Linyanti may refer to:
- Linyanti, a settlement in the Zambezi Region of Namibia
- Linyanti Combined School
- Linyanti Constituency
- Linyanti River
Linyanti may refer to:

The Zambezi Region is one of Namibia's fourteen regions, situated in the north-eastern part of the country along the Zambezi River where it gets its name from. The region's capital is the town of Katima Mulilo. The Katima Mulilo Airport is 18 kilometres south-west of the town, while the village of Bukalo is located 43 kilometres south-east of Katima Mulilo. Formerly known as the Caprivi Region until 2013, it has eight electoral constituencies and a population of 142,373 according to the 2023 census.

The Cuando River is a river in south-central Africa flowing through Angola and Namibia's Caprivi Strip and into the Linyanti Swamp on the northern border of Botswana. Below the swamp, the river is called the Linyanti River and, farther east, the Chobe River, before it flows into the Zambezi River.

Linyanti Constituency is located in Namibia's Zambezi Region. The constituency derives its name from the Linyanti River. It has a population of 10,425 and covers an area of 1,804 square kilometres, resulting in a population density of approximately 5.78 people per square kilometre.

Chobe National Park is Botswana's first national park, and also the most biologically diverse. Located in the north of the country, it is Botswana's third largest park, after Central Kalahari Game Reserve and Gemsbok National Park.

The Kalahari Basin, also known as the Kalahari Depression, Okavango Basin or the Makgadikgadi Basin, is an endorheic basin and large lowland area covering approximately 725,293 km2 (280,037 sq mi) — mostly within Botswana and Namibia, but also parts of Angola, South Africa, Zambia, and Zimbabwe. The outstanding physical feature in the basin, and occupying the centre, is the large Kalahari Desert.

Shakawe is a village located in the northwest corner of Botswana at the beginning of the Okavango Delta, close to Namibia and Angola. Shakawe is awakening from its former status as a sleepy little outpost on the Okavango. For travellers, Shakawe means a Botswana entry or exit stamp or a staging post for a visit to the Tsodilo Hills, 40 km away. For Southern African holiday-makers, it is most often the start of a fishing trip in the Okavango Panhandle. It also provides access to the Caprivi Strip. The record high temperature ever registered in Shakawe was 39.6 °C (103.3 °F). The lowest temperature registered in Shakawe was −6.1 °C (21.0 °F).

The wildlife of Botswana refers to the flora and fauna of this country. Botswana is around 90% covered in savanna, varying from shrub savanna in the southwest in the dry areas to tree savanna consisting of trees and grass in the wetter areas. Even under the hot conditions of the Kalahari Desert, many species survive; in fact the country has more than 2500 species of plants and 650 species of trees. Vegetation and its wild fruits are also extremely important to rural populations living in the desert and are the principal source of food, fuel and medicine for many inhabitants.
Yeyi is a Bantu language spoken by many of the approximately 50,000 Yeyi people along the Okavango River in Namibia and Botswana. Yeyi, influenced by Juu languages, is one of several Bantu languages along the Okavango with clicks. Indeed, it has the largest known inventory of clicks of any Bantu language, with dental, alveolar, palatal, and lateral articulations. Though most of its older speakers prefer Yeyi in normal conversation, it is being gradually phased out in Botswana by a popular move towards Tswana, with Yeyi only being learned by children in a few villages. Yeyi speakers in the Caprivi Strip of north-eastern Namibia, however, retain Yeyi in villages, but may also speak the regional lingua franca, Lozi.
Mutau is a village in the north eastern part of Namibia in the Caprivi region. It is situated along the Linyanti road. The name Mutau means "big lion". mutau played a big role in the community wellbeing. Mutau was one of the few settler to arrive in the caprivi region.
Linyanti Combined School is a school in the Linyanti Constituency in Namibia's far north-eastern Caprivi Strip. It is situated about 80 kilometres (50 mi) west of Katima Mulilo and was established in 1945.
Lusata Festival is an annual festival for all Mafwe tribal people of Namibia and nearby countries. The Mafwe people are one of the largest ethnic groups in the Caprivi Region. They speak ChiFwe. The festival celebrates traditional values, commemorates the past, and looks forward to the future. It occurs annually in the last week of September. The festival's name is a reference to the royal mace an ivory-encrusted stick.
The Mayuni Conservancy is a conservation area in Linyanti Constituency, in Namibia's northeastern Caprivi Region, along the eastern bank of the Cuando River.
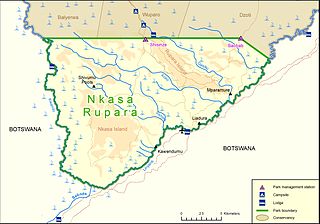
Nkasa Rupara National Park, also Nkasa Lupala National Park, formerly Mamili National Park, is a national park in Namibia. It is centered on the Nkasa and Rupara islands on the Kwando/Linyanti River in the south-western corner of East Caprivi. Botswana lies to the west, south and east, and Sangwali village to the north. It is Namibia's largest formally protected wetland area. It is one of Namibia’s protected areas that benefits local communities surrounding parks. The unfenced park forms a trans-boundary link for wildlife migration between Angola, Botswana, Namibia and Zambia. Nkasa Rupara is part of the Kavango Zambezi Transfrontier Conservation Area.

Judea Lyaboloma is a constituency in Namibia's Zambezi Region. The administrative centre of the constituency is the settlement of Sangwali, situated 130 kilometres south-west of the region's capital, Katima Mulilo. It has a population of 8,738 and covers an area of 1,723 km², resulting in a population density of approximately 5.071/km².
Boniface Bebi was a Mamili, or tribal king, of the Mafwe in Namibia, from 1987 to 1999. Born in Linyanti, South West Africa, he succeeded Richard Muhinda in 1987, as the sixth recorded King of the Mafwe. After being involved in the Caprivi conflict, in which autonomy was sought for the Lozi people of the Caprivi Strip, he fled for Botswana, which granted him political asylum, after which Denmark granted him and Mishake Muyongo political asylum. His first-born child, Hoster Bebi, died in 2000; he lost a son while in Danish exile.
The C49 is a tarred road in the Caprivi Strip of Namibia. It leaves and rejoins the B8, at Katima Mulilo and Kongola, respectively.