Cat5 or CAT5 may refer to:
Colon commonly refers to:

Luis Muñoz Marín International Airport (LMM), previously known as the Isla Verde International Airport, is the primary international airport of Puerto Rico serving the capital municipality of San Juan and its metropolitan area. Covering 1,600 acres, SJU is located in the beach-front district of Isla Verde in the municipality of Carolina. Named after Luis Muñoz Marín, the first elected governor of the archipelago and island, it is, as of 2023, the 39th busiest airport by passenger boarding, 28th by international passenger traffic, and 24th by cargo throughput within the United States. With 12,197,553 million passengers in 2023, SJU is the busiest airport in the Caribbean, where it serves as a major gateway into the region.

Carolina is a city and municipality on the northeastern coastal plain of Puerto Rico, immediately east of San Juan and Trujillo Alto, north of Gurabo and Juncos, and west of Canóvanas and Loíza. Part of the San Juan metropolitan area, Carolina is spread over 12 barrios and the downtown area and administrative center of Carolina Pueblo. In the coastal region of the municipality lies the resort and residential district of Isla Verde, where the main international airport of Puerto Rico, the Luis Muñoz Marín International Airport, is located. Carolina is the third most populated municipality in the archipelago and island.
ALS is a chronic and fatal form of motor neuron disease; also known as Lou Gehrig's disease in the US, or Charcot's disease in the French-speaking world.
Eta is the seventh letter of the Greek alphabet.

Hurricane Lenny was the strongest November Atlantic hurricane since the 1932 Cuba hurricane. It was the twelfth tropical storm, eighth hurricane, and record-breaking fifth Category 4 hurricane in the 1999 Atlantic hurricane season. Lenny formed on November 13 in the western Caribbean Sea at around 18:00 UTC and went on to form and maintain an unusual and unprecedented easterly track for its entire duration, which gave it the common nickname, "Wrong Way Lenny". It attained hurricane status south of Jamaica on November 15 and passed south of Hispaniola and Puerto Rico over the next few days. Lenny rapidly intensified over the northeastern Caribbean on November 17, attaining peak winds of 155 mph (249 km/h) about 21 mi (34 km) south of Saint Croix in the United States Virgin Islands. It gradually weakened while moving through the Leeward Islands, eventually dissipating on November 23 over the open Atlantic Ocean.
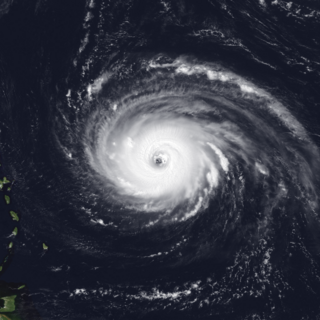
Hurricane Luis was a long lived and powerful Category 4 hurricane. It was the strongest hurricane to make landfall and the third-most intense hurricane recorded during the 1995 Atlantic hurricane season. The storm, along with Humberto, Iris, and Karen, was one of four simultaneous tropical systems in the Atlantic basin.
Seaborne Virgin Island Inc, operating as Seaborne Airlines, is a FAR Part 121 airline headquartered in Carolina, Puerto Rico, near the territory's capital of San Juan. It operates a seaplane shuttle service between St. Croix and St. Thomas. Originally headquartered on St. Croix in the US Virgin Islands, the company relocated to Puerto Rico in 2014.

San Luis Río Colorado is a city and also the name of its surrounding municipality in the state of Sonora, Mexico. In the 2020 census, the city had a population of 176,685. The city is the fourth-largest community in the state, and the municipality is also the fourth-largest in terms of population. Lying in the northwestern corner of Sonora, the city marks the state border with Baja California. It also stands on the international border with the United States, adjacent to San Luis, Arizona. It is located about 75 km from Mexicali. The municipality covers an area of 8,412.75 km² in the Sonoran Desert.
CAT4 or Cat 4 may refer to:

Los Mochis is a coastal city in northern Sinaloa, Mexico. It serves as the municipal seat of the municipality of Ahome. As of the 2010 census, the population was 362,613, which was 61 percent of the municipality's population.

The Copa Luis Villarejo is an association football league in Puerto Rico. Created in 2016, it is open to all clubs that are affiliated with the Puerto Rican Football Federation.

"Almost Like Praying" is a song written by Lin-Manuel Miranda and recorded by him and numerous other artists under the collective name Artists for Puerto Rico. The song was released on October 6, 2017 by Atlantic Records to support relief efforts in Puerto Rico in response to Hurricane Maria, which struck the island in September 2017. Proceeds from the song are to be donated to the victims and survivors of the hurricane. The song debuted at number 20 on the Billboard Hot 100 and number one on the Billboard Digital Songs Sales chart, selling 111,000 downloads and achieving 5.2 million streams in its first week of availability in the US. On February 8, 2018, a salsa remix of the song was released.
Events in the year 2022 in Costa Rica.
This page is based on this
Wikipedia article Text is available under the
CC BY-SA 4.0 license; additional terms may apply.
Images, videos and audio are available under their respective licenses.







