Liutward was the archchancellor of the Carolingian Empire from 878 and the bishop of Vercelli from 880 by appointment of Charles the Fat. Never liked by the nobility, he was trusted by Charles as a confidant and go-between with the papacy.
In 887, he was accused by Charles of having an affair with the Empress Richardis and though the empress successfully underwent the ordeal of fire, he was banished from court. Liutward's men abducted the daughter of Unroch III of Friuli from a convent in Brescia and forced her to marry one of his relatives. This provoked enmity between Liutward, the chief Carolingian prelate in Lombardy, and Berengar of Friuli, the chief secular magnate.
The famed poet of the age, Notker of St Gall, dedicated a series of verses to him between the years 881 and 887.

Arnulf of Carinthia was the duke of Carinthia who overthrew his uncle Emperor Charles the Fat to become the Carolingian king of East Francia from 887, the disputed king of Italy from 894 and the disputed emperor from February 22, 896, until his death at Regensburg, Bavaria.
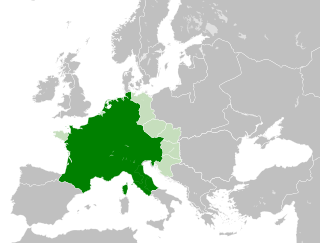
The Carolingian Empire (800–887) was a Frankish-dominated empire in western and central Europe during the Early Middle Ages. It was ruled by the Carolingian dynasty, which had ruled as kings of the Franks since 751 and as kings of the Lombards in Italy from 774. In 800, the Frankish king Charlemagne was crowned emperor in Rome by Pope Leo III in an effort to transfer the Roman Empire from the Byzantine Empire to Western Europe. The Carolingian Empire is sometimes considered the first phase in the history of the Holy Roman Empire.

Charles III, also known as Charles the Fat, was the emperor of the Carolingian Empire from 881 to 887. A member of the Carolingian dynasty, Charles was the youngest son of Louis the German and Hemma, and a great-grandson of Charlemagne. He was the last Carolingian emperor of legitimate birth and the last to rule a united kingdom of the Franks.
Louis the Blind was the king of Provence from 11 January 887, King of Italy from 12 October 900, and briefly Holy Roman Emperor, as Louis III, between 901 and 905. His father was a Bosonid and his mother was a Carolingian. He was blinded after a failed invasion of Italy in 905.
Aribo was margrave of the Carolingian March of Pannonia from 871 until his death. He is recognised as a progenitor of the Aribonid dynasty.

Berengar I was the king of Italy from 887. He was Holy Roman Emperor between 915 and his death in 924. He is usually known as Berengar of Friuli, since he ruled the March of Friuli from 874 until at least 890, but he had lost control of the region by 896.

East Francia or the Kingdom of the East Franks was a successor state of Charlemagne's empire ruled by the Carolingian dynasty until 911. It was created through the Treaty of Verdun (843) which divided the former empire into three kingdoms.

Godfrid, Godafrid, Gudfrid, or Gottfrid was a Danish Viking leader of the late ninth century. He had probably been with the Great Heathen Army, descended on the continent, and became a vassal of the emperor Charles the Fat, controlling most of Frisia between 882 and 885.

Fulk the Venerable was archbishop of Reims from 883 until his death. He was a key figure in the political conflicts of the West Frankish kingdom that followed the dissolution of the Carolingian Empire in the late ninth century.
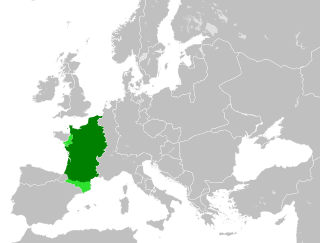
In medieval historiography, West Francia or the Kingdom of the West Franks constitutes the initial stage of the Kingdom of France and extends from the year 843, from the Treaty of Verdun, to 987, the beginning of the Capetian dynasty. It was created from the division of the Carolingian Empire following the death of Louis the Pious, with its neighbor East Francia eventually evolving into the Kingdom of Germany.

Saint Richardis, also known as Richgard, Richardis of Swabia and Richarde de Souabe in French, was the Holy Roman Empress as the wife of Charles the Fat. She was renowned for her piety and was the first abbess of Andlau. Repudiated by her husband, Richardis later became a Christian model of devotion and just rule. She was canonised in 1049.
Engelschalk II was the margrave of the March of Pannonia in the late ninth century in opposition to Aribo. In his day, the march orientalis corresponded to a front along the Danube from the Traungau to the Szombathely and Raba rivers and including the Vienna basin.
Walfred was the Count of Verona and then Margrave of Friuli in the last decades of the ninth century.
Bernard or Bernhard was the only child of Emperor Charles the Fat. He was born of an unknown concubine and was thus considered illegitimate. Charles tried to make him his heir, but failed in two attempts.

The March of Carinthia was a frontier district (march) of the Carolingian Empire created in 889. Before it was a march, it had been a principality or duchy ruled by native-born Slavic princes at first independently and then under Bavarian and subsequently Frankish suzerainty. The realm was divided into counties which, after the succession of the Carinthian duke to the East Frankish throne, were united in the hands of a single authority. When the march of Carinthia was raised into a Duchy in 976, a new Carinthian march was created. It became the later March of Styria.
Liutbert was the Archbishop of Mainz from 863 until his death. He also became Abbot of Ellwangen in 874 and is reckoned the first Archchancellor of Germany. He was one of the major organisers—along with Henry of Franconia—of the vigorous and successful defence of East Francia against Viking attack during his last decade.
Wibod was the Bishop of Parma from 855 until his death. He was, during the reigns of Louis II, Carloman, Charles III, and Berengar I, the most important power-broker in Emilia.
Geilo was the Bishop of Langres from 880 until his death. His episcopate coincided mostly with the emperorship of Charles the Fat and after 885 he is a leading ecclesiastical figure at the imperial court. Geilo increased the landholdings and comital rights of the diocese of Langres immensely in his short tenure, a sign of political sagacity. Geilo has been painted as a villain, an ambitious prelate trying to extend his see's temporal authority as far as it could go under the reign of weak Carolingians.
The Wilhelminers were a noble Bavarian family of the 9th century. They rose to prominence mid-century under the brothers William and Engelschalk I, sons of William I, the founder of the family. The family held the March of Pannonia until 871, but their possession of it was the cause of a dispute, the Wilhelminer War, with the Aribonids. In the dispute the Wilhelminers had the support of Arnulf of Carinthia and Svatopluk of Moravia.
The siege of Asselt was a Frankish siege of the Viking camp at Ascloha (Asselt) in the Meuse valley in the year 882. Though the Vikings were not forced by arms to abandon their camp, they were compelled to come to terms whereby their leader, Godfrid, was converted to Christianity.









