Related Research Articles

The First Punic War was the first of three wars fought between Rome and Carthage, the two main powers of the western Mediterranean in the early 3rd century BC. For 23 years, in the longest continuous conflict and greatest naval war of antiquity, the two powers struggled for supremacy. The war was fought primarily on the Mediterranean island of Sicily and its surrounding waters, and also in North Africa. After immense losses on both sides, the Carthaginians were defeated.
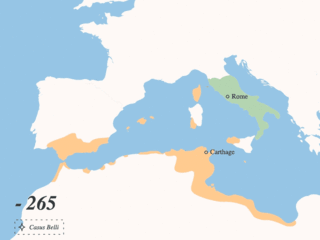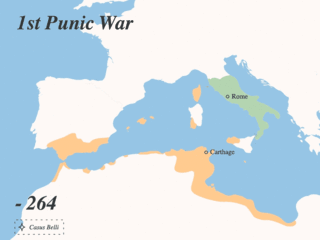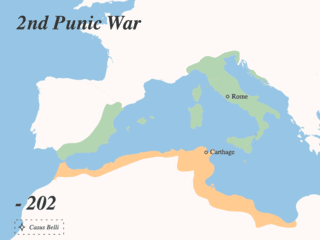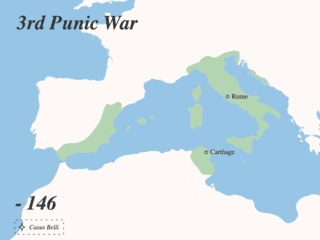
The Punic Wars were a series of wars between 264 and 146 BC fought between Rome and Carthage. Three conflicts between these states took place on both land and sea across the western Mediterranean region and involved a total of forty-three years of warfare. The Punic Wars are also considered to include the four-year-long revolt against Carthage which started in 241 BC. Each war involved immense materiel and human losses on both sides.
This article concerns the period 149 BC – 140 BC.

The Third Punic War was the third and last of the Punic Wars fought between Carthage and Rome. The war was fought entirely within Carthaginian territory, in what is now northern Tunisia. When the Second Punic War ended in 201 BC one of the terms of the peace treaty prohibited Carthage from waging war without Rome's permission. Rome's ally, King Masinissa of Numidia, exploited this to repeatedly raid and seize Carthaginian territory with impunity. In 149 BC Carthage sent an army, under Hasdrubal, against Masinissa, the treaty notwithstanding. The campaign ended in disaster as the Battle of Oroscopa ended with a Carthaginian defeat and the surrender of the Carthaginian army. Anti-Carthaginian factions in Rome used the illicit military action as a pretext to prepare a punitive expedition.

The siege of Carthage was the main engagement of the Third Punic War fought between Carthage and Rome. It consisted of the nearly-three-year siege of the Carthaginian capital, Carthage. In 149 BC, a large Roman army landed at Utica in North Africa. The Carthaginians hoped to appease the Romans, but despite the Carthaginians surrendering all of their weapons, the Romans pressed on to besiege the city of Carthage. The Roman campaign suffered repeated setbacks through 149 BC, only alleviated by Scipio Aemilianus, a middle-ranking officer, distinguishing himself several times. A new Roman commander took over in 148 BC, and fared equally badly. At the annual election of Roman magistrates in early 147 BC, the public support for Scipio was so great that the usual age restrictions were lifted to allow him to be appointed commander in Africa.

Publius Cornelius Scipio Africanus Aemilianus, known as Scipio Aemilianus or Scipio Africanus the Younger, was a Roman general and statesman noted for his military exploits in the Third Punic War against Carthage and during the Numantine War in Spain. He oversaw the final defeat and destruction of the city of Carthage. He was a prominent patron of writers and philosophers, the most famous of whom was the Greek historian Polybius. In politics, he opposed the populist reform program of his murdered brother-in-law, Tiberius Gracchus.
Lucius Manlius Vulso Longus was a Roman general and statesman, who served as consul of the Roman Republic in 256 and 250 BC. He is remembered for his military successes; his military achievements, especially the Battle of Cape Ecnomus, significantly contributed to the victory of the Romans in the First Punic War.

Gaius Lutatius Catulus was a Roman statesman and naval commander in the First Punic War. He was born a member of the plebeian gens Lutatius. His cognomen "Catulus" means "puppy". There are no historical records of his life prior to consulship, but his career probably followed the standard cursus honorum, beginning with service in the cavalry and continuing with the positions of military tribune and quaestor.
Gaius Livius Drusus was a Roman politician who was consul in 147 BC, together with Scipio Aemilianus.

The Numantine War was the last conflict of the Celtiberian Wars fought by the Romans to subdue those people along the Ebro. It was a twenty-year conflict between the Celtiberian tribes of Hispania Citerior and the Roman government. It began in 154 BC as a revolt of the Celtiberians of Numantia on the Douro. The first phase of the war ended in 151, but in 143, war flared up again with a new insurrection in Numantia.

Publius Cornelius Scipio Nasica Corculum was a politician of the Roman Republic. Born into the illustrious family of the Cornelii Scipiones, he was one of the most important Roman statesmen of the second century BC, being consul two times in 162 and 155 BC, censor in 159 BC, pontifex maximus in 150 BC, and finally princeps senatus in 147 BC.
Gaius Hostilius Mancinus was a politician and general of the Roman Republic. He is mostly known for his defeat against the Numantines as consul in 137 BC and the humiliating treaty he signed afterwards in order to save his army.
Aulus Atilius Serranus was a consul in the year 170 BC, together with Aulus Hostilius Mancinus.
Aulus Hostilius Mancinus was consul of the Roman Republic, together with Aulus Atilius Serranus, in 170 BC. He had been an urban praetor in 180 BC. When he was consul he was given the command of the Third Macedonian War for that year.

The gens Hostilia was an ancient family at Rome, which traced its origin to the time of Romulus. The most famous member of the gens was Tullus Hostilius, the third King of Rome; however, all of the Hostilii known from the time of the Republic were plebeians. Several of the Hostilii were distinguished during the Punic Wars. The first of the family to obtain the consulship was Aulus Hostilius Mancinus in 170 BC.
Lucius Marcius Censorinus was a Roman politician and military leader of the Middle Republic, serving as consul with Manius Manilius in 149 BC and censor in 147 BC. He led the fleet during the first phase of the Third Punic War.
The Battle of the Port of Carthage was a naval battle of the Third Punic War fought in 147 BC between the Carthaginians and the Roman Republic.
The gens Manilia was a plebeian family at ancient Rome. Members of this gens are frequently confused with the Manlii, Mallii, and Mamilii. Several of the Manilii were distinguished in the service of the Republic, with Manius Manilius obtaining the consulship in 149 BC; but the family itself remained small and relatively unimportant.
The Battle of Oroscopa was fought between a Carthaginian army of more than 30,000 men commanded by the general Hasdrubal and a Numidian force of unknown size under its king, Masinissa. It took place in late 151 BC near the ancient town of Oroscopa in what is now north western Tunisia. The battle resulted in a heavy Carthaginian defeat.
References
- ↑ La Longa Mancini, Federico. "Famiglia Mancini - Origini". nobili-napoletani.it (in Italian). Retrieved 9 August 2014.
- ↑ Flower, Harriet I. (23 June 2014). The Cambridge Companion to the Roman Republic. Cambridge University Press. pp. 39–. ISBN 978-1-107-03224-8.
- ↑ Beckmann, Martin (27 June 2011). The Column of Marcus Aurelius: The Genesis and Meaning of a Roman Imperial Monument. UNC Press Books. pp. 208–. ISBN 978-0-8078-7777-7.
- ↑ Appian Pun. 110–114; Livy Epit. 51; Pliny the Elder HN 35.4. s. 7; Cicero Lael. 25