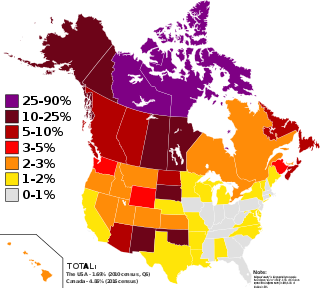
In Canada, indigenous groups comprise the First Nations, Inuit and Métis. Although Indian is a term still commonly used in legal documents, the descriptors Indian and Eskimo have fallen into disuse in Canada, and most consider them to be pejorative. Aboriginal peoples as a collective noun is a specific term of art used in some legal documents, including the Constitution Act, 1982, though in most Indigenous circles Aboriginal has also fallen into disfavour.
First Nations is a term used to identify those Indigenous Canadian peoples who are neither Inuit nor Métis. Traditionally, First Nations in Canada were peoples who lived south of the tree line, and mainly south of the Arctic Circle. There are 634 recognized First Nations governments or bands across Canada. Roughly half are located in the provinces of Ontario and British Columbia.
In Canada, an Indian reserve is specified by the Indian Act as a "tract of land, the legal title to which is vested in Her Majesty, that has been set apart by Her Majesty for the use and benefit of a band."
The Indian Register is the official record of people registered under the Indian Act in Canada, called status Indians or registered Indians. People registered under the Indian Act have rights and benefits that are not granted to other First Nations people, Inuit, or Métis, the chief benefits of which include the granting of reserves and of rights associated with them, an extended hunting season, easier access to firearms, an exemption from federal and provincial taxes on reserve, and more freedom in the management of gaming and tobacco franchises via less government interference and taxes.

The Assembly of First Nations (AFN) is an assembly of Canadian First Nations represented by their chiefs. Established in 1982 and modelled on the United Nations General Assembly, it emerged from the National Indian Brotherhood, which dissolved in the late 1970s.
First Nations in Alberta are a group of people who live in the Canadian province of Alberta. The First Nations are peoples recognized as Indigenous peoples or Plains Indians in Canada excluding the Inuit and the Métis. According to the 2011 Census, a population of 116,670 Albertans self-identified as First Nations. Specifically there were 96,730 First Nations people with registered Indian Status and 19,945 First Nations people without registered Indian Status. Alberta has the third largest First Nations population among the provinces and territories. From this total population, 47.3% of the population lives on an Indian reserve and the other 52.7% live in urban centres. According to the 2011 Census, the First Nations population in Edmonton totalled at 31,780, which is the second highest for any city in Canada. The First Nations population in Calgary, in reference to the 2011 Census, totalled at 17,040. There are 48 First Nations or "bands" in Alberta, belonging to nine different ethnic groups or "tribes" based on their ancestral languages.
Treaty 6 is the sixth of the numbered treaties that were signed by the Canadian Crown and various First Nations between 1871 and 1877. It is one of a total of 11 numbered treaties signed between the Canadian Crown and First Nations. Specifically, Treaty 6 is an agreement between the Crown and the Plains and Woods Cree, Assiniboine, and other band governments at Fort Carlton and Fort Pitt. Key figures, representing the Crown, involved in the negotiations were Alexander Morris, Lieutenant Governor of the North-West Territories; James McKay, The Minister of Agriculture for Manitoba; and W.J. Christie, the Chief Factor of the Hudson's Bay Company. Chief Mistawasis and Chief Ahtahkakoop represented the Carlton Cree.
First Nations in British Columbia constitute many First Nations governments and peoples in the province of British Columbia. Many of these Indigenous Canadians are affiliated in tribal councils. Ethnic groups include the Haida, Coast Salish, Kwakwaka'wakw, Gitxsan, Tsimshian, Nisga'a and other examples of the Pacific Northwest Coast cultures, and also various Interior Salish and Athapaskan peoples, and also the Ktunaxa.
First Nations in Saskatchewan constitute many Native Canadian band governments. First Nations ethnicities in the province include the Cree, Assiniboine, Saulteaux, Lakota, Dene and Dakota. Historically, the Atsina and Blackfoot could also be found at various times.
The George Gordon First Nation is a First Nations band government located near the village of Punnichy, Saskatchewan, in Canada. The nation has an enrolled population of 3,752 people, 1,191 of whom live on the band's reserves. Chief Byron Bitternose leads the First Nation. Their territory is located on the Gordon 86 reserve, as arranged by Treaty 4.

The Numbered Treaties are a series of eleven treaties signed between the First Nations, one of three groups of Indigenous peoples in Canada, and the reigning monarch of Canada from 1871 to 1921. These agreements were created to allow the Government of Canada to pursue settlement and resource extraction in the affected regions, which include modern-day Alberta, British Columbia, Manitoba, Ontario, Saskatchewan, and the Northwest Territories. These treaties expanded the Dominion of Canada with large tracts of land in exchange for promises made to the indigenous people of the area. These terms were dependent on individual negotiations and so specific terms differed with each treaty.
A tribal chief or chieftain is the leader of a tribal society or chiefdom.
In the United States, an American Indian tribe, Native American tribe, Alaska Native village, tribal nation, or similar concept is any extant or historical clan, tribe, band, nation, or other group or community of Native Americans in the United States. Modern forms of these entities are often associated with land or territory of an Indian reservation. "Federally recognized Indian tribe" is a legal term of art in United States law with a specific meaning.
In Canada, an Indian band or band, sometimes referred to as a First Nation band or simply a First Nation, is the basic unit of government for those peoples subject to the Indian Act. Bands are typically small groups of people: the largest in the country, the Six Nations of the Grand River First Nation had 22,294 members in September 2005, and many have a membership below 100 people. Each First Nation is typically represented by a band council chaired by an elected chief, and sometimes also a hereditary chief. As of 2013, there were 614 bands in Canada. Membership in a band is controlled in one of two ways: for most bands, membership is obtained by becoming listed on the Indian Register maintained by the government. As of 2013, there were 253 First Nations which had their own membership criteria, so that not all status Indians are members of a band.

Treaty 8, which concluded with the June 21, 1899 signing by representatives of the Crown and various First Nations of the Lesser Slave Lake area, is the most comprehensive of the one of eleven Numbered Treaties. The agreement encompassed a land mass of approximately 840,000 km2 (320,000 sq mi). Treaty territory, which includes thirty-nine First Nation communities in northern Alberta, northwestern Saskatchewan, northeastern British Columbia, and the southwest portion of the Northwest Territories, making it the largest of the numbered treaty in terms of area. The treaty was negotiated just south of present-day Grouard, Alberta.

Politics of Saskatchewan relate to the Canadian federal political system, along with the other Canadian provinces. Saskatchewan has a lieutenant-governor, who is the representative of the Crown in right of Saskatchewan; premier, Scott Moe, leading the Cabinet; and a unicameral legislature.

Maskwacis Cultural College (MCC) is a private post-secondary institution within the Four Nations of Maskwacis, Alberta, Canada. MCC offers programs from basic adult literacy, two-year college diplomas, to university transfer programs.
Indigenous or Aboriginal self-government refers to proposals to give governments representing the Indigenous peoples in Canada greater powers of government. These proposals range from giving Aboriginal governments powers similar to that of local governments in Canada to demands that Indigenous governments be recognized as sovereign, and capable of "nation-to-nation" negotiations as legal equals to the Crown, as well as many other variations.

The Gwichʼin Tribal Council is a First Nations organization representing the Gwichʼin people of northern Canada, owning approximately 23,884 square kilometres of land in Yukon and the Northwest Territories. It was created in 1992 with the final ratification of the Gwichʼin Comprehensive Land Claim Agreement with the Government of Canada. Negotiations to achieve a Final Agreement, and thus, Gwichʼin self-government, are ongoing.
First Nations or first peoples may refer to:







