Lists of ancient tribes in the Balkans
Lists of ancient tribes in the Balkans
Judah or Yehuda is the name of a biblical patriarch, Judah. It may also refer to:

An eponym is a person, place, or thing after whom or which someone or something is, or is believed to be, named. The adjectives derived from eponym include eponymous and eponymic.
Germanic may refer to:
According to the Hebrew Bible, the Tribe of Simeon was one of the twelve tribes of Israel. The Book of Judges locates its territory inside the boundaries of the Tribe of Judah. It is usually counted as one of the ten lost tribes, but as its territory was south of Judah and gradually being absorbed by Judah, it can not be considered one of the tribes of the Kingdom of Israel and would certainly not been effected by the Assyrian sack of the kingdom.

The Thracians were an Indo-European speaking people, who inhabited large parts of Eastern and Southeastern Europe in ancient history. Thracians resided mainly in the Balkans, but were also located in Asia Minor and other locations in Eastern Europe.

In Ancient Greece, the municipality meant the assembly of citizens as the dominant political body and then the administrative subdivision of ancient Attica, the continuation of which is present-day Attica, a region of Greece. Demes as simple subdivisions of land in the countryside seem to have existed in the 6th century BC and earlier, but did not acquire particular significance until the reforms of Cleisthenes in 508 BC. In those reforms, enrollment in the citizen-lists of a deme became the requirement for citizenship; prior to that time, citizenship had been based on membership in a phratry, or family group. At this same time, demes were established in the main city of Attica itself, where they had not previously existed; in all, at the end of Cleisthenes' reforms, Attica was divided into 139 demes to which one can be added Berenikidai, Apollonieis, and Antinoeis. The establishment of demes as the fundamental units of the state weakened the gene, or aristocratic family groups, that had dominated the phratries.

The Vangiones appear first in history as an ancient Germanic tribe of unknown provenance. They threw in their lot with Ariovistus in his bid of 58 BC to invade Gaul through the Doubs river valley and lost to Julius Caesar in a battle probably near Belfort. After some Celts evacuated the region in fear of the Suebi, the Vangiones, who had made a Roman peace, were allowed to settle among the Mediomatrici in northern Alsace.. They gradually assumed control of the Celtic city of Burbetomagus, later Worms.
A tribe in anthropology is a human social group.
The Twelve Tribes of Israel are, according to Hebrew scriptures, the descendants of the biblical patriarch Jacob, also known as Israel, through his twelve sons through his wives, Leah and Rachel, and his concubines, Bilhah and Zilpah, who collectively form the Israelite nation. Some modern scholars dispute whether there ever were twelve Israelite tribes, and think that the number 12 more likely signifies a symbolic invented tradition as part of a national founding myth.

Epirus was an ancient Greek state and kingdom located in the geographical region of Epirus, in north-western Greece and southern Albania. Home to the ancient Epirotes, the state was bordered by the Aetolian League to the south, Ancient Thessaly and Ancient Macedonia to the east, and Illyrian tribes to the north. The Greek king Pyrrhus is known to have made Epirus a powerful state in the Greek realm that was comparable to the likes of Ancient Macedonia and Ancient Rome. Pyrrhus' armies also attempted an assault against the state of Ancient Rome during their unsuccessful campaign in what is now modern-day Italy.
Krobyzoi is a Thracian, Getae or Dacian tribe.
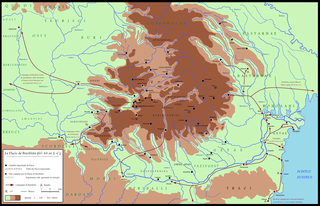
The Albocenses were a Dacian tribe that inhabited the area of Banat with the towns of Kovin, Trans Tierna, Ad Medias II, Kladovo, Apu, Arcidava, Centum Putea, Ram (Lederata) and Praetorium I. They lived between the Timiş River (Tibiscus) and north of the Saldenses, south of the Biephi. It is believed that the tribe migrated to Spain in Roman times.
Bharata may refer to:
Dan or DAN may refer to:

This article is an overview of the kings of the United Kingdom of Israel as well as those of its successor states and classical period kingdoms ruled by the Hasmonean dynasty and Herodian dynasty.