
The Common Desktop Environment (CDE) is a desktop environment for Unix and OpenVMS, based on the Motif widget toolkit. It was part of the UNIX 98 Workstation Product Standard, and was for a long time the "classic" Unix desktop associated with commercial Unix workstations.

GNU is an operating system and an extensive collection of computer software. GNU is composed wholly of free software, most of which is licensed under the GNU Project's own General Public License (GPL).

An operating system (OS) is system software that manages computer hardware and software resources and provides common services for computer programs.

Matthias Ettrich is a German computer scientist and founder of the KDE and LyX projects.

SCO, The SCO Group, The TSG Group, Caldera Systems, and Caldera International are the various names of an American software company that became known for acquiring the Santa Cruz Operation's Server Software and Services divisions, and UnixWare and OpenServer technologies, and then, under CEO Darl McBride, pursuing a series of legal battles known as the SCO-Linux controversies.

The GNU Project is a free-software, mass-collaboration project, first announced on September 27, 1983 by Richard Stallman at MIT. Its aim is to give computer users freedom and control in their use of their computers and computing devices, by collaboratively developing and providing software that is based on the following freedom rights: users are free to run the software, share it, study it and modify it. GNU software guarantees these freedom-rights legally, and is therefore free software; the use of the word "free" always being taken to refer to freedom.

UnixWare is a Unix operating system. It was originally released by Univel, a jointly owned venture of AT&T's Unix System Laboratories (USL) and Novell. It was then taken over by Novell. Via Santa Cruz Operation (SCO) it went on to Caldera Systems, Caldera International, and The SCO Group before it was sold to UnXis. UnixWare is typically deployed as a server rather than a desktop. Binary distributions of UnixWare are available for x86 architecture computers. UnixWare is primarily marketed as server operating system.
The SCO–Linux disputes are a series of legal and public disputes between the software company SCO Group (SCO) and various Linux vendors and users. The SCO Group alleges that its license agreements with IBM means that source code that IBM wrote and donated to be incorporated into Linux was added in violation of SCO's contractual rights. Members of the Linux community disagree with SCO's claims; IBM, Novell and Red Hat have ongoing claims against SCO.

Xinuos OpenServer, previously SCO UNIX and SCO Open Desktop, is a closed source computer operating system developed by Santa Cruz Operation (SCO), later acquired by SCO Group, and now owned by Xinuos. Early versions of OpenServer were based on UNIX System V, while the later OpenServer 10 is based on FreeBSD.
In computing, minimalism refers to the application of minimalist philosophies and principles in the design and use of hardware and software. Minimalism, in this sense, means designing systems that use the least hardware and software resources possible.
Linux adoption is the adoption of Linux computer operating systems (OS) by households, nonprofit organizations, businesses, and governments.
The Portland Project is an initiative by freedesktop.org aiming at easing the portability of application software between desktop environments and kernels by designing cross-platform APIs and offering implementations thereof as libraries to independent software vendors (ISVs).

Linux is a family of free and open-source software operating systems based on the Linux kernel, an operating system kernel first released on September 17, 1991 by Linus Torvalds. Linux is typically packaged in a Linux distribution.
A desktop environment is a collection of software designed to give functionality and a certain look and feel to an operating system.
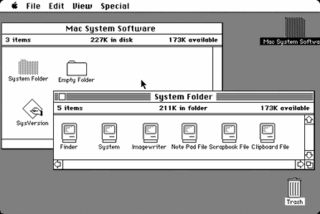
The family of Macintosh operating systems developed by Apple Inc. includes the graphical user interface-based operating systems it has designed for use with its Macintosh series of personal computers since 1984, as well as the related system software it once created for compatible third-party systems.
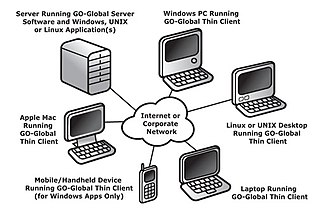
GraphOn GO-Global is remote access/application publishing software that allows users to access and run Windows, Linux, and UNIX applications installed on a central server. GO-Global displays the application's user interface on personal computers and other client devices running a variety of operating systems, including UNIX, Linux, Mac OS X, Windows, Windows Mobile, and Pocket PC. GO-Global can be used to Web-enable existing applications without the need to modify existing code. Applications appear on the client device either in a Web browser or within a loose window on the desktop.
The Application Programming Interface for Windows (APIW) Standard is a specification of the Microsoft Windows 3.1 API drafted by Willows Software. It is the successor to previously proposed Public Windows Interface standard. It was created in an attempt to establish a vendor-neutral, platform-independent, open standard of the 16-bit Windows API not controlled by Microsoft.











