Year 1017 (MXVII) was a common year starting on Tuesday of the Julian calendar.
The 1010s was a decade of the Julian Calendar which began on January 1, 1010, and ended on December 31, 1019.

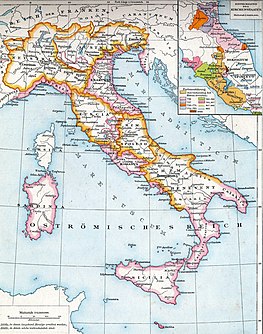
The Catepanateof Italy was a province of the Byzantine Empire, comprising mainland Italy south of a line drawn from Monte Gargano to the Gulf of Salerno. Amalfi and Naples, although north of that line, maintained allegiance to Constantinople through the catepan. The Italian region of Capitanata derives its name from the Catepanate.

Ultraman Leo is a Japanese tokusatsu TV show and is the 7th show in the Ultra Series. Produced by Tsuburaya Productions, Ultraman Leo was aired between April 12, 1974, and March 28, 1975, with a total of 51 episodes. Tatsumi Nikamoto was the in-suit actor of Ultraman Leo.
Argyrus was a Lombard nobleman and Byzantine general, son of the Lombard hero Melus. He was born in Bari.
Rainulf Drengot was a Norman adventurer and mercenary in southern Italy. In 1030 he became the first count of Aversa. He was a member of the Drengot family.

Basil Boioannes, called Bugiano in Italian, was the Byzantine catapan of Italy and one of the greatest Byzantine generals of his time. His accomplishments enabled the Empire to reestablish itself as a major force in southern Italy after centuries of decline. Yet, the Norman adventurers introduced into the power structure of the Mezzogiorno would be the eventual beneficiaries.
Guaimar III was the Lombard prince of Salerno from around 994 to his death. Under his reign, Salerno entered an era of great splendour. Opulenta Salernum was the inscription on his coins. He made Amalfi, Gaeta and Sorrento his vassals and annexed much of Byzantine Apulia and Calabria.
The Battle of Cannae was a battle that took place in 1018 between the Byzantines under the Catepan of Italy Basil Boioannes and the Lombards under Melus of Bari. The Lombards had also hired some Norman cavalry mercenaries under their leader Gilbert Buatère, while Boioannes had a detachment of elite Varangian Guard sent to him at his request to combat the Normans.
Osmond Drengot was one of the first Norman adventurers in the Mezzogiorno. He was the son of a petty, but rich, lord of Carreaux, at Bosc-Hyons in the region of Rouen. Carreaux gives his family the alternate name of de Quarrel.
Gilbert Buatère was one of the first Norman adventurers in the Mezzogiorno. He was the eldest son of a petty, but rich, lord of Carreaux, near Avesnes-en-Bray in the region of Rouen. Carreaux gives his family, the Drengot, the alternate name of de Quarrel.
Basil Mesardonites was the Catapan of Italy, representing the Byzantine Emperor there, from 1010 to 1016 or 1017. He succeeded the catapan John Kourkouas, who died fighting the Lombards, then in rebellion under Melus, early in 1010. In March, Basil disembarked with reinforcements from Constantinople and Leo Tornikios Kontoleon, the strategos of Cephalonia. Basil immediately besieged the rebels in Bari. The Greek citizens of the city negotiated with Basil and forced the Lombard leaders, Melus and Dattus, to flee. Basil entered the city on June 11, 1011 and reestablished Byzantine authority. He did not follow his victory up with any severe reactions. He simply sent the family of Melus, including his son Argyrus, to Constantinople. Basil's next move was to ally to the Greek Empire as many Lombard principalities as possible. He visited Salerno in October, where Prince Guaimar III was nominally a Byzantine vassal. He then moved on to Monte Cassino, which monastery was sheltering Dattus on its lands. Basil nevertheless confirmed all the privileges of the monastery over its property in Greek territory. The abbot, Atenulf, was a brother of the prince of Capua, Pandulf IV. The monastery then promptly expelled Dattus and he fled to papal territory. Basil held the Greek catapanate in peace until his death in 1016, or, according to Lupus Protospatharius, 1017. He was replaced by the aforementioned strategos of Cephalonia, Leo.
Kontoleon Tornikios was the Catapan of Italy from May to September 1017. He was originally the strategos of Cephallenia. As strategos, he accompanied the catapan Basil Mesardonites to Apulia in 1011. Basil died in 1016 and Leo was nominated to replace him, arriving in May. At the time, Melus of Bari had risen in revolt again, this time with a band of Normans. Leo sent Leo Passianos with an army against him. Passianos and Melus met on the Fortore at Arenula. The battle was either indecisive or a victory for Melus. Tornikios then took command himself and led them into a second encounter near Civita. This second battle was a victory for Melus, though Lupus Protospatharius and the anonymous chronicler of Bar record a defeat. A third battle, a decisive victory for Melus, occurred at Vaccaricia, near the site of later Troia. The entire region from the Fortore to Trani had fallen to Melus and in September, Tornikios was relieved of his duties in favour of Basil Boiannes.
Rudolph Drengot was one of the Drengot family of Norman adventureres who came to Southern Italy with his brothers, Gilbert, Asclettin, Osmond, and Ranulf.
John Kourkouas was the Byzantine catepan of Italy from 1008 to his death. Belonging to the Kourkouas family, he was of Armenian descent.
Dattus was a Lombard leader from Bari, the brother-in-law of Melus of Bari. He joined his brother-in-law in a 1009 revolt against Byzantine authority in southern Italy.

The Norman conquest of southern Italy lasted from 999 to 1139, involving many battles and independent conquerors. In 1130 these territories in southern Italy united as the Kingdom of Sicily, which included the island of Sicily, the southern third of the Italian Peninsula, the archipelago of Malta and parts of North Africa.
Leo Tornikios was a mid-11th century Byzantine general and noble. In 1047, he rebelled against his uncle, the Byzantine Emperor, Constantine IX Monomachos. He raised an army in Thrace and marched on the capital, Constantinople, which he besieged. After two failed assaults he withdrew, his army deserted him and he was captured. At Christmas 1047, he was blinded and no more is known of him.