

The MD-82 is a Vietnamese anti-personnel blast mine, that is broadly similar to the United States M14 mine, although the fuzing system is different.


The MD-82 is a Vietnamese anti-personnel blast mine, that is broadly similar to the United States M14 mine, although the fuzing system is different.

The Claymore mine is a directional anti-personnel mine developed for the United States Armed Forces. Its inventor, Norman MacLeod, named the mine after a large medieval Scottish sword. Unlike a conventional land mine, the Claymore may be command-detonated, and is directional, shooting a wide pattern of metal balls into a kill zone. The Claymore can also be activated by a booby-trap tripwire firing system for use in area denial operations.

C-4 or Composition C-4 is a common variety of the plastic explosive family known as Composition C, which uses RDX as its explosive agent. C-4 is composed of explosives, plastic binder, plasticizer to make it malleable, and usually a marker or odorizing taggant chemical. C-4 has a texture similar to modelling clay and can be molded into any desired shape. C-4 is relatively insensitive and can be detonated only by the shock wave from a detonator or blasting cap.

R4M, abbreviation for Rakete, 4 kilogramm, Minenkopf, also known by the nickname Orkan due to its distinctive smoke trail when fired, was a folding-fin air-to-air rocket used by the Luftwaffe at the end of World War II.

The McDonnell Douglas MD-80 is a series of five-abreast single-aisle airliners developed by McDonnell Douglas. It was produced by the developer company until August 1997 and then by Boeing Commercial Airplanes. The MD-80 was the second generation of the DC-9 family, originally designated as the DC-9-80 and later stylized as the DC-9 Super 80 . Stretched, enlarged wing and powered by higher bypass Pratt & Whitney JT8D-200 engines, the aircraft program was launched in October 1977. The MD-80 made its first flight on October 18, 1979, and was certified on August 25, 1980. The first airliner was delivered to launch customer Swissair on September 13, 1980, which introduced it into service on October 10, 1980.

.32 ACP is a centerfire pistol cartridge. It is a semi-rimmed, straight-walled cartridge developed by firearms designer John Browning, initially for use in the FN M1900 semi-automatic pistol. It was introduced in 1899 by Fabrique Nationale, and is also known as the 7.65 mm Browning Short.

A minelayer is any warship, submarine, military aircraft or land vehicle deploying explosive mines. Since World War I the term "minelayer" refers specifically to a naval ship used for deploying naval mines. "Mine planting" was the term for installing controlled mines at predetermined positions in connection with coastal fortifications or harbor approaches that would be detonated by shore control when a ship was fixed as being within the mine's effective range.

Baiyin is a prefecture-level city in northeastern Gansu province, People's Republic of China. Established in the 1950s as a base for mining non-ferrous metals, its mines are becoming exhausted in recent decades, requiring the city to reinvent its economy. Located around 60 km (37 mi) from Gansu's capital Lanzhou, it is part of the Lanzhou-Baiyin Economic Belt.

The M14 mine "Toepopper" is a small anti-personnel land mine first deployed by the United States circa 1955. The M14 mechanism uses a belleville spring to flip a firing pin downwards into a stab detonator when pressure is applied. Once deployed, the M14 is very difficult to detect because it is a minimum metal mine, i.e. most of its components are plastic. Because of this, the design was later modified to ease mine clearance with the addition of a steel washer, glued onto the base of the mine.
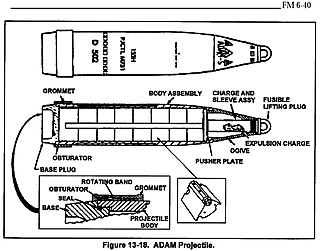
Area denial artillery munition (ADAM) is a family of United States land mines and 155 mm artillery projectiles.

The TM-46 mine is a large, circular, metal-cased Soviet anti-tank mine. It uses either a pressure or tilt-rod fuze, which is screwed into the top. Anti-tank mines with this type of fuze were capable of inflicting much more damage to armored vehicles, when compared to a typical anti-personnel mine.

The PMN series of blast anti-personnel mines were designed and manufactured in the Soviet Union. They are one of the most widely used and commonly found devices during demining operations. They are sometimes nicknamed "black widow" because of their dark casings.

Nepticulidae is a family of very small moths with a worldwide distribution. They are characterised by eyecaps over the eyes. These pigmy moths or midget moths, as they are commonly known, include the smallest of all living moths, with a wingspan that can be as little as 3 mm in the case of the European pigmy sorrel moth, but more usually 3.5–10 mm. The wings of adult moths are narrow and lanceolate, sometimes with metallic markings, and with the venation very simplified compared to most other moths.
The FMK-1 is a small circular Argentina anti-personnel blast mine which, when fitted with a stiffened pressure plate, is also used as the fuze for the FMK-3 and FMK-5 anti-tank mines. The mine has a circular plastic body, with a number of small ribs running vertically around the outside of the mine, with the circular detonator and striker protruding on each side. The pressure plate has a distinctive six pointed star shape ribbing for stiffness. The bottom of the mine has small base plug inside which a small stud is installed. The stud increases the activation pressure of the mine. A metal detector disc can be added to the bottom of the mine, but it is not often used. It is actually in service with the Argentine Army.

The Thamshavn Line was Norway's first electric railway, running from 1908 to 1974 in what is now Trøndelag county. Today it is operated as a heritage railway and is the world's oldest railway running on its original alternating current electrification scheme, using 6.6 kV 25 Hz AC. It was built to transport pyrites from the mines at Løkken Verk to the port at Thamshavn, as well as passengers. There were six stations: Thamshavn, Orkanger, Bårdshaug, Fannrem, Solbusøy and Svorkmo. The tracks were extended to Løkken Verk in 1910.

The G-5 was a Soviet motor torpedo boat design built before and during World War II. Approximately 300 were built, of which 73 were lost during the war. Four were exported to the Spanish Republican Navy during the Spanish Civil War and others were transferred to North Korea after the war. Three were captured by the Finns, but only two were used before all three had to be returned to the Soviets after the Moscow Armistice in 1944.
Hytrosaviridae is a family of double-stranded DNA viruses that infect insects. The name is derived from Hytrosa, sigla from the Greek Hypertrophia for 'hypertrophy' and 'sialoadenitis' for 'salivary gland inflammation.'

This is a timeline of the war in Donbas for the year 2020.
This article includes a list of references, related reading, or external links, but its sources remain unclear because it lacks inline citations .(December 2014) |