Low Saxon is a group of Low German dialects spoken in the Netherlands, Lower Saxony and most of Schleswig-Holstein.
Contents
Low Saxon or Lower Saxon may also refer to:
Low Saxon is a group of Low German dialects spoken in the Netherlands, Lower Saxony and most of Schleswig-Holstein.
Low Saxon or Lower Saxon may also refer to:

The Frisian languages are a closely related group of West Germanic languages, spoken by about 500,000 Frisian people, who live on the southern fringes of the North Sea in the Netherlands and Germany. The Frisian languages are the closest living language group to the Anglic languages; the two groups make up the Anglo-Frisian languages group and together with the Low German dialects these form the North Sea Germanic languages. However, modern English and Frisian are not mutually intelligible, nor are Frisian languages intelligible among themselves, owing to independent linguistic innovations and foreign influences.

German is a West Germanic language mainly spoken in Western and Central Europe. It is the most widely spoken and official or co-official language in Germany, Austria, Switzerland, Liechtenstein, and the Italian province of South Tyrol. It is also an official language of Luxembourg and Belgium, as well as a recognized national language in Namibia. Outside Germany, it is also spoken by German communities in France (Alsace), Czech Republic, Poland, Slovakia, and Hungary (Sopron).

Low Saxon, also known as West Low German are a group of Low German dialects spoken in parts of the Netherlands, northwestern Germany and southern Denmark. It is one of two dialect groups, the other being East Low German.

Westphalia is a region of northwestern Germany and one of the three historic parts of the state of North Rhine-Westphalia. It has an area of 20,210 square kilometres (7,800 sq mi) and 7.9 million inhabitants.

Frisia is a cross-border cultural region in Northwestern Europe. Stretching along the Wadden Sea, it encompasses the north of the Netherlands and parts of northwestern Germany. The region is traditionally inhabited by the Frisians, a West Germanic ethnic group.
Saxon language may refer to:
Northern Low Saxon is a subgroup of Low Saxon dialects of Low German. As such, it covers a great part of the West Low German-speaking areas of northern Germany, with the exception of the border regions where South Low Saxon is spoken, and Gronings dialect in the Netherlands.

Eastphalian, or Eastfalian, is a dialect of Low German, spoken in southeastern parts of Lower Saxony and western parts of Saxony-Anhalt in Germany.
East Frisian Low German, East Frisian Low Saxon, East Frisian Frisio-Saxon or simply called East Frisian is a Northern Low Saxon dialect spoken in the East Frisian peninsula of northwestern Lower Saxony.
Westphalian or Westfalish is one of the major dialect groups of Low German. Its most salient feature is its diphthongization. For example, speakers say iäten instead of etten or äten for "to eat".

Low German is a West Germanic language spoken mainly in Northern Germany and the northeastern Netherlands. The dialect of Plautdietsch is also spoken in the Russian Mennonite diaspora worldwide.
Frisian language may refer to:
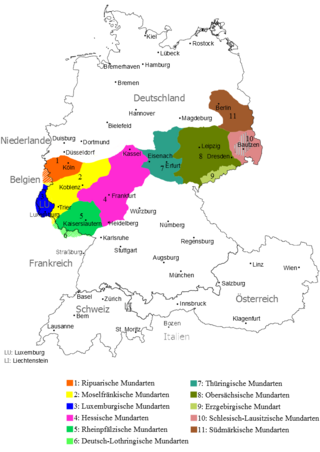
Upper Saxon is an East Central German dialect spoken in much of the modern German state of Saxony and in adjacent parts of southeastern Saxony-Anhalt and eastern Thuringia. As of the early 21st century, it is mostly extinct and a new regiolect has emerged instead. Though colloquially called "Saxon", it is not to be confused with the Low Saxon dialect group in Northern Germany. Upper Saxon is closely linked to the Thuringian dialect spoken in the adjacent areas to the west.

Central German or Middle German is a group of High German languages spoken from the Rhineland in the west to the former eastern territories of Germany.
Northern Germany is a linguistic, geographic, socio-cultural and historic region in the northern part of Germany which includes the coastal states of Schleswig-Holstein, Mecklenburg-Vorpommern and Lower Saxony and the two city-states Hamburg and Bremen. It contrasts with Southern Germany, Western Germany and Eastern Germany.

Franconian or Frankish is a collective term traditionally used by linguists to refer to many West Germanic languages, some of which are spoken in what formed the historical core area of Francia during the Early Middle Ages.
Low German is a Germanic language spoken mainly in Northern Germany and in Northeastern Netherlands.

The official language of Germany is German, with over 95 percent of the country speaking Standard German or a dialect of German as their first language. This figure includes speakers of Northern Low Saxon, a recognized minority or regional language that is not considered separately from Standard German in statistics. Recognized minority languages have official status as well, usually in their respective regions.

The 1614 Low German Bible is a rare, illustrated folio edition in Low German of Martin Luther's High German translation of the Bible. Illustrations in the bible are woodcuts from the Hans Stern publishing family in early Lüneburg, Germany.
Low Lusatian German or the Low Lusatian dialect is a variety of Central German spoken in northern Saxony and southern Brandenburg within the regions of Lower Lusatia (Cottbus) and the northern part of Upper Lusatia (Hoyerswerda). It is well-defined from the Low German dialects around and north of Berlin, as well as the Upper Saxon dialect group of present-day Saxony and the Slavic language of the Sorbs.