Related Research Articles
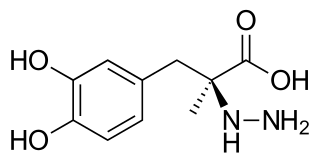
Carbidopa (Lodosyn) is a drug given to people with Parkinson's disease in order to inhibit peripheral metabolism of levodopa. This property is significant in that it allows a greater proportion of administered levodopa to cross the blood–brain barrier for central nervous system effect, instead of being peripherally metabolised into substances unable to cross said barrier.

Benserazide is a peripherally acting aromatic L-amino acid decarboxylase or DOPA decarboxylase inhibitor, which is unable to cross the blood–brain barrier.

Zonisamide, sold under the brand name Zonegran among others, is a medication used to treat the symptoms of epilepsy and Parkinson's disease. Chemically it is a sulfonamide. It serves as an anticonvulsant used primarily as an adjunctive therapy in adults with Parkinson's disease, partial-onset seizures; infantile spasm, mixed seizure types of Lennox–Gastaut syndrome, myoclonic and generalized tonic clonic seizure. Despite this it is also sometimes used as a monotherapy for partial-onset seizures.
Carbidopa/levodopa, also known as levocarb and co-careldopa, is the combination of the two medications carbidopa and levodopa. It is primarily used to manage the symptoms of Parkinson's disease, but it does not slow down the disease or stop it from getting worse. It is taken by mouth. It can take two to three weeks of treatment before benefits are seen. Each dose then begins working in about ten minutes to two hours with a duration of effect of about five hours.

Entacapone, sold under the brand name Comtan among others, is a medication commonly used in combination with other medications for the treatment of Parkinson's disease. Entacapone together with levodopa and carbidopa allows levodopa to have a longer effect in the brain and reduces Parkinson's disease signs and symptoms for a greater length of time than levodopa and carbidopa therapy alone.
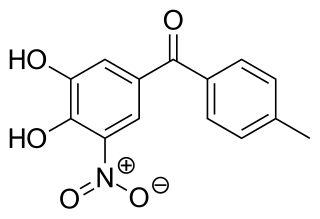
Tolcapone, sold under the brand name Tasmar, is a medication used to treat Parkinson's disease (PD). It is a selective, potent and reversible nitrocatechol-type inhibitor of the enzyme catechol-O-methyltransferase (COMT). It has demonstrated significant liver toxicity, which has led to suspension of marketing authorisations in a number of countries.
In the management of Parkinson's disease, due to the chronic nature of Parkinson's disease (PD), a broad-based program is needed that includes patient and family education, support-group services, general wellness maintenance, exercise, and nutrition. At present, no cure for the disease is known, but medications or surgery can provide relief from the symptoms.

Dihydroergocryptine (DHEC), sold under the brand names Almirid and Cripar among others, is a dopamine agonist of the ergoline group that is used as an antiparkinson agent in the treatment of Parkinson's disease. It is taken by mouth.

A catechol-O-methyltransferase inhibitor is a drug that inhibits the enzyme catechol-O-methyltransferase. This enzyme methylates catecholamines such as dopamine, norepinephrine and epinephrine. It also methylates levodopa. COMT inhibitors are indicated for the treatment of Parkinson's disease in combination with levodopa and an aromatic L-amino acid decarboxylase inhibitor. The therapeutic benefit of using a COMT inhibitor is based on its ability to prevent the methylation of levodopa to 3-O-methyldopa, thus increasing the bioavailability of levodopa. COMT inhibitors significantly decrease off time in people with Parkinson's disease also taking carbidopa/levodopa.

Brasofensine is a phenyltropane dopamine reuptake inhibitor that had been under development by Bristol-Myers Squibb and defunct company NeuroSearch for the treatment of Parkinson's and Alzheimer's diseases.
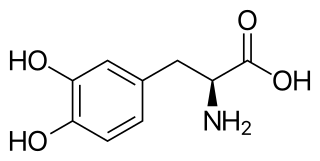
Levodopa, also known as L-DOPA and sold under many brand names, is a dopaminergic medication which is used in the treatment of Parkinson's disease and certain other conditions like dopamine-responsive dystonia and restless legs syndrome. The drug is usually used and formulated in combination with a peripherally selective aromatic L-amino acid decarboxylase (AAAD) inhibitor like carbidopa or benserazide. Levodopa is taken by mouth, by inhalation, through an intestinal tube, and by administration into fat.
Carbidopa/levodopa/entacapone, sold under the brand name Stalevo among others, is a dopaminergic fixed-dose combination medication that contains carbidopa, levodopa, and entacapone for the treatment of Parkinson's disease.

An aromatic L-amino acid decarboxylase inhibitor (synonyms: DOPA decarboxylase inhibitor, extracerebral decarboxylase inhibitor, DDCI and AAADI) is a medication of type enzyme inhibitor which inhibits the synthesis of dopamine by the enzyme aromatic L-amino acid decarboxylase (AADC, AAAD, or DOPA decarboxylase). It is used to inhibit the decarboxylation of L-DOPA to dopamine outside the brain, i.e. in the blood. This is primarily co-administered with L-DOPA to combat Parkinson's disease. Administration can prevent common side-effects, such as nausea and vomiting, as a result of interaction with D2 receptors in the vomiting center (or cheomoreceptor trigger zone) located outside the blood–brain barrier.

Safinamide, sold under the brand name Xadago, is a medication used as treatment for Parkinson's disease with "off" episodes; it has multiple modes of action, including the inhibition of monoamine oxidase B.

Parkinson's disease (PD), or simply Parkinson's, is a neurodegenerative disease of mainly the central nervous system that affects both the motor and non-motor systems of the body. The symptoms usually emerge slowly, and, as the disease progresses, non-motor symptoms become more common. Usual symptoms include tremors, slowness of movement, rigidity, and difficulty with balance, collectively known as parkinsonism. Parkinson's disease dementia, falls and neuropsychiatric problems such as sleep abnormalities, psychosis, mood swings, or behavioral changes may also arise in advanced stages.
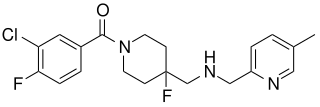
Befiradol is an experimental drug being studied for the treatment of levodopa-induced dyskinesia. It is a potent and selective 5-HT1A receptor full agonist.
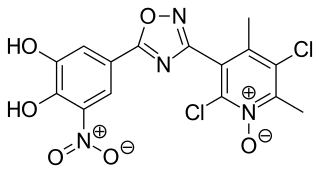
Opicapone, sold under the brand name Ongentys, is a medication which is administered together with levodopa in people with Parkinson's disease. Opicapone is a catechol-O-methyltransferase (COMT) inhibitor.

Monoamine precursors are precursors of monoamines and monoamine neurotransmitters in the body. The amino acids L-tryptophan and L-5-hydroxytryptophan are precursors of serotonin and melatonin, while the amino acids L-phenylalanine, L-tyrosine, and L-DOPA (levodopa) are precursors of dopamine, epinephrine (adrenaline), and norepinephrine (noradrenaline).
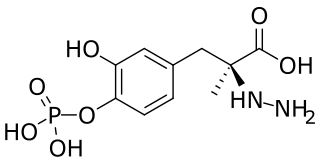
Foscarbidopa/foslevodopa, sold under the brand name Vyalev, is a fixed-dose combination medication used for the treatment of Parkinson's disease. It is a combination of prodrugs for levodopa and carbidopa that was developed by AbbVie.
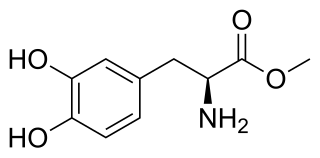
Melevodopa/carbidopa, sold under the brand name Sirio, is a combination of melevodopa, a prodrug of the dopamine precursor and hence non-selective dopamine receptor agonist levodopa (L-DOPA), and carbidopa, a peripherally selective aromatic L-amino acid decarboxylase (AAAD) inhibitor, which is used in the treatment of Parkinson's disease in Italy. It is taken orally in the form of tablets.
References
- ↑ "Levodopa".
- 1 2 3 4 "Madopar Product Information". Medsinfo. 8 July 2019. Retrieved 2 September 2024.
- 1 2 3 "Prolopa Product information". Health Canada . 25 April 2012. Retrieved 8 January 2023.
- 1 2 3 "Madopar 100 mg/25 mg Dispersible Tablets - Summary of Product Characteristics (SmPC)". (emc). 8 April 2020. Retrieved 9 January 2023.