
The London, Brighton and South Coast Railway was a railway company in the United Kingdom from 1846 to 1922. Its territory formed a rough triangle, with London at its apex, practically the whole coastline of Sussex as its base, and a large part of Surrey. It was bounded on its western side by the London and South Western Railway (L&SWR), which provided an alternative route to Portsmouth. On its eastern side the LB&SCR was bounded by the South Eastern Railway (SER)—later one component of the South Eastern and Chatham Railway (SE&CR)—which provided an alternative route to Bexhill, St Leonards-on-Sea, and Hastings. The LB&SCR had the most direct routes from London to the south coast seaside resorts of Brighton, Eastbourne, Worthing, Littlehampton and Bognor Regis, and to the ports of Newhaven and Shoreham-by-Sea. It served the inland towns and cities of Chichester, Horsham, East Grinstead and Lewes, and jointly served Croydon, Tunbridge Wells, Dorking and Guildford. At the London end was a complicated suburban and outer-suburban network of lines emanating from London Bridge and Victoria, and shared interests in two cross-London lines.
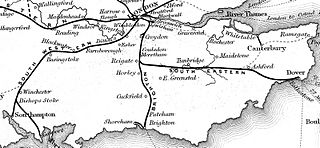
The London and Brighton Railway (L&BR) was a railway company in England which was incorporated in 1837 and survived until 1846. Its railway ran from a junction with the London and Croydon Railway (L&CR) at Norwood – which gives it access from London Bridge, just south of the River Thames in central London. It ran from Norwood to the South Coast at Brighton, together with a branch to Shoreham-by-Sea.
William Stroudley was an English railway engineer, and was one of the most famous steam locomotive engineers of the nineteenth century, working principally for the London, Brighton and South Coast Railway (LB&SCR). He designed some of the most famous and longest-lived steam locomotives of his era, several of which have been preserved.

Brighton railway works was one of the earliest railway-owned locomotive repair works, founded in 1840 by the London and Brighton Railway in Brighton, England, and thus pre-dating the more famous railway works at Crewe, Doncaster and Swindon. The works grew steadily between 1841 and 1900 but efficient operation was always hampered by the restricted site, and there were several plans to close it and move the facility elsewhere. Nevertheless, between 1852 and 1957 more than 1200 steam locomotives as well as prototype diesel electric and electric locomotives were constructed there, before the eventual closure of the facility in 1962.

The London, Brighton and South Coast Railway B1 Class is a class of 0-4-2 express passenger steam locomotives, known from the name of the first, No. 214, as the "Gladstones".

The London, Brighton and South Coast Railway E3 Class were 0-6-2T side tank steam locomotives. One prototype was designed by William Stroudley shortly before his death, but was completed by R. J. Billinton, who later built sixteen further locomotives.
Robert John Billinton was the Locomotive, Carriage, Wagon and Marine Superintendent of the London, Brighton and South Coast Railway from 1890 until his death.
Douglas Earle Marsh (1862–1933) was an English railway engineer, and was the Locomotive, Carriage and Wagon Superintendent of the London, Brighton and South Coast Railway from November 1904 until his early retirement on health grounds in July 1911.

The LB&SCR D2 class, 0-4-2 suburban passenger locomotives, were designed by William Stroudley of the London Brighton and South Coast Railway in 1876. They were developed from his successful "D-tank" class of 1873.

The London, Brighton and South Coast Railway (LB&SCR) B2 class was a class of small 4-4-0 steam locomotives intended for express passenger work on the LB&SCR London to Portsmouth line. They were designed by R. J. Billinton and built at Brighton works from 1895 to 1897. They proved to be reliable locomotives but barely adequate for the heaviest trains and acquired the nickname Grasshoppers. As a result the B3 class was developed from the B2, and the B2X class was later rebuilt from these locomotives with larger boilers.

The LB&SCR Richmond class, 0-4-2 express passenger locomotives, were designed by William Stroudley of the London Brighton and South Coast Railway in 1877. They were a larger version of his "Lyons" class (D2) which were in turn developed from his successful "D-tank" class of 1873.

The LB&SCR G class were powerful 2-2-2 locomotives, designed by William Stroudley of the London Brighton and South Coast Railway in 1874.

The London, Brighton and South Coast Railway H2 class was a class of 4-4-2 steam locomotives for express passenger work. They were designed when D. E. Marsh was officially Locomotive Superintendent, and were built at Brighton Works in 1911 and 1912.

The LB&SCR I3 class was a class of 4-4-2 steam tank locomotives designed by D. E. Marsh for suburban passenger service on the London, Brighton and South Coast Railway.

The LB&SCR J1 and J2 classes were 4-6-2 steam tank locomotives designed by D. E. Marsh for express passenger services on the London, Brighton and South Coast Railway.