Related Research Articles

The High Mobility Multipurpose Wheeled Vehicle is a family of light, four-wheel drive military trucks and utility vehicles produced by AM General. It has largely supplanted the roles previously performed by the original jeep, and others such as the Vietnam War-era M151 Jeep, the M561 "Gama Goat", their M718A1 and M792 ambulance versions, the Commercial Utility Cargo Vehicle, and other light trucks. Primarily used by the United States military, it is also used by numerous other countries and organizations and even in civilian adaptations.

Military vehicles are commonly armoured to withstand the impact of shrapnel, bullets, shells, rockets, and missiles, protecting the personnel inside from enemy fire. Such vehicles include armoured fighting vehicles like tanks, aircraft, and ships.

A gun truck is an armored vehicle with one or more crew-served weapons, typically based on a military truck. Gun trucks often have improvised vehicle armor, such as scrap metal, concrete, gravel, or sandbags, which is added to a heavy truck.

The ULTRA AP is a concept combat vehicle that was unveiled in September 2005 by the Georgia Tech Research Institute, the applied research arm of the Georgia Institute of Technology, under contract from the Office of Naval Research. The Ultra AP was followed in 2009 by the ULTRA II, which was more focused on further developing the crew compartment.
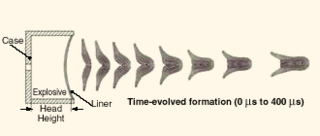
An explosively formed penetrator (EFP), also known as an explosively formed projectile, a self-forging warhead, or a self-forging fragment, is a special type of shaped charge designed to penetrate armor effectively, from a much greater standoff range than standard shaped charges, which are more limited by standoff distance. As the name suggests, the effect of the explosive charge is to deform a metal plate into a slug or rod shape and accelerate it toward a target. They were first developed as oil well perforators by American oil companies in the 1930s, and were deployed as weapons in World War II.

The M1117 Armored Security Vehicle is an internal security vehicle based on the V-100 and V-150 Commando series of armored cars. It was developed in the late 1990s for service with the United States' Military Police Corps. The first prototypes appeared in February 1997 and serial production of the M1117 commenced between 1999 and early 2000.

The Joint Light Tactical Vehicle (JLTV) program was a U.S. Army, U.S. Marine Corps and Special Operations Command competition to select a vehicle to partially replace the Humvee fleet with a family of more survivable vehicles having a greater payload. Early studies for the JLTV program were approved in 2006. The JLTV program incorporates lessons learned from the earlier Future Tactical Truck Systems program and other associated efforts.

Mine-Resistant Ambush Protected is a term for United States military light tactical vehicles produced as part of the MRAP program that are designed specifically to withstand improvised explosive device (IED) attacks and ambushes. The United States Department of Defense MRAP program began in 2007 as a response to the increased threat of IEDs during the Iraq War. From 2007 until 2012, the MRAP program deployed more than 12,000 vehicles in the Iraq War and War in Afghanistan.
Plasan is an Israeli-based company that now specializes in survivability solutions for all domains, the design, development and manufacture of protected vehicles, and most recently maneuvering robotics.
The Bull is an armored personnel carrier with a v-shaped hull designed in a combined effort between Ceradyne, Ideal Innovations Inc. (I-3), and Oshkosh Corporation in response to the MRAP II competition. "The Bull" is a trade-mark of Ideal Innovations, Inc. (I-3).

The Humvee replacement process was an effort by the U.S. military to replace the current AM General Humvee multi-purpose motor vehicle. The Humvee had evolved several times since its introduction in 1985, and is now used in tactical roles for which it was not originally intended. The U.S. military pursued several initiatives to replace it, both in the short and long term. The short-term replacement efforts utilize commercial off-the-shelf (COTS) vehicles, while the long-term efforts focused on building requirements for the Humvee replacement and technology research and evaluation in the form of various prototype vehicles.

Improvised vehicle armour is a form of vehicle armour consisting of protective materials added to a vehicle such as a car, truck, or tank in an irregular and extemporized fashion using available materials. Typically, improvised armour is added in the field and it was not originally part of the design, an official up-armour kit, nor centrally planned and distributed. Improvised armour is used to protect occupants from small arms, crew-served weapons, artillery fire, and mines. Improvised additions have included metal plate, scrap metal, sandbags, concrete, wood, and, since at least the 2000s, Kevlar. These materials vary widely in their ballistic protection.

The XR311 was a prototype military vehicle of US origin that was procured in limited numbers during the 1970s. It was originally developed as the High Mobility Combat Vehicle, or HMCV.

Frag Kit 6 is a vehicular armor upgrade kit developed by the U.S. Army Research Laboratory to defeat explosively formed projectiles (EFP), a type of armor penetrator often utilized in improvised explosive devices (IED). It is designed to be added on armored vehicles such as the MRAP and unarmored Humvee. Like the Chobham armor, the exact materials and the way it works is classified information.

The M1151 Enhanced Armament Carrier is an improved version of the standard Humvee (HMMWV) designed to replace the M1025A2 used by the United States Armed Forces as a response to United States Central Command requirements.

The URO VAMTAC is a Spanish four-wheel drive military vehicle manufactured by UROVESA. Externally it is similar in appearance and design to the Humvee of the United States Military due to similar requirements. More than 2,000 of the vehicles have been delivered to the Spanish Armed Forces. Several other countries operate the VAMTAC as well, and it has seen in service most recently in Afghanistan and Syria. The vehicle comes in three models, named I3, S3 and ST5, and has several configurations.

The Future Tactical Truck System (FTTS) was a United States Armed Forces program for which the Operational Requirements Document was drawn up during 2003. FTTS was a proposed two vehicle modular family that was to replace the AM General High Mobility Multipurpose Wheeled Vehicle, Family of Medium Tactical Vehicles (FMTV), Oshkosh M977 Heavy Expanded Mobility Tactical Truck (HEMTT), Palletized Load System (PLS), and all remaining M35, M809 and M939 series of 2.5 and 5 ton trucks. The FTTS-UV was to replace the HMMWV, while the FTTS-MSV was to replace all other types.

The Ground Mobility Vehicle (GMV) is a U.S. Special Operations Command, (US)SOCOM program, initially modifying Humvees into several variants for use by the United States special operations forces (SOF).
The Armor Survivability Kit (ASK) is an armor kit developed by the U.S. Army Research Laboratory (ARL) in 2003 to protect vehicles like the Humvee from small arms, explosive device fragments, and rocket-propelled grenades (RPGs).
References
- 1 2 Svan, Jennifer (September 26, 2006). "Army Humvees in midst of safety makeover". Stars and Stripes.
- 1 2 History of the U.S. Army Research Laboratory. U.S. Army Research Laboratory. 2017.
- ↑ Update on the use of combat helmets, vehicle armor and body armor by ground forces in Operation Iraqi Freedom and Operation Enduring Freedom : hearing before the Tactical Air and Land Forces Subcommittee of the Committee on Armed Services, House of Representatives, One Hundred Ninth Congress, second session : hearing held, June 15, 2006. Washington: U.S. G.P.O. 2007.
- ↑ Brook, Tom (May 2, 2007). "Humvee doors can trap troops". Archived from the original on June 29, 2017.
- ↑ Leipold (June 15, 2007). "Army Recognizes Greatest Inventions for 2006".