Kushiro is a city in Kushiro Subprefecture on the island of Hokkaido, Japan. Located along the coast of the North Pacific Ocean, it serves as the subprefecture's capital and it is the most populated city in the eastern part of the island.
Asante, also known as Ashanti, Ashante, or Asante Twi, is one of the principal members of the Akan dialect continuum. It is one of the three mutually intelligible dialects of Akan which are collectively known as Twi, the others being Bono and Akuapem. There are over 3.8 million speakers of the Asante language, mainly concentrated in Ghana and southeastern Cote D'Ivoire, and especially in and around the Ashanti Region of Ghana.
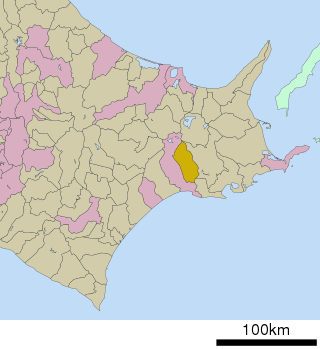
Akan is a district in Kushiro Subprefecture, Hokkaido, Japan. It includes Akan National Park, which has many dormant volcanoes.
Akan is a group of several closely related languages within the wider Central Tano languages. These languages are the principal native languages of the Akan people of Ghana, spoken over much of the southern half of Ghana. About 80% of Ghana's population can speak an Akan language as a first or second language, and about 44% of Ghanaians are native speakers. There are populations of polyglots in Ghana who speak an Akan language as a third language. They are also spoken in parts of Côte d'Ivoire.
The Akan people are a Kwa group living primarily in present-day Ghana and in parts of Ivory Coast and Togo in West Africa. The Akan speak dialects within the Central Tano branch of the Potou–Tano subfamily of the Niger–Congo family. Subgroups of the Akan people include: the Agona, Akuapem, Akwamu, Akyem, Anyi, Ashanti, Baoulé, Bono, Chakosi, Fante, Kwahu, Sefwi, Wassa, Ahanta, and Nzema, among others. The Akan subgroups all have cultural attributes in common; most notably the tracing of royal matrilineal descent in the inheritance of property, and for succession to high political office. All Akans are considered royals in status, but not all are in royal succession or hold titles.
Bono State was a trading state created by the Bono people, located in what is now southern Ghana. Bonoman was a medieval Akan state that stretched across the modern Ghanaian regions of Bono, Bono East and Ahafo and the Eastern Ivory Coast. It is generally accepted as the origin of the subgroups of the Akan people who migrated out of the state at various times to create new Akan states in search of gold. The gold trade, which started to boom in Bonoman as early as the 14th century, led to the Akan War, as well as increased power and wealth in the region, beginning in the Middle Ages.
The Bono, also called the Brong and the Abron, are an Akan people of West Africa. Bonos are normally tagged Akan piesie or Akandifo of which Akan is a derivative name. Bono is the genesis and cradle of Akans. Bono is one of the largest ethnic group of Akan and are matrilineal people. Bono people speak the Bono Twi of Akan language. Twi language, thus the dialect of Bono is a derivative of a Bono King Nana Twi. In the late fifteenth century, the Bono people founded the Gyaaman kingdom as extension of Bono state in what is now Ghana and Côte d'Ivoire.

Ghana is a multilingual country in which about eighty languages are spoken. Of these, English, which was inherited from the colonial era, is the official language and lingua franca. Of the languages indigenous to Ghana, Akan is the most widely spoken in the south. Dagbani, Dagare, Sisaala, Waale, and Gonja are among the most widely spoken in the northern part of the country.
Articles related to Ghana include:
Bono, also known as Abron, Brong, and Bono Twi, is a Central Tano language common to the Bono people and a major dialect of the Akan dialect continuum, and thus mutually intelligible with the principal Akan dialects of Asante and Akuapem, collectively known as Twi. It is spoken by 1.2 million in Ghana, primarily in the Central Ghanaian region of Brong-Ahafo, and by over 300,000 in eastern Ivory Coast.
Afro-Jamaicans are Jamaicans of predominantly African descent. They represent the largest ethnic group in the country.

Akan Volcanic Complex is a volcanic group of volcanoes that grew out of the Akan caldera. It is located within Akan National Park, about 50 km Northwest of Kushiro in eastern Hokkaidō, Japan.
The Akan people appear to have used a traditional system of timekeeping based on a six-day week. The Gregorian seven-day week is known as nnawɔtwe (eight-days). The combination of these two system resulted in periods of 40 days, known as adaduanan.

Akan River is a river in Hokkaidō, Japan.

Akan religion comprises the traditional beliefs and religious practices of the Akan people of Ghana and eastern Ivory Coast. Akan religion is referred to as Akom. Although most Akan people have identified as Christians since the early 20th century, Akan religion remains practiced by some and is often syncretized with Christianity. The Akan have many subgroups, so the religion varies greatly by region and subgroup. Similar to other traditional religions of West and Central Africa such as West African Vodun, Yoruba religion, or Odinani, Akan cosmology consists of a senior god who generally does not interact with humans and many gods who assist humans.

Twi is a variety of the Akan language spoken in southern and central Ghana by several million people, mainly of the Akan people, the largest of the seventeen major ethnic groups in Ghana. Twi has about 4.4 million speakers.
Akuapem, also known as Akuapim, Akwapem Twi, and Akwapi, is one of the principal members of the Akan dialect continuum, along with Bono and Asante, with which it is collectively known as Twi, and Fante, with which it is mutually intelligible. There are 626,000 speakers of Akuapem, mainly concentrated in Ghana and southeastern Cote D'Ivoire. It is the historical literary and prestige dialect of Akan, having been chosen as the basis of the Akan translation of the Bible.

The Akan Drum is a drum that was made in West Africa and was later found in the Colony of Virginia in North America. It is now one of the oldest African-American objects in the British Museum and possibly one of the oldest surviving anywhere. The drum is a reminder of all three continents' involvement in the estimated twelve million people transported across the Atlantic Ocean as part of the transatlantic slave trade. The drum is normally displayed in Room 26, the North American gallery, in the British Museum.
The traditional Jamaican Maroon religion, otherwise known as Kumfu, was developed by a mixing of West and Central African religious practices in Maroon communities. While the traditional religion of the Maroons was absorbed by Christianity due to conversions in Maroon communities, many old practices continued on. Some have speculated that Jamaican Maroon religion helped the development of Kumina and Convince. The religious Kromanti dance is still practiced today but not always with the full religious connotation as in the past.