
An armoured fighting vehicle or armored fighting vehicle (AFV) is an armed combat vehicle protected by armour, generally combining operational mobility with offensive and defensive capabilities. AFVs can be wheeled or tracked. Examples of AFVs are tanks, armoured cars, assault guns, self-propelled artilleries, infantry fighting vehicles (IFV), and armoured personnel carriers (APC).

A land mine, or landmine, is an explosive weapon often concealed under or camouflaged on the ground, and designed to destroy or disable enemy targets as they pass over or near it. Land mines are divided into two types: anti-tank mines, which are designed to disable tanks or other vehicles; and anti-personnel mines, designed to injure or kill people.

A naval mine is a self-contained explosive weapon placed in water to damage or destroy surface ships or submarines. Similar to anti-personnel and other land mines, and unlike purpose launched naval depth charges, they are deposited and left to wait until, depending on their fuzing, they are triggered by the approach of or contact with any vessel.

The M24 Chaffee was an American light tank used during the later part of World War II; it was also used in post–World War II conflicts including the Korean War, and by the French in the War in Algeria and the First Indochina War. In British service it was given the service name Chaffee after the United States Army general, Adna R. Chaffee Jr., who helped develop the use of tanks in the United States armed forces. Although the M41 Walker Bulldog was developed as a replacement, M24s were not mostly removed from U.S. and NATO armies until the 1960s and remained in service with some Third World countries.

The Space Shuttle Solid Rocket Booster (SRB) was the first solid-propellant rocket to be used for primary propulsion on a vehicle used for human spaceflight. A pair of them provided 85% of the Space Shuttle's thrust at liftoff and for the first two minutes of ascent. After burnout, they were jettisoned, and parachuted into the Atlantic Ocean, where they were recovered, examined, refurbished, and reused.

The M728 Combat Engineer Vehicle (CEV) is a full-tracked vehicle used for breaching, obstacle removal, and pioneering operations. Production commenced in 1965 and ceased in 1987. A total of 312 of all variants of these armored engineer vehicles were produced.

Mercury-Redstone 1 (MR-1) was the first Mercury-Redstone uncrewed flight test in Project Mercury and the first attempt to launch a Mercury spacecraft with the Mercury-Redstone Launch Vehicle. Intended to be an uncrewed sub-orbital spaceflight, it was launched on November 21, 1960 from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, Florida. The launch failed in an abnormal fashion: immediately after the Mercury-Redstone rocket started to move, it shut itself down and settled back on the pad, after which the capsule jettisoned its escape rocket and deployed its recovery parachutes. The failure has been referred to as the "four-inch flight", for the approximate distance traveled by the launch vehicle.

An anti-tank or AT mine is a type of land mine designed to damage or destroy vehicles including tanks and armored fighting vehicles.

The German S-mine, known by enemy Allied Forces as the "Bouncing Betty" on the Western Front and "frog-mine" on the Eastern Front, is the best-known version of a class of mines known as bounding mines. When triggered, these mines are launched into the air and then detonated at about one metre (3 ft) from the ground. The explosion projects a lethal spray of shrapnel in all directions. The S-mine was an anti-personnel mine developed by Germany in the 1930s and used extensively by German forces during World War II. It was designed to be used in open areas against unshielded infantry. Two versions were produced, designated by the year of their first production: the SMi-35 and SMi-44. There are only minor differences between the two models.

Viking was a series of twelve sounding rockets designed and built by the Glenn L. Martin Company under the direction of the U.S. Naval Research Laboratory (NRL). Designed to supersede the German V-2 as a research vehicle, the Viking was the most advanced large, liquid-fueled rocket developed in the United States in the late 1940s, providing much engineering experience while returning valuable scientific data from the edge of space between 1949 and 1955. Viking 4, launched in 1950, was the first sounding rocket to be launched from the deck of a ship.

Insurgency weapons and tactics (IWAT) are weapons and tactics, most often involving firearms or explosive devices, intended for use by insurgents to engage in guerrilla warfare against an occupier, or for use by rebels against an established government. One type of insurgency weapon are "homemade" firearms made by non-professionals, such as the Błyskawica (Lightning) submachine gun produced in underground workshops by the Polish resistance movement. One weapon that is part of the conventional military arsenal but which has been taken up to great effect by insurgents, is the RPG. Two examples of an improvised weapon used by insurgents would be the improvised explosive devices used in Iraq and the Molotov cocktails used against vehicles and tanks. Two tactics used by many insurgents are assassinations and suicide bomb attacks. The latter tactic is used when an insurgent has a bomb strapped to them or in their car, which provides a low-tech way for insurgents to get explosives close to critical enemy targets.

The M4 Sherman tank was produced in several variants, a result of mass production spread across several manufacturers and several years. It was also the basis for a number of related vehicles and Shermans have been modified by several nations, ranging from upgrades to complete hull conversions for another task. Originally designed in 1941, M4 variants were still used by Israel during the 1967 and 1973 wars with its Arab neighbors.
Tank development both evolved considerably from World War II and played a key role during the Cold War (1947–1991). The period pitted the nations of the Eastern Bloc and the North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO) against each other.
The L9 bar mine is a large rectangular British anti-tank landmine. The bar mine's principal advantage is its long length, and therefore its trigger length. A typical anti-tank landmine is circular, and a vehicle's wheels or tracks, which make up only a small proportion of its total width, must actually press on the mine to activate it. To increase the probability of a vehicle striking the mine, the mine's effective trigger width must be increased.

The PARM 1 (DM12) and its improved version (DM22) is a German off-route mine that fires a fin stabilized rocket. PARM stands for PanzerAbwehrRichtMine, anti-tank directional mine.
Geophysical MASINT is a branch of Measurement and Signature Intelligence (MASINT) that involves phenomena transmitted through the earth and manmade structures including emitted or reflected sounds, pressure waves, vibrations, and magnetic field or ionosphere disturbances.

A mine-clearing line charge is a device used to create a breach in minefields under combat conditions. While there are many types, the basic design is for many explosive charges connected on a line to be projected onto the minefield and then exploded, detonating any buried mines, thus clearing a path for troops to cross.
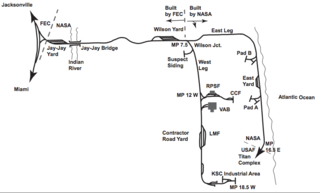
The NASA Railroad is a Class III industrial short-line railroad at the Kennedy Space Center in Cape Canaveral, Florida. The railroad consists of 38 miles (61 km) of track connecting the mainline of the Florida East Coast Railway and trackage at the Cape Canaveral Space Force Station. NASA uses the railroad to deliver large or bulk materials to support its operations, particularly solid rocket boosters and chemicals such as helium and oxygen for rocket fuel.

The United States has produced tanks since their inception in World War I, up until the present day. While there were several American experiments in tank design, the first American tanks to see service were copies of French light tanks and a joint heavy tank design with the United Kingdom.
















