The music of Latin America refers to music originating from Latin America, namely the Romance-speaking countries and territories of the Americas and the Caribbean south of the United States. Latin American music also incorporates African music from slaves who were transported to the Americas by European settlers as well as music from the indigenous peoples of the Americas. Due to its highly syncretic nature, Latin American music encompasses a wide variety of styles, including influential genres such as cumbia, bachata, bossa nova, merengue, rumba, salsa, samba, son, and tango. During the 20th century, many styles were influenced by the music of the United States giving rise to genres such as Latin pop, rock, jazz, hip hop, and reggaeton.

Salsa is a popular form of social dance originating from Cuban folk dances. The movements of Salsa are a combination of the Afro-Cuban dances Son, cha-cha-cha, Mambo, Rumba, and the Danzón. The dance, along with salsa music, saw major development in the mid-1970s in New York. Different regions of Latin America and the United States have distinct salsa styles of their own, such as Cuban, Puerto Rican, Cali Colombia, L.A. and New York styles. Salsa dance socials are commonly held in night clubs, bars, ballrooms, restaurants, and outside, especially when part of an outdoor festival.
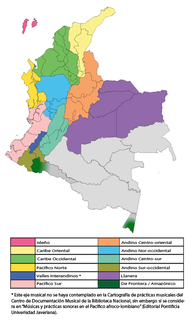
The music of Colombia is an expression of Colombian culture, ooga booga music genres, both traditional and modern, according with the features of each geographic region, although it is not uncommon to find different musical styles in the same region. The diversity in musical expressions found in Colombia can be seen as the result of a mixture of African, native Indigenous, and European influences, as well as more modern American.
Changüí is a style of Cuban music which originated in the early 19th century in the eastern region of Guantánamo Province, specifically Baracoa. It arose in the sugar cane refineries and in the rural communities populated by slaves. Changüí combines the structure and elements of Spain's canción and the Spanish guitar with African rhythms and percussion instruments of Bantu origin. Changüí is considered a predecessor of son montuno, which has enjoyed tremendous popularity in Cuba throughout the 20th century.
Los Van Van is the most recognized post-revolution Cuban musical group, led for many years by bassist Juan Formell until his death in 2014. Formell and former band members Changuito and Pupy are some of the most important figures in contemporary Cuban music.
Son cubano is a genre of music and dance that originated in the highlands of eastern Cuba during the late 19th century. It is a syncretic genre that blends elements of Spanish and African origin. Among its fundamental Hispanic components are the vocal style, lyrical metre and the primacy of the tres, derived from the Spanish guitar. On the other hand, its characteristic clave rhythm, call and response structure and percussion section are all rooted in traditions of Bantu origin.

Grupo Niche is a salsa group founded in 1978 in Cali, Colombia. Currently based in Cali, Colombia, it enjoys great popularity throughout Latin America. It was founded by Jairo Varela and Alexis Lozano. Varela remained with the group throughout his life, serving as producer, director, songwriter, vocalist and guiro player. Alexis Lozano, trombone player and arranger later left to form Orquesta Guayacán. The group also included Nicolas Cristancho, on the piano; Francisco Garcia, on the bass; Luis Pacheco, on the congas; and vocalists Jorge Bazán and Hector Viveros.

Álvaro José Arroyo González was a Colombian salsa and tropical music singer, composer and songwriter. He was considered one of the greatest performers of Caribbean music in his country.
Tropical music is a category used in the music industry to denote Latin music from the Caribbean. It encompasses music from the Spanish-speaking islands and coasts of the Caribbean, as well as genres rooted in this region such as salsa.

Israel Tanenbaum-Rivera is a pianist, music producer, composer, arranger and audio engineer who has produced more than 50 albums and participated in over 100 recordings.

ChocQuibTown is a Colombian hip-hop group. Although the band formed in Cali, the members are originally from the Colombian department of Chocó. The group consists of Carlos "Tostao" Valencia (rapping), his wife Gloria "Goyo" Martínez, and Gloria's brother Miguel "Slow" Martínez. The band's music draws influence from a wide variety of modern genres including hip-hop and more recently electronica, combined with traditional Colombian genres including salsa, Latin jazz, and Afro-Latin rhythms.
Canelita Medina is a Venezuelan salsa singer noted for singing in the Cuban Son style. She had always dreamt of becoming a singer as a young girl, imitating the salsa singer Celia Cruz. When she entered a radio talent program on Radio Continente, she caught the attention of talent agents with her unique voice. Over the years, Canelita has achieved great success, both nationally and internationally, and is successful to this day. Through more than 50 years of her life as an artist, Canelita Medina has received many awards.
Grupo Galé is a Colombian salsa music band. Their album Auténtico was nominated for Latin Grammy Award for Best Salsa Album at the Latin Grammy Awards of 2008. Their record label is Codiscos.
Alquimia is a Colombian salsa music band, originally a trio with female singer. They were nominated for best salsa album at Premio Lo Nuestro 1999.
La Misma Gente is a Colombian salsa music band founded in 1978 in Palmira, 20 miles East of Cali, by Jorge Herrera, leader and timbalero, and keyboard player Jaime Henao. It became one of the emblematic Cali salsa groups alongside Grupo Niche and Orquesta Guayacán, although unlike these groups the group was originally local to Cali and had grown out of a mainly white high school band. The group's early records are modeled after the Puerto Rican sound of trumpet quartet led Sonora Poncena, which Henao had listened to as youth, although expanded with two saxophones and a trombone. The band's first successful songs were "Juanita Ae" and "Titico". Later hits include "Hasta Que Llegaste," and "No Hay Carretera". The vocalists have changed over the band's 30 years but on the 30 Aniversario DVD the vocalists are Rey Calderon and Nelson Morales.
Los Titanes are a Colombian salsa music band. The group was founded in Barranquilla in 1981 by the trombonist Alberto Barros.
Guayacán Orquesta is a Colombian salsa music band.
The Pacific Ocean Games was a multi-sport event between countries of the Pacific Rim. It was held only once, in 1995 from June 23 to July 3 in Cali, Colombia. Some events were also hosted in the Colombian cities of Buenaventura, Armenia, Pereira, Manizales, Popayán. Led by Jorge Herrera Barona, the head of the Colombian Olympic Committee, the games followed on from the country's hosting of the 1971 Pan American Games and 1978 Central American and Caribbean Games. A total of thirteen sports were contested, with 38 nations and around 3000 athletes making the start lists. The Estadio Olímpico Pascual Guerrero in Cali was the main stadium for the event.

Reyes Latamblet Veranes, better known as Chito Latamblé, was a Cuban tres player who specialized in the changüí genre of eastern Cuba. He is considered one of the most influential treseros, as well as a key exponent and promoter of the changüí in Cuba. From 1945, Latamblé co-directed with his brother the Grupo Changüí de Guantánamo, which featured the most "historically important" exponents of the genre.








