
A fluid flowing around an object exerts a force on it. Lift is the component of this force that is perpendicular to the oncoming flow direction. It contrasts with the drag force, which is the component of the force parallel to the flow direction. Lift conventionally acts in an upward direction in order to counter the force of gravity, but it can act in any direction at right angles to the flow.
Boiling is the rapid vaporization of a liquid, which occurs when a liquid is heated to its boiling point, the temperature at which the vapour pressure of the liquid is equal to the pressure exerted on the liquid by the surrounding atmosphere. There are two main types of boiling: nucleate boiling where small bubbles of vapour form at discrete points, and critical heat flux boiling where the boiling surface is heated above a certain critical temperature and a film of vapor forms on the surface. Transition boiling is an intermediate, unstable form of boiling with elements of both types. The boiling point of water is 100 °C or 212 °F but is lower with the decreased atmospheric pressure found at higher altitudes.
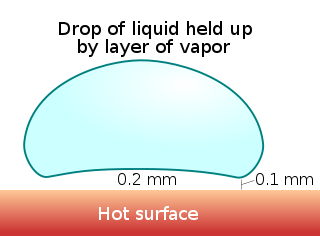
The Leidenfrost effect is a physical phenomenon in which a liquid, close to a surface that is significantly hotter than the liquid's boiling point, produces an insulating vapor layer that keeps the liquid from boiling rapidly. Because of this repulsive force, a droplet hovers over the surface, rather than making physical contact with it. The effect is named after the German doctor Johann Gottlob Leidenfrost, who described it in A Tract About Some Qualities of Common Water.

A heat exchanger is a system used to transfer heat between a source and a working fluid. Heat exchangers are used in both cooling and heating processes. The fluids may be separated by a solid wall to prevent mixing or they may be in direct contact. They are widely used in space heating, refrigeration, air conditioning, power stations, chemical plants, petrochemical plants, petroleum refineries, natural-gas processing, and sewage treatment. The classic example of a heat exchanger is found in an internal combustion engine in which a circulating fluid known as engine coolant flows through radiator coils and air flows past the coils, which cools the coolant and heats the incoming air. Another example is the heat sink, which is a passive heat exchanger that transfers the heat generated by an electronic or a mechanical device to a fluid medium, often air or a liquid coolant.

Latent heat is energy released or absorbed, by a body or a thermodynamic system, during a constant-temperature process — usually a first-order phase transition.

A boiler is a closed vessel in which fluid is heated. The fluid does not necessarily boil. The heated or vaporized fluid exits the boiler for use in various processes or heating applications, including water heating, central heating, boiler-based power generation, cooking, and sanitation.

Heat transfer is a discipline of thermal engineering that concerns the generation, use, conversion, and exchange of thermal energy (heat) between physical systems. Heat transfer is classified into various mechanisms, such as thermal conduction, thermal convection, thermal radiation, and transfer of energy by phase changes. Engineers also consider the transfer of mass of differing chemical species, either cold or hot, to achieve heat transfer. While these mechanisms have distinct characteristics, they often occur simultaneously in the same system.
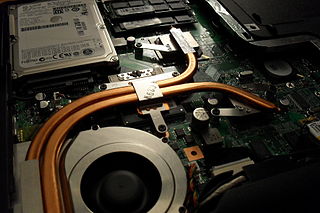
A heat pipe is a heat-transfer device that employs phase transition to transfer heat between two solid interfaces.

In fluid mechanics, two-phase flow is a flow of gas and liquid — a particular example of multiphase flow. Two-phase flow can occur in various forms, such as flows transitioning from pure liquid to vapor as a result of external heating, separated flows, and dispersed two-phase flows where one phase is present in the form of particles, droplets, or bubbles in a continuous carrier phase.

A steam explosion is an explosion caused by violent boiling or flashing of water or ice into steam, occurring when water or ice is either superheated, rapidly heated by fine hot debris produced within it, or heated by the interaction of molten metals. Pressure vessels, such as pressurized water (nuclear) reactors, that operate above atmospheric pressure can also provide the conditions for a steam explosion. The water changes from a solid or liquid to a gas with extreme speed, increasing dramatically in volume. A steam explosion sprays steam and boiling-hot water and the hot medium that heated it in all directions, creating a danger of scalding and burning.
Thermal hydraulics is the study of hydraulic flow in thermal fluids. The area can be mainly divided into three parts: thermodynamics, fluid mechanics, and heat transfer, but they are often closely linked to each other. A common example is steam generation in power plants and the associated energy transfer to mechanical motion and the change of states of the water while undergoing this process. Thermal-hydraulic analysis can determine important parameters for reactor design such as plant efficiency and coolability of the system.
Regenerative cooling, in the context of rocket engine design, is a configuration in which some or all of the propellant is passed through tubes, channels, or in a jacket around the combustion chamber or nozzle to cool the engine. This is effective because the propellants are often cryogenic. The heated propellant is then fed into a special gas-generator or injected directly into the main combustion chamber.
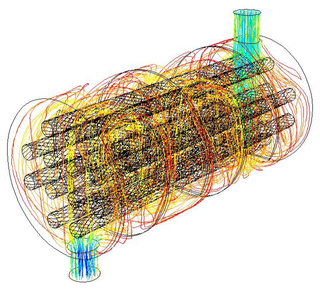
A shell and tube heat exchanger is a class of heat exchanger designs. It is the most common type of heat exchanger in oil refineries and other large chemical processes, and is suited for higher-pressure applications. As its name implies, this type of heat exchanger consists of a shell with a bundle of tubes inside it. One fluid runs through the tubes, and another fluid flows over the tubes to transfer heat between the two fluids. The set of tubes is called a tube bundle, and may be composed of several types of tubes: plain, longitudinally finned, etc.

A boiler explosion is a catastrophic failure of a boiler. There are two types of boiler explosions. One type is a failure of the pressure parts of the steam and water sides. There can be many different causes, such as failure of the safety valve, corrosion of critical parts of the boiler, or low water level. Corrosion along the edges of lap joints was a common cause of early boiler explosions.
Critical heat flux (CHF) describes the thermal limit of a phenomenon where a phase change occurs during heating, which suddenly decreases the efficiency of heat transfer, thus causing localised overheating of the heating surface.
Glacial surges are short-lived events where a glacier can advance substantially, moving at velocities up to 100 times faster than normal. Surging glaciers cluster around a few areas. High concentrations of surging glaciers occur in the Karakoram, Pamir Mountains, Svalbard, the Canadian Arctic islands, Alaska and Iceland, although overall it is estimated that only one percent of all the world's glaciers ever surge. In some glaciers, surges can occur in fairly regular cycles, with 15 to 100 or more surge events per year. In other glaciers, surging remains unpredictable. In some glaciers, however, the period of stagnation and build-up between two surges typically lasts 10 to 200 years and is called the quiescent phase. During this period the velocities of the glacier are significantly lower, and the glaciers can retreat substantially.
Economizers, or economisers (UK), are mechanical devices intended to reduce energy consumption, or to perform useful function such as preheating a fluid. The term economizer is used for other purposes as well. Boiler, power plant, heating, refrigeration, ventilating, and air conditioning (HVAC) uses are discussed in this article. In simple terms, an economizer is a heat exchanger.

A boiler or steam generator is a device used to create steam by applying heat energy to water. Although the definitions are somewhat flexible, it can be said that older steam generators were commonly termed boilers and worked at low to medium pressure but, at pressures above this, it is more usual to speak of a steam generator.
In engineering, physics, and chemistry, the study of transport phenomena concerns the exchange of mass, energy, charge, momentum and angular momentum between observed and studied systems. While it draws from fields as diverse as continuum mechanics and thermodynamics, it places a heavy emphasis on the commonalities between the topics covered. Mass, momentum, and heat transport all share a very similar mathematical framework, and the parallels between them are exploited in the study of transport phenomena to draw deep mathematical connections that often provide very useful tools in the analysis of one field that are directly derived from the others.
Compressor surge is a form of aerodynamic instability in axial compressors or centrifugal compressors. The term describes violent air flow oscillating in the axial direction of a compressor, which indicates the axial component of fluid velocity varies periodically and may even become negative. In early literature, the phenomenon of compressor surge was identified by audible thumping and honking at frequencies as low as 1 Hertz, pressure pulsations throughout the machine, and severe mechanical vibration.












