Related Research Articles

A V12 engine is a twelve-cylinder piston engine where two banks of six cylinders are arranged in a V configuration around a common crankshaft. V12 engines are more common than V10 engines. However, they are less common than V8 engines.
Lincoln is the luxury vehicle division of American automobile manufacturer Ford. Marketed among the top luxury vehicle brands in the United States for nearly its entire existence, Lincoln has competed closely against its General Motors counterpart Cadillac. The division has the distinction of establishing the personal luxury car segment with the 1940 Lincoln Continental; more recently, the 1998 Lincoln Navigator would be the first full-size luxury SUV.

The Cadillac Motor Car Division is a division of the American automobile manufacturer General Motors Company (GM) that designs and builds luxury vehicles. Its major markets are the United States, Canada, and China. Cadillac models are distributed in 34 additional markets worldwide. Cadillac automobiles are at the top of the luxury field within the United States. In 2019, Cadillac sold 390,458 vehicles worldwide, a record for the brand.

Mercury is a defunct division of the American automobile manufacturer Ford Motor Company. Created in 1938 by Edsel Ford, Mercury was marketed as an entry-level premium brand for nearly its entire existence, bridging the price gap between the Ford and Lincoln model lines. Competing against Oldsmobile within General Motors, Mercury also competed most directly against Chrysler's DeSoto.

Allard Motor Company Limited was a London-based low-volume car manufacturer founded in 1945 by Sydney Allard in small premises in Clapham, south-west London. Car manufacture almost ceased within a decade. It produced approximately 1900 cars before it became insolvent and ceased trading in 1958. Before the war, Allard supplied some replicas of a Bugatti-tailed special of his own design from Adlards Motors in Putney.

The Ford Country Squire is a series of station wagons that was assembled by American automaker Ford. The premium station wagon of the Ford division, the Country Squire was distinguished by its external woodgrain trim. From the 1950 to 1991 model years, eight generations of the Country Squire were produced. Following the discontinuation of Edsel, Mercury marketed the Mercury Colony Park as a divisional counterpart of the Country Squire, sharing bodywork and trim.

The Lincoln Continental is a series of mid-sized and full-sized luxury cars produced by Lincoln, a division of the American automaker Ford Motor Company. The model line was introduced following the construction of a personal vehicle for Edsel Ford, who commissioned a coachbuilt 1939 Lincoln-Zephyr convertible, developed as a vacation vehicle to attract potential Lincoln buyers. In what would give the model line its name, the exterior was given European "continental" styling elements, including a rear-mounted spare tire.

The Chevrolet El Camino is a pickup / coupé utility vehicle that was produced by Chevrolet between 1959–60 and 1964–1987. Unlike a standard pickup truck, the El Camino was adapted from the standard two-door Chevrolet station wagon platform and integrated the cab and cargo bed into the body.

The Ford Fairmont is a compact car that was produced by Ford from the 1978 to the 1983 model years. The successor of the Ford Maverick, the Fairmont was the third generation of compact sedans sold by Ford in North America; Lincoln-Mercury marketed the model line as the Mercury Zephyr. In contrast to Maverick, the Fairmont was a completely new design, no longer based upon the Ford Falcon.
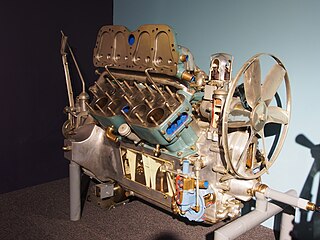
Cadillac was the first automobile maker in the world to mass-produce V8 engines. The company has produced many generations and variations of V8s since 1914. In 2010, when the Northstar engine series ended production, it became the last General Motors division to retain its own proprietary V8 design. This changed when Cadillac created the twin-turbo 'Blackwing' engine in 2019..

The Ford flathead V8 is a V8 engine with a flat cylinder head designed by the Ford Motor Company and built by Ford and various licensees. During the engine's first decade of production, when overhead-valve engines were used by only a small minority of makes, it was usually known simply as the Ford V‑8, and the first car model in which it was installed, the Model 18, was often called simply the "Ford V‑8", after its new engine. Although the V8 configuration was not new when the Ford V8 was introduced in 1932, the latter was a market first in the respect that it made an 8-cylinder affordable and a V engine affordable to the emerging mass market consumer for the first time. It was the first independently designed and built V8 engine produced by Ford for mass production, and it ranks as one of the company's most important developments. A fascination with ever-more-powerful engines was perhaps the most salient aspect of the American car and truck market for a half century, from 1923 until 1973. The engine was intended to be used for big passenger cars and trucks; it was installed in such until 1953, making the engine's 21-year production run for the U.S. consumer market longer than the 19-year run of the Ford Model T engine for that market. The engine was on Ward's list of the 10 best engines of the 20th century. It was a staple of hot rodders in the 1950s, and it remains famous in the classic car hobbies even today, despite the huge variety of other popular V8s that followed.
The Lincoln Y-block V8 engine was Ford's earliest OHV V8 engine, introduced by Lincoln in the 1952 model year. Like the later and better-known but even more short-lived Ford Y-block engine, its block's deep skirts gave the block the appearance of the letter Y from the front.

The Lincoln Custom is a custom limousine and long-wheelbase touring sedan that was built by Lincoln in 1941 and 1942 and the lower level series Lincoln produced in 1955. Initially it was a replacement for the large Model K Lincolns and earlier luxury cars of the 1920s and 1930s. Later it was simply the lower level series.

The Lincoln Capri is an automobile that was sold by the Lincoln division of Ford Motor Company from 1952 to 1959. A full-size luxury car, the Lincoln Capri derives its name from an Italian island in the Gulf of Naples. Introduced as a premium trim variant of the two-door Lincoln Cosmopolitan, the Capri was introduced in 1952 as a stand-alone model line serving as the premium Lincoln. With the introduction of the Lincoln Premiere, the Capri replaced the Cosmopolitan as the standard Lincoln product line.

The Lincoln K series is a luxury vehicle that was produced by the Lincoln Motor Company. The second motor line produced by the company, the Model K was developed from the Model L, including a modernized chassis on a longer wheelbase. In 1931, Lincoln introduced a V-12 engine, becoming a feature of the company for nearly 20 years.

The Lincoln-Zephyr is a line of luxury cars that was produced by the Lincoln division of Ford from 1936 to 1942. Bridging the gap between the Ford V8 DeLuxe and the Lincoln Model K, the Lincoln-Zephyr expanded Lincoln to a second model line, competing against the Chrysler Airstream, LaSalle, and the Packard One-Twenty.

Ford Motor Company's Lincoln division produced two other L-head V12 engines from 1932, but required a more compact unit for their new streamlined Lincoln-Zephyr line. As Ford had just introduced their Flathead V8, this was the logical starting point for a new Lincoln V12 line. The Lincoln-Zephyr V12 would quickly replace the previous-generation V12, just as the Lincoln-Zephyr car replaced the rest of the Lincoln line, and would be the company's primary engine through 1948.

The Ford line of cars was again refreshed for 1952, although remaining similar to the all-new 1949 Fords. This time, curved one-piece windshield glass joined a new "Mileage Maker" straight-6 engine with 101 hp. The 226 CID (3.7 L) L-head straight-6 was replaced by an overhead valve 215 CID (3.5 L) Mileage Maker with 101 hp (75 kW), while the old 239 CID (3.9 L) Flathead V8 remained with 110 hp (82 kW). This design would continue through the 1954 model year, with an updated design offered in 1955.

The Lincoln EL-Series is a full-size luxury car that was marketed and sold by the Lincoln division of Ford Motor Company from the 1949 to 1951 model years. For the 1949 model year, Ford introduced redesigned model lines for all three of its divisions. To share development costs, Ford combined its separate Lincoln and Mercury divisions into the Lincoln-Mercury Division following World War II. As a result, the redesigned postwar Lincoln shared much of its design with the redesigned 1949 Mercury Eight.
References
- David L. Lewis (2005). 100 Years of Ford. Publications International. pp. 82–. ISBN 0-7853-7988-6.