Related Research Articles
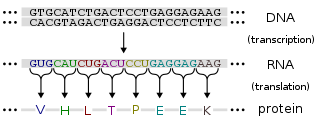
Protein production is the biotechnological process of generating a specific protein. It is typically achieved by the manipulation of gene expression in an organism such that it expresses large amounts of a recombinant gene. This includes the transcription of the recombinant DNA to messenger RNA (mRNA), the translation of mRNA into polypeptide chains, which are ultimately folded into functional proteins and may be targeted to specific subcellular or extracellular locations.

Poliovirus, the causative agent of polio, is a serotype of the species Enterovirus C, in the family of Picornaviridae. There are three poliovirus serotypes: types 1, 2, and 3.
Indiana vesiculovirus, formerly Vesicular stomatitis Indiana virus is a virus in the family Rhabdoviridae; the well-known Rabies lyssavirus belongs to the same family. VSIV can infect insects, cattle, horses and pigs. It has particular importance to farmers in certain regions of the world where it infects cattle. This is because its clinical presentation is identical to the very important foot and mouth disease virus.

Adenoviruses are medium-sized, nonenveloped viruses with an icosahedral nucleocapsid containing a double-stranded DNA genome. Their name derives from their initial isolation from human adenoids in 1953.
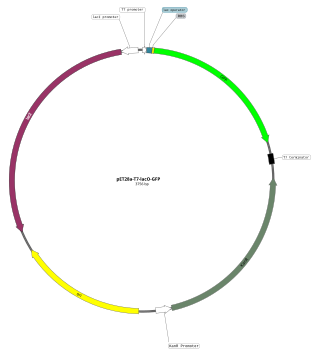
An expression vector, otherwise known as an expression construct, is usually a plasmid or virus designed for gene expression in cells. The vector is used to introduce a specific gene into a target cell, and can commandeer the cell's mechanism for protein synthesis to produce the protein encoded by the gene. Expression vectors are the basic tools in biotechnology for the production of proteins.

Baculoviridae is a family of viruses. Arthropods, among the most studied being Lepidoptera, Hymenoptera and Diptera, serve as natural hosts. Currently, 85 species are placed in this family, assigned to four genera.

Jean-Pierre Lecocq was a Belgian molecular biologist and entrepreneur.

A virus is a tiny infectious agent that reproduces inside the cells of living hosts. When infected, the host cell is forced to rapidly produce thousands of identical copies of the original virus. Unlike most living things, viruses do not have cells that divide; new viruses assemble in the infected host cell. But unlike simpler infectious agents like prions, they contain genes, which allow them to mutate and evolve. Over 4,800 species of viruses have been described in detail out of the millions in the environment. Their origin is unclear: some may have evolved from plasmids—pieces of DNA that can move between cells—while others may have evolved from bacteria.

A virus is a submicroscopic infectious agent that replicates only inside the living cells of an organism. Viruses infect all life forms, from animals and plants to microorganisms, including bacteria and archaea. Viruses are found in almost every ecosystem on Earth and are the most numerous type of biological entity. Since Dmitri Ivanovsky's 1892 article describing a non-bacterial pathogen infecting tobacco plants and the discovery of the tobacco mosaic virus by Martinus Beijerinck in 1898, more than 11,000 of the millions of virus species have been described in detail. The study of viruses is known as virology, a subspeciality of microbiology.
A subunit vaccine is a vaccine that contains purified parts of the pathogen that are antigenic, or necessary to elicit a protective immune response. Subunit vaccine can be made from dissembled viral particles in cell culture or recombinant DNA expression, in which case it is a recombinant subunit vaccine.
Baculovirus gene transfer into Mammalian cells, known from scientific research articles as BacMam, is the use of baculovirus to deliver genes to mammalian cells. Baculoviruses are insect cell viruses that can be modified to express proteins in mammalian cells. The unmodified baculovirus is able to enter those cells; however, its genes are not expressed unless a mammalian recognizable promoter is incorporated upstream of a gene of interest. Both unmodified baculovirus and its modified counterpart are unable to replicate in humans and are thus non-infectious.

A genetically modified virus is a virus that has been altered or generated using biotechnology methods, and remains capable of infection. Genetic modification involves the directed insertion, deletion, artificial synthesis or change of nucleotide bases in viral genomes. Genetically modified viruses are mostly generated by the insertion of foreign genes intro viral genomes for the purposes of biomedical, agricultural, bio-control, or technological objectives. The terms genetically modified virus and genetically engineered virus are used synonymously.
High Five (BTI-Tn-5B1-4) is an insect cell line that originated from the ovarian cells of the cabbage looper, Trichoplusia ni. It was developed by the Boyce Thompson Institute for Plant Research.

The Early 35 kDa protein, or P35 in short, is a baculoviral protein that inhibits apoptosis in the cells infected by the virus. Although baculoviruses infect only invertebrates in nature, ectopic expression of P35 in vertebrate animals and cells also results in inhibition of apoptosis, thus indicating a universal mechanism. P35 has been shown to be a caspase inhibitor with a very wide spectrum of activity both in regard to inhibited caspase types and to species in which the mechanism is conserved.
Polly Roy OBE is a professor and Chair of Virology at The London School of Hygiene and Tropical Medicine. She attended a number of schools which included Columbia University Medical School, Rutgers University, University of Alabama, and University of Oxford. In 2001 she became a part of The London School of Hygiene and Tropical Medicine and, along with being the chair of Virology, is also the co-organiser of the medical microbiology course. The virus that she has dedicated most of her career to is Bluetongue disease that affects sheep and cattle. She became interested in this virus after attending a symposium and was intrigued by the fact that not much was known about the virus that was causing such a nasty and sometimes fatal disease.
Mary Katharine Levinge Collins, Lady Hunt is a British Professor of virology and the director of the Queen Mary University of London Blizard Institute. She served as Provost at the Okinawa Institute of Science and Technology in Japan. Formerly, Collins taught in the Division of Infection and Immunity at University College London, and was the head of the Division of Advanced Therapies at the National Institute for Biological Standards and Control, and the Director of the Medical Research Council Centre for Medical Molecular Virology. Her research group studies the use of viruses as vectors for introducing new genes into cells, which can be useful for experimental cell biology, for clinical applications such as gene therapy, and as cancer vaccines.

Dame Sarah Catherine Gilbert FRS is an English vaccinologist who is a Professor of Vaccinology at the University of Oxford and co-founder of Vaccitech. She specialises in the development of vaccines against influenza and emerging viral pathogens. She led the development and testing of the universal flu vaccine, which underwent clinical trials in 2011.
Helicoverpa zea nudivirus 2 is an enveloped, rod-shaped, nonoccluded, double stranded DNA (dsDNA) sexually transmitted virus whose natural host is the corn earworm moth. At about 440 by 90 nm, it is the causative agent of the only sexually transmitted viral disease of any insect. It was originally identified in a colony of corn earworm moths established and maintained in Stoneville, Mississippi, U.S. and was found to be responsible for the sterility of those infected.
Max Duane Summers is an American molecular biologist and inventor, known for his work on the Baculovirus Expression Vector System (BEVS).
William Paul Duprex is a British scientist and advocate for vaccines and global health. He serves as Director of the University of Pittsburgh's Center for Vaccine Research and Regional Biocontainment Laboratory. Duprex holds the Jonas Salk Chair in Vaccine Research. He is also a professor of microbiology and molecular genetics at the University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine and serves as Editor-in-Chief of the Journal of General Virology, which is published by the Microbiology Society, and a senior editor of mSphere, published by the American Society for Microbiology. Duprex is an expert in measles and mumps viruses and studies viral spillover from animals to humans, including the SARS-CoV-2 virus that caused the COVID-19 pandemic. Duprex is a Fellow of the American Academy of Microbiology.
References
- ↑ "Linda's Story". www.brookes.ac.uk. Retrieved 15 September 2020.
- ↑ "Athena SWAN Charter for women in science" (PDF). www.ecu.ac.uk. Retrieved 15 September 2020.
- 1 2 "Staff Profiles". www.brookes.ac.uk. Retrieved 15 September 2020.
- ↑ The Baculovirus Expression System. Springer. ISBN 978-94-010-5047-0.
- ↑ "Oxford Expression Technologies Limited". beta.companieshouse.gov.uk. Retrieved 15 September 2020.
- ↑ "Meet the Board". oetltd.com. Retrieved 15 September 2020.
- ↑ Greenway, Tony (4 March 2020). "Why the insect cell system is a boost for vaccine development". Oxford Mail. Retrieved 15 September 2020.
- ↑ Hughes, Tim (4 September 2020). "Coronavirus vaccine may be available next year following grant to Oxford Brookes University's OET". Oxford Mail. Retrieved 15 September 2020.