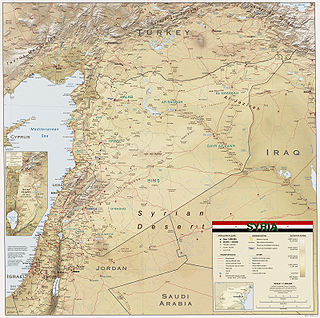
Syria is located in West Asia, north of the Arabian Peninsula, at the eastern end of the Mediterranean Sea. It is bordered by Turkey to the north, Lebanon and Israel to the west and southwest, Iraq to the east, and Jordan to the south. It consists of mountain ranges in the west and a steep area inland. In the east is the Syrian Desert and in the south is the Jabal al-Druze Range. The former is bisected by the Euphrates valley. A dam built in 1973 on the Euphrates created a reservoir named Lake Assad, the largest lake in Syria. The highest point in Syria is Mount Hermon on the Lebanese border at 2,814 metres or 9,232 feet. Between the humid Mediterranean coast and the arid desert regions lies a semiarid steep zone extending across three-quarters of the country, which receives hot, dry winds blowing across the desert. Syria is extensively depleted, with 28 percent of the land arable, 4 percent dedicated to permanent crops, 46 percent utilized as meadows and pastures, and only 3 percent forest and woodland.

The Guiana Shield is one of the three cratons of the South American Plate. It is a 1.7 billion-year-old Precambrian geological formation in northeast South America that forms a portion of the northern coast. The higher elevations on the shield are called the Guiana Highlands, which is where the table-like mountains called tepuis are found. The Guiana Highlands are also the source of some of the world's most well-known waterfalls such as Angel Falls, Kaieteur Falls and Cuquenan Falls.

Vinson Massif is a large mountain massif in Antarctica that is 21 km (13 mi) long and 13 km (8 mi) wide and lies within the Sentinel Range of the Ellsworth Mountains. It overlooks the Ronne Ice Shelf near the base of the Antarctic Peninsula. The massif is located about 1,200 kilometres (750 mi) from the South Pole. Vinson Massif was discovered in January 1958 by U.S. Navy aircraft. In 1961, the Vinson Massif was named by the Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names (US-ACAN), after Carl G. Vinson, United States congressman from the state of Georgia, for his support for Antarctic exploration. On November 1, 2006, US-ACAN declared Mount Vinson and Vinson Massif to be separate entities. Vinson Massif lies within the unrecognised Chilean claim under the Antarctic Treaty System.
A massif is a principal mountain mass, such as a compact portion of a mountain range, containing one or more summits. In mountaineering literature, a massif is frequently used to denote the main mass of an individual mountain.

The Massif Central is a highland region in south-central France consisting of mountains and plateaus. It covers about 15% of mainland France.

Sky islands are isolated mountains surrounded by radically different lowland environments. The term originally referred to those found on the Mexican Plateau and has extended to similarly isolated high-elevation forests. The isolation has significant implications for these natural habitats. The American Southwest region began warming up between c. 20,000 and 10,000 years BP and atmospheric temperatures increased substantially, resulting in the formation of vast deserts that isolated the sky islands. Endemism, altitudinal migration, and relict populations are some of the natural phenomena to be found on sky islands.

The Dead Cities or Forgotten Cities are a group of 700 abandoned settlements in northwest Syria between Aleppo and Idlib. Around 40 villages grouped in eight archaeological parks situated in north-western Syria provide an insight into rural life in Late Antiquity and during the Byzantine period. Most of the villages, which date from the 1st to 7th centuries, were abandoned between the 8th and 10th centuries. The settlements feature the well-preserved architectural remains of buildings such as dwellings, pagan temples, churches, cisterns and bathhouses. Important dead cities include the Church of Saint Simeon Stylites, Dahis, Serjilla, Ruweiha and al Bara.

The Ethiopian Highlands is a rugged mass of mountains in Ethiopia in Northeast Africa. It forms the largest continuous area of its elevation in the continent, with little of its surface falling below 1,500 m (4,900 ft), while the summits reach heights of up to 4,550 m (14,930 ft). It is sometimes called the "Roof of Africa" due to its height and large area. It is the only country in the region with such a high elevated surface. This elevated surface is bisected diagonally by the Great East African Rift System which extends from Syria to Mozambique across the East African Lakes. Most of the Ethiopian Highlands are part of central and northern Ethiopia, and its northernmost portion reaches into Eritrea.
Antiochia ad Taurum was a Hellenistic city in ancient Syria east of Mount Amanus of the Taurus mountain range. Later identified as 'ad Taurum montem' in the Commagene province of Syria.

Kurd Mountain or Kurd Dagh is a highland region in northwestern Syria and southeastern Turkey. It is located in the Aleppo Governorate of Syria and Kilis Province of Turkey. The Kurd Mountain should not be confused with the neighboring Jabal al-Akrad, which is located further southwest in Latakia Governorate.

Aleppo Governorate is one of the fourteen governorates of Syria. It is the most populous governorate in Syria with a population of more than 4,867,000, almost 23% of the total population of Syria. The governorate is the fifth in area with an area of 18,482 km2 (7,136 sq mi), or 18,498 km2, about 10% of the total area of Syria. The capital is the city of Aleppo.

The Eastern Mediterranean conifer-sclerophyllous-forests, also known as the Eastern Mediterranean conifer-forests, is an ecoregion in the eastern Mediterranean Basin. It covers portions of Turkey, Syria, Iraq, Lebanon, Israel, Palestinian territories, Jordan, and Saudi Arabia.
Mount Simeon or Mount Simon, also called Mount Laylūn (Arabic: جبل ليلون, is a highland region in Aleppo Governorate in northern Syria. The mountain is located in the Mount Simeon and Aʻzāz districts of Aleppo Governorate.

Ottoman Syria is a historiographical term used to describe the group of divisions of the Ottoman Empire within the region of Levant, usually defined as being east of the Mediterranean Sea, west of the Euphrates River, north of the Arabian Desert and south of the Taurus Mountains.

The Guinea Highlands is a densely forested mountainous plateau extending from central Guinea through northern Sierra Leone and Liberia to western Ivory Coast. The highlands include a number of mountains, ranges and plateaus, including the Fouta Djallon highlands in central Guinea, the Loma Mountains in Sierra Leone, the Simandou and Kourandou massifs in southeastern Guinea, the Nimba Range at the border of Guinea, Liberia, and Ivory Coast, and the Monts du Toura in western Ivory Coast.

The Aleppo plateau is a low, gently undulating plateau of northern Syria. It lies at the northern end of the junction between the Arabian Plate and the African Plate at the Dead Sea Rift. The plateau lies mostly in the Aleppo Governorate and Idlib Governorate. Aleppo is located in the north-center of the plateau.

Aintab plateau or Gaziantep plateau is the westernmost part of Turkey's Southeastern Anatolia Region. It forms the northwestern end of the Arabian plate where it meets the Anatolian sub-plate at the East Anatolian Fault. The plateau lies in the Turkish provinces of Gaziantep, Kilis, and Adıyaman. It is a low, gently undulating plateau. In antiquity, this was the region of Commagene. Gaziantep (Aintab) is located nearly in the south-center of the plateau.
Harim Mountains are highlands in the north of Idlib Governorate in northwestern Syria. The mountains are located in the Harim and Jisr Shughur districts of Idlib Governorate.
Mount Zāwiya or Mount Rīḥā (also in medieval times: Banī-ʻUlaym Mountain is a highland region in Idlib Governorate in northwestern Syria. Around 36 towns and villages exist in the Mount Zawiya region. The biggest towns are Rīḥā and Maʻarrat an-Nuʻmān.

Mount Ḥaṣṣ or Mount Aḥaṣṣ is a 500-metre-high plateau on the northern fringe of the Syrian Desert. It is located in the Safīrah District of Aleppo Governorate in Syria.













