
Henry Thomas Colebrooke FRS FRSE FLS was an English orientalist and mathematician. He has been described as "the first great Sanskrit scholar in Europe".

Robert Morrison, FRS, was an Anglo-Scottish Protestant missionary to Portuguese Macao, Qing-era Guangdong, and Dutch Malacca, who was also a pioneering sinologist, lexicographer, and translator considered the "Father of Anglo-Chinese Literature".

John Robert Morrison was a British interpreter and colonial official in China. Born in Macau, his father was Robert Morrison, the first Protestant missionary in China. After his father's death in 1834, Morrison replaced him as Chinese Secretary and Interpreter to the Superintendents of British Trade in China. In 1843, he was appointed as Acting Colonial Secretary of Hong Kong and a member of the Executive and Legislative Councils, but died eight days later in Hong Kong from fever.

John Borthwick Gilchrist was a Scottish surgeon, linguist, philologist and Indologist. Born and educated in Edinburgh, he spent most of his early career in India, where he made a study of the local languages. In later life, he returned to Britain and lived in Edinburgh and London. In his final years, he moved to Paris, where he died at the age of 81.
Wat Ngong (1785–1867), also known by various other names, was a Chinese Protestant convert, evangelist, and writer from Guangzhou during the Qing dynasty. He was an early lithographer in Malacca, Macao, Guangzhou, and Hong Kong, possibly the first Chinese to master the craft.

Cai Gao (1788–1818), also known as Tsae A-ko and by various other names, was the first Protestant convert in mainland China. He has also been called the first Western-style type-cutter and letterpress printer.
Francis Johnson was a British linguist.
Teen Ta Tseang Keun or Tëen ta tsëang keun meaning "Heaven's Great General", was a Chinese constellation (星官) in the region of Lóu (婁宿天區). It contained stars of the western constellations Andromeda and Triangulum. Allen based identification of Chinese star names by the English astronomer John Williams (1797–1874) and the naturalist John Reeves. But Allen lacked last word kuen as Tien Ta Tseang and also transliterated it as Tsien Ta Tseang.

Peter Perring Thoms was an English printer and Chinese language translator based in Canton (Guangzhou) and Macau, China.

Mandarin was the common spoken language of administration of the Chinese empire during the Ming and Qing dynasties. It arose as a practical measure, due to the mutual unintelligibility of the varieties of Chinese spoken in different parts of China. Knowledge of this language was thus essential for an official career, but it was never formally defined. The language was a koiné based on Mandarin dialects. The southern variant spoken around Nanjing was prevalent in the late Ming and early Qing eras, but a form based on the Beijing dialect became dominant by the mid-19th century and developed into Standard Chinese in the 20th century. In some 19th-century works, it was called the court dialect.
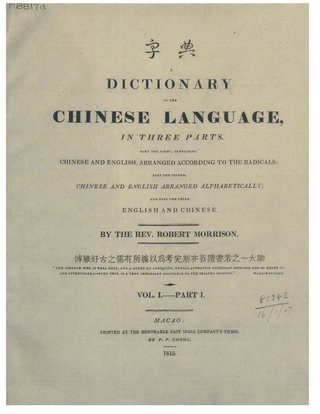
A Dictionary of the Chinese Language, in Three Parts or Morrison's Chinese dictionary (1815-1823), compiled by the Anglo-Scottish missionary Robert Morrison was the first Chinese-English, English-Chinese dictionary. Part I is Chinese-English arranged by the 214 Kangxi radicals, Part II is Chinese-English arranged alphabetically, and Part III is English-Chinese also arranged alphabetically. This groundbreaking reference work is enormous, comprising 4,595 pages in 6 quarto volumes and including 47,035 head characters taken from the 1716 Kangxi Dictionary. However, Morrison's encyclopedic dictionary had flaws, notably failing to distinguish aspirated consonants: the pronunciation taou is given for both aspirated táo and unaspirated dào.

The Chinese and English Dictionary: Containing All the Words in the Chinese Imperial Dictionary, Arranged According to the Radicals (1842), compiled by the English Congregationalist missionary Walter Henry Medhurst (1796–1857), is the second major Chinese–English dictionary after Robert Morrison's pioneering (1815–1823) A Dictionary of the Chinese Language. Medhurst's intention was to publish an abridged and cheaper dictionary that still contained all the 47,035 head characters from the (1716) Kangxi Dictionary, which Morrison's huge dictionary included. Medhurst reversed and revised into his Chinese–English dictionary in compiling the (1847–1848) English and Chinese Dictionary in Two Volumes.

A Syllabic Dictionary of the Chinese Language: Arranged According to the Wu-Fang Yuen Yin, with the Pronunciation of the Characters as Heard in Peking, Canton, Amoy, and Shanghai or the Hàn-Yīng yùnfǔ 漢英韻府, compiled by the American sinologist and missionary Samuel Wells Williams in 1874, is a 1,150-page bilingual dictionary including 10,940 character headword entries, alphabetically collated under 522 syllables. Williams' dictionary includes, in addition to Mandarin, Chinese variants from Middle Chinese and four regional varieties of Chinese, according to the 17th-century Wufang yuanyin 五方元音 "Proto-sounds of Speech in All Directions".

A Chinese–English Dictionary (1892), compiled by the British consular officer and sinologist Herbert Allen Giles (1845–1935), is the first Chinese–English encyclopedic dictionary. Giles started compilation after being rebuked for criticizing mistranslations in Samuel Wells Williams' (1874) A Syllabic Dictionary of the Chinese Language. The 1,461-page first edition contains 13,848 Chinese character head entries alphabetically collated by Beijing Mandarin pronunciation romanized in the Wade–Giles system, which Giles created as a modification of Thomas Wade's (1867) system. Giles' dictionary furthermore gives pronunciations from nine regional varieties of Chinese, and three Sino-Xenic languages Japanese, Korean, and Vietnamese. Giles revised his dictionary into the 1,813-page second edition (1912) with the addition of 67 entries and numerous usage examples.
William H. Allen and Company was a bookselling and publishing business in London, England, at first known for issuing works related to the British colonies. It operated from headquarters in Leadenhall Street, later moving to Waterloo Place. Early owners and staff included James P. Allen, William Ferneley Allen, and William Houghton Allen.

Earl Talbot was launched in 1797 as an East Indiaman for the British East India Company (EIC). She made one complete voyage to Madras and China between 1797 and 1798. She was lost in October 1800 on her second voyage for the EIC.

Qianshan is a subdistrict of Xiangzhou District, Zhuhai, in Guangdong Province in the People's Republic of China. Formerly an important military base overseeing the Portuguese-administered enclave of Macao, it is now a Chinese manufacturing center, with particular emphasis on household appliances, airconditioners, and printing supplies.
Callawapore was a type of calico manufactured in Madras, India. It was produced in blue and white colors. Piece goods of various qualities and dimensions were produced in and around Madras. Callawapore was one of the materials exported to England in the nineteenth century.

Yang (羊) is a Chinese surname. It is romanized Joeng in Cantonese romanization. According to a 2013 study, it was the 391st most common name in China; it was shared by 136,000 people, or 0.01% of the population, being most popular in Hainan. It is the 202nd name in the Hundred Family Surnames poem.