
The Canadian Shield, also called the Laurentian Plateau, is a geologic shield, a large area of exposed Precambrian igneous and high-grade metamorphic rocks. It forms the North American Craton, the ancient geologic core of the North American continent. Glaciation has left the area with only a thin layer of soil, through which exposures of igneous bedrock resulting from its long volcanic history are frequently visible. As a deep, common, joined bedrock region in eastern and central Canada, the Shield stretches north from the Great Lakes to the Arctic Ocean, covering over half of Canada and most of Greenland; it also extends south into the northern reaches of the United States.

Rodinia was a Mesoproterozoic and Neoproterozoic supercontinent that assembled 1.26–0.90 billion years ago and broke up 750–633 million years ago. Valentine & Moores 1970 were probably the first to recognise a Precambrian supercontinent, which they named 'Pangaea I'. It was renamed 'Rodinia' by McMenamin & McMenamin 1990 who also were the first to produce a reconstruction and propose a temporal framework for the supercontinent.

The Torngat Mountains are a mountain range on the Labrador Peninsula at the northern tip of Newfoundland and Labrador and eastern Quebec. They are part of the Arctic Cordillera. The mountains form a peninsula that separates Ungava Bay from the Atlantic Ocean.

Kenorland was one of the earliest known supercontinents on Earth. It is thought to have formed during the Neoarchaean Era c. 2.72 billion years ago by the accretion of Neoarchaean cratons and the formation of new continental crust. It comprised what later became Laurentia, Baltica, Western Australia and Kalaharia.

Columbia, also known as Nuna or Hudsonland, was one of Earth's ancient supercontinents. It was first proposed by John J.W. Rogers and M. Santosh in 2002 and is thought to have existed approximately 2,500 to 1,500 million years ago, in the Paleoproterozoic Era. The assembly of the supercontinent was likely completed during global-scale collisional events from 2100 to 1800 million years ago.
Arctica or Arctida was an ancient continent which formed approximately 2.565 billion years ago in the Neoarchean era. It was made of Archaean cratons, including the Siberian Craton, with its Anabar/Aldan shields in Siberia, and the Slave, Wyoming, Superior, and North Atlantic cratons in North America. Arctica was named by Rogers 1996 because the Arctic Ocean formed by the separation of the North American and Siberian cratons. Russian geologists writing in English call the continent "Arctida" since it was given that name in 1987, alternatively the Hyperborean craton, in reference to the hyperboreans in Greek mythology.

Baltica is a paleocontinent that formed in the Paleoproterozoic and now constitutes northwestern Eurasia, or Europe north of the Trans-European Suture Zone and west of the Ural Mountains. The thick core of Baltica, the East European Craton, is more than three billion years old and formed part of the Rodinia supercontinent at c. 1 Ga.

Siberia, also known as Angaraland and Angarida, is an ancient craton in the heart of Siberia. Today forming the Central Siberian Plateau, it was an independent continent before the Permian period. The Verkhoyansk Sea, a passive continental margin, was fringing the Siberian Craton to the east in what is now the East Siberian Lowland.

The Trans-Hudson orogeny or Trans-Hudsonian orogeny was the major mountain building event (orogeny) that formed the Precambrian Canadian Shield and the North American Craton, forging the initial North American continent. It gave rise to the Trans-Hudson orogen (THO), or Trans-Hudson Orogen Transect (THOT), which is the largest Paleoproterozoic orogenic belt in the world. It consists of a network of belts that were formed by Proterozoic crustal accretion and the collision of pre-existing Archean continents. The event occurred 2.0–1.8 billion years ago.

The Wyoming Craton is a craton in the west-central United States and western Canada – more specifically, in Montana, Wyoming, southern Alberta, southern Saskatchewan, and parts of northern Utah. Also called the Wyoming Province, it is the initial core of the continental crust of North America.
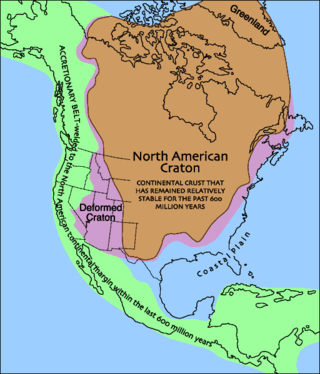
Laurentia or the North American Craton is a large continental craton that forms the ancient geological core of North America. Many times in its past, Laurentia has been a separate continent, as it is now in the form of North America, although originally it also included the cratonic areas of Greenland and also the northwestern part of Scotland, known as the Hebridean Terrane. During other times in its past, Laurentia has been part of larger continents and supercontinents and itself consists of many smaller terranes assembled on a network of Early Proterozoic orogenic belts. Small microcontinents and oceanic islands collided with and sutured onto the ever-growing Laurentia, and together formed the stable Precambrian craton seen today.

The geology of Saskatchewan can be divided into two main geological regions, the Precambrian Canadian Shield and the Phanerozoic Western Canadian Sedimentary Basin. Within the Precambrian shield exists the Athabasca sedimentary basin. Meteorite impacts have altered the natural geological formation processes. The prairies were most recently affected by glacial events in the Quaternary period.

The Iapetus Suture is one of several major geological faults caused by the collision of several ancient land masses forming a suture. It represents in part the remains of what was once the Iapetus Ocean. Iapetus was the father of Atlas in Greek mythology, making his an appropriate name for what used to be called the 'Proto-Atlantic Ocean'. When the Atlantic Ocean opened, in the Cretaceous period, it took a slightly different line from that of the Iapetus suture, with some originally Laurentian rocks being left behind in north-west Europe and other, Avalonian, rocks remaining as part of Newfoundland.
A paleocontinent or palaeocontinent is a distinct area of continental crust that existed as a major landmass in the geological past. There have been many different landmasses throughout Earth's time. They range in sizes, some are just a collection of small microcontinents while others are large conglomerates of crust. As time progresses and sea levels rise and fall more crust can be exposed making way for larger landmasses. The continents of the past shaped the evolution of organisms on Earth and contributed to the climate of the globe as well. As landmasses break apart, species are separated and those that were once the same now have evolved to their new climate. The constant movement of these landmasses greatly determines the distribution of organisms on Earth's surface. This is evident with how similar fossils are found on completely separate continents. Also, as continents move, mountain building events (orogenies) occur, causing a shift in the global climate as new rock is exposed and then there is more exposed rock at higher elevations. This causes glacial ice expansion and an overall cooler global climate. Which effects the overall global climate trend of Earth. The movement of the continents greatly affects the overall dispersal of organisms throughout the world and the trend in climate throughout Earth's history. Examples include Laurentia, Baltica and Avalonia, which collided together during the Caledonian orogeny to form the Old Red Sandstone paleocontinent of Laurussia. Another example includes a collision that occurred during the late Pennsylvanian and early Permian time when there was a collision between the two continents of Tarimsky and Kirghiz-Kazakh. This collision was caused because of their askew convergence when the paleoceanic basin closed.
Forgotten continent may refer to:

Laurentia is a bioregion atop the Laurentian craton in eastern North America, centering on the Great Lakes.
Laurentia is a Canadian drama film, directed by Mathieu Denis and Simon Lavoie and released in 2011. A meditation on Québécois identity which draws its title from the philosophical concept of Laurentie that was an early precursor to the contemporary Quebec sovereignty movement, the film stars Emmanuel Schwartz as Louis Desprès, an audiovisual technician in Montreal who sinks into a malaise of depression and identity crisis as he becomes increasingly distrustful and suspicious of his new anglophone immigrant neighbour Jay Kashyap.











