Computer vision is an interdisciplinary scientific field that deals with how computers can gain high-level understanding from digital images or videos. From the perspective of engineering, it seeks to understand and automate tasks that the human visual system can do.
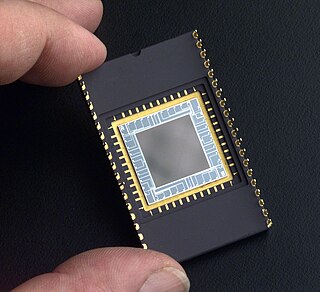
A charge-coupled device (CCD) is an integrated circuit containing an array of linked, or coupled, capacitors. Under the control of an external circuit, each capacitor can transfer its electric charge to a neighboring capacitor. CCD sensors are a major technology used in digital imaging.

In photography and videography, HDR or high-dynamic-range imaging is the set of techniques used to reproduce a greater range of luminosity than that which is possible with standard photographic techniques. Standard techniques allow differentiation only within a certain range of brightness. Outside this range, no features are visible because in the brighter areas everything appears pure white, and pure black in the darker areas. The ratio between the maximum and the minimum of the tonal value in an image is known as the dynamic range. HDR is useful for recording many real-world scenes containing very bright, direct sunlight to extreme shade, or very faint nebulae. High-dynamic-range (HDR) images are often created by capturing and then combining several different, narrower range, exposures of the same subject matter.

Forward-looking infrared (FLIR) cameras, typically used on military and civilian aircraft, use a thermographic camera that senses infrared radiation.

Motion capture is the process of recording the movement of objects or people. It is used in military, entertainment, sports, medical applications, and for validation of computer vision and robots. In filmmaking and video game development, it refers to recording actions of human actors, and using that information to animate digital character models in 2-D or 3-D computer animation. When it includes face and fingers or captures subtle expressions, it is often referred to as performance capture. In many fields, motion capture is sometimes called motion tracking, but in filmmaking and games, motion tracking usually refers more to match moving.

Super CCD is a proprietary charge-coupled device that has been developed by Fujifilm since 1999. The Super CCD uses octagonal, rather than rectangular, pixels. This allows a higher horizontal and vertical resolution to be achieved than a traditional sensor of an equivalent pixel count.

Image noise is random variation of brightness or color information in images, and is usually an aspect of electronic noise. It can be produced by the image sensor and circuitry of a scanner or digital camera. Image noise can also originate in film grain and in the unavoidable shot noise of an ideal photon detector. Image noise is an undesirable by-product of image capture that obscures the desired information.

Digital photography uses cameras containing arrays of electronic photodetectors to produce images focused by a lens, as opposed to an exposure on photographic film. The captured images are digitized and stored as a computer file ready for further digital processing, viewing, electronic publishing, or digital printing. They are combined with other digital images obtained from scanography and other methods that are often used in digital art or media art.
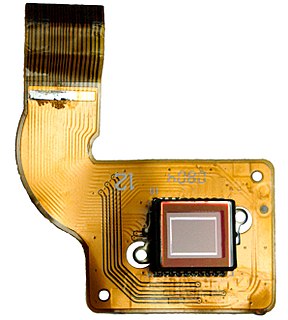
An image sensor or imager is a sensor that detects and conveys information used to make an image. It does so by converting the variable attenuation of light waves into signals, small bursts of current that convey the information. The waves can be light or other electromagnetic radiation. Image sensors are used in electronic imaging devices of both analog and digital types, which include digital cameras, camera modules, camera phones, optical mouse devices, medical imaging equipment, night vision equipment such as thermal imaging devices, radar, sonar, and others. As technology changes, electronic and digital imaging tends to replace chemical and analog imaging.

Image stabilization (IS) is a family of techniques that reduce blurring associated with the motion of a camera or other imaging device during exposure.

An active-pixel sensor (APS) is an image sensor where each pixel sensor unit cell has a photodetector and one or more active transistors. In a metal–oxide–semiconductor (MOS) active-pixel sensor, MOS field-effect transistors (MOSFETs) are used as amplifiers. There are different types of APS, including the early NMOS APS and the much more common complementary MOS (CMOS) APS, also known as the CMOS sensor, which is widely used in digital camera technologies such as cell phone cameras, web cameras, most modern digital pocket cameras, most digital single-lens reflex cameras (DSLRs), and mirrorless interchangeable-lens cameras (MILCs). CMOS sensors emerged as an alternative to charge-coupled device (CCD) image sensors and eventually outsold them by the mid-2000s.
OmniVision Technologies Inc. is a Chinese company that is publicly traded as part of Will Semiconductor. The company designs and develops digital imaging products for use in mobile phones, notebooks, netbooks and webcams, security and surveillance cameras, entertainment, automotive and medical imaging systems. Headquartered in Santa Clara, California, OmniVision Technologies has offices in the US, Western Europe and Asia.
Range imaging is the name for a collection of techniques that are used to produce a 2D image showing the distance to points in a scene from a specific point, normally associated with some type of sensor device.

Medipix is a family of photon counting and particle tracking pixel detectors developed by an international collaboration, hosted by CERN.
Canesta is a fabless semiconductor company that was founded in April, 1999, by Cyrus Bamji, Abbas Rafii, and Nazim Kareemi.

A time-of-flight camera is a range imaging camera system employing time-of-flight techniques to resolve distance between the camera and the subject for each point of the image, by measuring the round trip time of an artificial light signal provided by a laser or an LED. Laser-based time-of-flight cameras are part of a broader class of scannerless LIDAR, in which the entire scene is captured with each laser pulse, as opposed to point-by-point with a laser beam such as in scanning LIDAR systems. Time-of-flight camera products for civil applications began to emerge around 2000, as the semiconductor processes allowed the production of components fast enough for such devices. The systems cover ranges of a few centimeters up to several kilometers.
SoftKinetic was a Belgian company founded by Eric Krzeslo and Thibaud Remacle which develops gesture recognition hardware and software for real-time range imaging (3D) cameras. It was founded in July 2007. SoftKinetic provides gesture recognition solutions based on its technology to the interactive digital entertainment, consumer electronics, health & fitness, and serious game industries. SoftKinetic technology has been applied to interactive digital signage and advergaming, interactive television, and physical therapy.

Indoor golf is an umbrella term for all activities in golf which can be carried out indoors. Venues include indoor driving ranges, chipping areas, putting greens, machines and home golf simulators. Many of these indoor facilities are businesses that include additional entertainment options as well as food and drink for customers.

pmdtechnologies ag is a developer of CMOS semiconductor 3D time-of-flight (ToF) components and a provider of engineering support in the field of digital 3D imaging. The company is named after the Photonic Mixer Device (PMD) technology used in its products to detect 3D data in real time. The corporate headquarters of the company is located in Siegen, Germany.
Zivid is a Norwegian machine vision technology company headquartered in Oslo, Norway. It designs and sells 3D color cameras with vision software that are used in autonomous industrial robot cells, collaborative robot (cobot) cells and other industrial automation systems.














