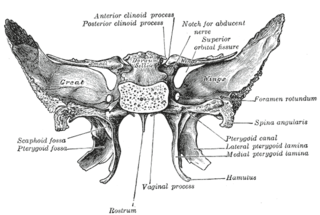
The pterygoid fossa is an anatomical term for the fossa formed by the divergence of the lateral pterygoid plate and the medial pterygoid plate of the sphenoid bone.

The pterygoid branches of the maxillary artery, irregular in their number and origin, supply the lateral pterygoid muscle and medial pterygoid muscle.
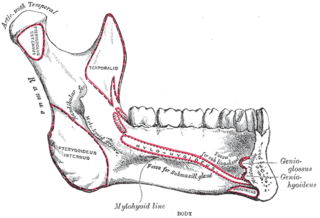
The pterygoid fovea is a concave surface on the uppermost medial side of the ramus of the mandible.