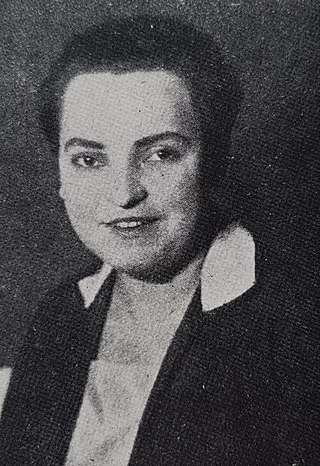Magnus T. Hirschfeld was a Jewish German physician and sexologist, whose citizenship was later revoked by the Nazi government. Hirschfeld was educated in philosophy, philology and medicine. An outspoken advocate for sexual minorities, Hirschfeld founded the Scientific-Humanitarian Committee and World League for Sexual Reform. He based his practice in Berlin-Charlottenburg during the Weimar period. Performance Studies and Rhetoric Professor Dustin Goltz characterized the committee as having carried out "the first advocacy for homosexual and transgender rights".

FannyAnn Viola Eddy was a Sierra Leonean LGBT activist who founded the Sierra Leone Lesbian and Gay Association (SSLGA) in 2002, the country's first LGBT organisation. Eddy advocated for LGBT rights in Sierra Leone as well as throughout Africa, and in April 2004 addressed the United Nations in Geneva to advocate for the passing of the Brazilian Resolution. She was murdered in her office in Freetown in September 2004, in a crime that remains unsolved.

LSVD+ – Verband Queere Vielfalt (LSVD+), German for the LSVD+ – Federation Queer Diversity, is the largest non-governmental LGBT rights organisation in Germany. It was founded in 1990 and is part of the International Lesbian, Gay, Bisexual, Trans and Intersex Association (ILGA).

The Scientific-Humanitarian Committee was founded by Magnus Hirschfeld in Berlin in May 1897, to campaign for social recognition of lesbian, gay, bisexual and transgender people, and against their legal persecution. It was the first LGBT rights organization in history. The motto of the organization was "Per scientiam ad justitiam", and the committee included representatives from various professions. The committee's membership peaked at about 700 people. In 1929, Kurt Hiller took over as chairman of the group from Hirschfeld. At its peak, the WhK had branches in approximately 25 cities in Germany, Austria and the Netherlands.
The Society for Human Rights was an American gay-rights organization established in Chicago in 1924. Society founder Henry Gerber was inspired to create it by the work of German doctor Magnus Hirschfeld and the Scientific-Humanitarian Committee and by the organisation Bund für Menschenrecht by Friedrich Radszuweit and Karl Schulz in Berlin. It was the first recognized gay rights organization in the United States, having received a charter from the state of Illinois, and produced the first American publication for homosexuals, Friendship and Freedom. A few months after being chartered, the group ceased to exist in the wake of the arrest of several of the Society's members. Despite its short existence and small size, the Society has been recognized as a precursor to the modern gay liberation movement.
The Hirschfeld-Eddy Foundation was founded in Berlin in June 2007. It is a foundation focused on human rights of lesbian, gay, bisexual and transgender (LGBT) people.

Henry Gerber was an early homosexual rights activist in the United States. Inspired by the work of Germany's Magnus Hirschfeld and his Scientific-Humanitarian Committee and by the organisation Bund für Menschenrecht by Friedrich Radszuweit and Karl Schulz, Gerber founded the Society for Human Rights (SHR) in 1924, the nation's first known homosexual organization, and Friendship and Freedom, the first known American homosexual publication. SHR was short-lived, as police arrested several of its members shortly after it incorporated. Although embittered by his experiences, Gerber maintained contacts within the fledgling homophile movement of the 1950s and continued to agitate for the rights of homosexuals. Gerber has been repeatedly recognized for his contributions to the LGBT movement.
This is a list of events in Lesbian, Gay, Bisexual, Transgender, Queer and Intersex (LGBTQ+) history in Germany.

Die Freundin was a popular Weimar-era German lesbian magazine published from 1924 to 1933. Founded in 1924, it was the world's first lesbian magazine, closely followed by Frauenliebe and Die BIF. The magazine was published from Berlin, the capital of Germany, by the Bund für Menschenrecht, run by gay activist and publisher Friedrich Radszuweit. The Bund was an organization for homosexuals which had a membership of 48,000 in the 1920s.
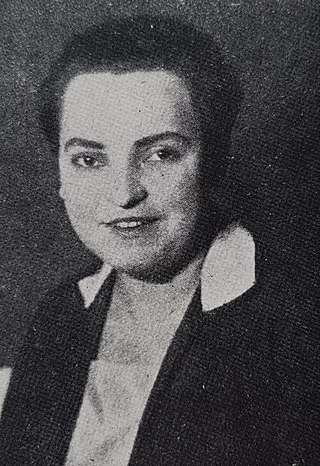
Selma "Selli" Engler was a leading activist of the lesbian movement in Berlin from about 1924 to 1931.

The National LGBT Federation (NXF) is a non-governmental organisation in Dublin, Ireland, which focuses on lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) rights.

The Yearbook for Intermediate Sexual Types was an annual publication of the Scientific-Humanitarian Committee, an early LGBT rights organization founded by German sexologist Magnus Hirschfeld in 1897. The periodical featured articles on scientific, literary, and political topics related to sexual and gender minorities. It was published regularly from 1899 to 1923 and more sporadically until 1933.

Ilse Kokula is a German sociologist, educator, author and lesbian activist in the field of lesbian life. She was awarded the Order of Merit of the Federal Republic of Germany.

Susann Rüthrich is a German politician of the Social Democratic Party (SPD) who has been serving as a member of the Bundestag from the state of Saxony since 2013.

The German Democratic Republic, a state in Central Europe that existed from 1949 to 1990 before merging with the Federal Republic of Germany, was dominated by heterosexual norms. However, homosexual East Germans experienced decriminalisation during the 1960s, followed by increasing social acceptance and visibility.

Die BIF – Blätter Idealer Frauenfreundschaften, subtitled Monatsschrift für weibliche Kultur, was a short-lived lesbian magazine of Weimar Germany, published from either 1925 or 1926 until 1927 in Berlin. Founded by lesbian activist Selli Engler, Die BIF was part of the first wave of lesbian publications in history and the world's first lesbian magazine to be published, edited and written solely by women.

Charlotte "Lotte" Hedwig Hahm was a prominent activist of the lesbian movement in Berlin during the Weimar Republic, National Socialist period, and after 1949, in the Federal Republic of Germany.

The Forum Queeres Archiv München in Munich, Germany, is an association and archive with collections focusing on LGBTQ+ history and culture in Munich, Bavaria and Germany. It opened in 1999 and was named forum homosexualität münchen – Lesben und Schwule in Geschichte und Kultur e.V. till 2019.

The first homosexual movement was a socio-political movement which thrived in Germany from the late nineteenth century until 1933. The movement began in Germany because of a confluence of factors, including the criminalization of sex between men and the country's relatively lax censorship. German writers in the mid-nineteenth century coined the word homosexual and criticized its criminalization. In 1897, Magnus Hirschfeld founded the world's first homosexual organization, the Scientific-Humanitarian Committee, whose aim was to use science to improve public tolerance of homosexuality and repeal Paragraph 175. During the German Empire, the movement was restricted to an educated elite, but it greatly expanded in the aftermath of World War I and the German Revolution.
Ursula Sillge is a German sociologist and LGBT activist. She organized the first national lesbian gathering in East Germany, and between 1970 and 1990 was one of the main lesbian activists in the country, pressing authorities to recognize the rights and allow visibility of the LGBT community. In 1986, she founded the Sunday Club in Berlin. It was the only secular association representing homosexuals in the 1980s, though it was not officially recognized. The organization became the first legal association to represent the LGBT community in East Germany when it was allowed to register in 1990. Sillge resigned as director of the Sunday Club in 1991 to found the LGBT archive known as the Lila Women's Archives. After the fall of the Berlin Wall, she was able to earn her doctorate. In addition to running the archives, she has published several works about homosexuality and women behind the Iron Curtain.