This page is based on this
Wikipedia article Text is available under the
CC BY-SA 4.0 license; additional terms may apply.
Images, videos and audio are available under their respective licenses.

In anatomy, the atlas (C1) is the most superior (first) cervical vertebra of the spine.

The humerus is a long bone in the arm that runs from the shoulder to the elbow. It connects the scapula and the two bones of the lower arm, the radius and ulna, and consists of three sections. The humeral upper extremity consists of a rounded head, a narrow neck, and two short processes. The body is cylindrical in its upper portion, and more prismatic below. The lower extremity consists of 2 epicondyles, 2 processes, and 3 fossae. As well as its true anatomical neck, the constriction below the greater and lesser tubercles of the humerus is referred to as its surgical neck due to its tendency to fracture, thus often becoming the focus of surgeons.

The tibia, also known as the shinbone or shankbone, is the larger, stronger, and anterior (frontal) of the two bones in the leg below the knee in vertebrates, and it connects the knee with the ankle bones. The tibia is found on the medial side of the leg next to the fibula and closer to the median plane or centre-line. The tibia is connected to the fibula by the interosseous membrane of the leg, forming a type of fibrous joint called a syndesmosis with very little movement. The tibia is named for the flute tibia. It is the second largest bone in the human body next to the femur. The leg bones are the strongest long bones as they support the rest of the body.

The spinal canal is the space in the vertebral column formed by the vertebrae through which the spinal cord passes. It is a process of the dorsal body cavity. This canal is enclosed within the vertebral foramen of the vertebrae. In the intervertebral spaces, the canal is protected by the ligamentum flavum posteriorly and the posterior longitudinal ligament anteriorly.

The sacroiliac joint or SI joint (SIJ) is the joint between the sacrum and the ilium bones of the pelvis, which are connected by strong ligaments. In humans, the sacrum supports the spine and is supported in turn by an ilium on each side. The joint is strong, supporting the entire weight of the upper body. It is a synovial plane joint with irregular elevations and depressions that produce interlocking of the two bones. The human body has two sacroiliac joints, one on the left and one on the right, that often match each other but are highly variable from person to person.

The obturator artery is a branch of the internal iliac artery that passes antero-inferiorly on the lateral wall of the pelvis, to the upper part of the obturator foramen, and, escaping from the pelvic cavity through the obturator canal, it divides into both an anterior and a posterior branch.

The wing of ilium is the large expanded portion which bounds the greater pelvis laterally. It presents for examination two surfaces—an external and an internal—a crest, and two borders—an anterior and a posterior.
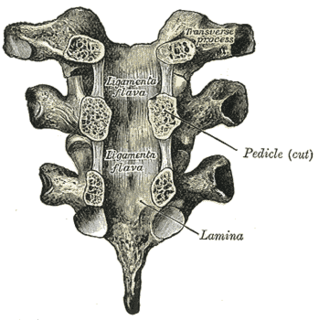
The ligamenta flava are ligaments of the spine.

The sacrococcygeal symphysis is an amphiarthrodial joint, formed between the oval surface at the apex of the sacrum, and the base of the coccyx.

The anterior sacrococcygeal ligament or ventral sacrococcygeal ligament consists of a few irregular fibers, which descend from the anterior surface of the sacrum to the front of the coccyx, blending with the periosteum.

The tectorial membrane of atlanto-axial joint is situated within the vertebral canal.

The posterior sacrococcygeal ligament or dorsal sacrococcygeal ligament is a ligament which stretches from the sacrum to the coccyx and thus dorsally across the sacrococcygeal symphysis shared by these two bones.
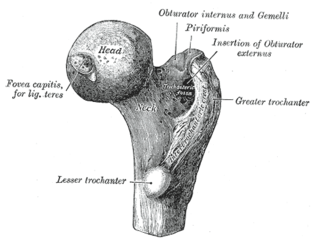
The femoral head is the highest part of the thigh bone (femur). It is supported by the femoral neck.

The Investing layer of deep cervical fascia is the most superficial part of the deep cervical fascia, and it encloses the whole neck.

The articular capsule is strong and dense.

The pelvis is either the lower part of the trunk of the human body between the abdomen and the thighs or the skeleton embedded in it.
Sacrococcygeal ligament can refer to:
Talocalcaneal ligament may refer to:


















