This article includes a list of references, related reading or external links, but its sources remain unclear because it lacks inline citations .(May 2012) (Learn how and when to remove this template message) |
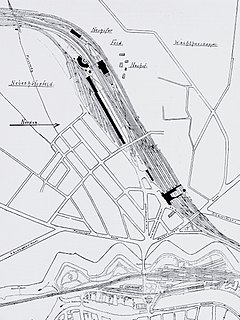
The Lauenburg-Hohnstorf Ferry (German: Trajekt Lauenburg-Hohnstorf or Lauenburg-Hohnstorfer Elb-Traject-Anstalt) was a railway ferry over the River Elbe between Hohnstorf on the left bank of the Elbe in the old Kingdom of Hanover (which became the Prussian province of Hanover in 1866) and Lauenburg in the Duchy of Lauenburg on the right bank which was then part of Denmark. From 15 March 1864 to 1 November 1878 the rail ferry linked the Lübeck–Lauenburg railway with the Lüneburg–Hohnstorf line. Both were sections of the Lübeck–Lüneburg railway.

The Kingdom of Hanover was established in October 1814 by the Congress of Vienna, with the restoration of George III to his Hanoverian territories after the Napoleonic era. It succeeded the former Electorate of Brunswick-Lüneburg, and joined 38 other sovereign states in the German Confederation in June 1815. The kingdom was ruled by the House of Hanover, a cadet branch of the House of Welf, in personal union with the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland until 1837. Since its monarch resided in London, a viceroy handled the administration of the Kingdom of Hanover.

Denmark, officially the Kingdom of Denmark, is a Nordic country and the southernmost of the Scandinavian nations. Denmark lies southwest of Sweden and south of Norway, and is bordered to the south by Germany. The Kingdom of Denmark also comprises two autonomous constituent countries in the North Atlantic Ocean: the Faroe Islands and Greenland. Denmark proper consists of a peninsula, Jutland, and an archipelago of 443 named islands, with the largest being Zealand, Funen and the North Jutlandic Island. The islands are characterised by flat, arable land and sandy coasts, low elevation and a temperate climate. Denmark has a total area of 42,924 km2 (16,573 sq mi), land area of 42,394 km2 (16,368 sq mi), and the total area including Greenland and the Faroe Islands is 2,210,579 km2 (853,509 sq mi), and a population of 5.8 million.

The Lübeck–Lüneburg railway line is a 77 kilometre-long, single-track non-electrified rail link from Lübeck on the Baltic coast of the German state of Schleswig-Holstein to Lüneburg in Lower Saxony. The line was opened in sections between 1851 and 1864 and is one of the oldest railways in Germany.