
An electronic musical instrument or electrophone is a musical instrument that produces sound using electronic circuitry. Such an instrument sounds by outputting an electrical, electronic or digital audio signal that ultimately is plugged into a power amplifier which drives a loudspeaker, creating the sound heard by the performer and listener.

MIDI is a technical standard that describes a communications protocol, digital interface, and electrical connectors that connect a wide variety of electronic musical instruments, computers, and related audio devices for playing, editing, and recording music.

Digital music technology encompasses digital instruments, computers, electronic effects units, software, or digital audio equipment by a performer, composer, sound engineer, DJ, or record producer to produce, perform or record music. The term refers to electronic devices, instruments, computer hardware, and software used in performance, playback, recording, composition, mixing, analysis, and editing of music.

Multitrack recording (MTR), also known as multitracking, is a method of sound recording developed in 1955 that allows for the separate recording of multiple sound sources or of sound sources recorded at different times to create a cohesive whole. Multitracking became possible in the mid-1950s when the idea of simultaneously recording different audio channels to separate discrete "tracks" on the same reel-to-reel tape was developed. A "track" was simply a different channel recorded to its own discrete area on the tape whereby their relative sequence of recorded events would be preserved, and playback would be simultaneous or synchronized.

An electronic keyboard, portable keyboard, or digital keyboard is an electronic musical instrument, an electronic derivative of keyboard instruments. Electronic keyboards include synthesizers, digital pianos, stage pianos, electronic organs and digital audio workstations. In technical terms, an electronic keyboard is a synthesizer with a low-wattage power amplifier and small loudspeakers.

FL Studio is a digital audio workstation (DAW) developed by the Belgian company Image-Line. It features a graphical user interface with a pattern-based music sequencer. The program is available in four different editions for Microsoft Windows and macOS.

GarageBand is a line of digital audio workstations developed by Apple for macOS, iPadOS, and iOS devices that allows users to create music or podcasts. GarageBand was originally released for macOS in 2004 and brought to iOS in 2011. The app’s music and podcast creation system enables users to create multiple tracks with pre-made MIDI keyboards, pre-made loops, an array of various instrumental effects, and voice recordings.
A scorewriter, or music notation program is software for creating, editing and printing sheet music. A scorewriter is to music notation what a word processor is to text, in that they typically provide flexible editing and automatic layout, and produce high-quality printed results.

A digital audio workstation (DAW) is an electronic device or application software used for recording, editing and producing audio files. DAWs come in a wide variety of configurations from a single software program on a laptop, to an integrated stand-alone unit, all the way to a highly complex configuration of numerous components controlled by a central computer. Regardless of configuration, modern DAWs have a central interface that allows the user to alter and mix multiple recordings and tracks into a final produced piece.
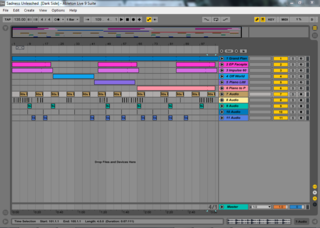
Ableton Live, also known as Live, is a digital audio workstation for macOS and Windows developed by the German company Ableton.
A rompler is an electronic musical instrument that plays pre-fabricated sounds based on audio samples. The term rompler is a blend of the terms ROM and sampler. In contrast to samplers, romplers do not record audio. Both may have additional sound editing features, such as layering several waveforms and modulation with ADSR envelopes, filters and LFOs.

A MIDI controller is any hardware or software that generates and transmits Musical Instrument Digital Interface (MIDI) data to MIDI-enabled devices, typically to trigger sounds and control parameters of an electronic music performance. They most often use a musical keyboard to send data about the pitch of notes to play, although a MIDI controller may trigger lighting and other effects. A wind controller has a sensor that converts breath pressure to volume information and lip pressure to control pitch. Controllers for percussion and stringed instruments exist, as well as specialized and experimental devices. Some MIDI controllers are used in association with specific digital audio workstation software. The original MIDI specification has been extended to include a greater range of control features.

A wind controller, sometimes referred to as a wind synthesizer, is an electronic wind instrument. It is usually a MIDI controller associated with one or more music synthesizers. Wind controllers are most commonly played and fingered like a woodwind instrument, usually the saxophone, with the next most common being brass fingering, particularly the trumpet. Models have been produced that play and finger like other acoustic instruments such as the recorder or the tin whistle. The most common form of wind controller uses electronic sensors to convert fingering, breath pressure, bite pressure, finger pressure, and other gesture or action information into control signals that affect musical sounds. The control signals or MIDI messages generated by the wind controller are used to control internal or external devices such as analog synthesizers or MIDI-compatible synthesizers, synth modules, softsynths, sequencers, or even non-instruments such as lighting systems.

Simmons is an electronic drum brand, which originally was a pioneering British manufacturer of electronic drums. Founded in 1978 by Dave Simmons, it supplied electronic kits from 1980 to 1998. The drums' distinctive, electronic sound can be found on countless albums from the 1980s. The company closed in 1999 and the Simmons name is currently owned by Guitar Center.

A guitar synthesizer is any one of a number of musical instrument systems that allow a guitarist to access synthesizer capabilities.
Orchestral enhancement is the technique of using orchestration techniques, architectural modifications, or electronic technologies to modify the sound, complexity, or color of a musical theatre, ballet or opera pit orchestra. Orchestral enhancements are used both to create new sounds and to add capabilities to existing orchestral ensembles.
The Kurzweil K250, manufactured by Kurzweil Music Systems, was an early electronic musical instrument which produced sound from sampled sounds compressed in ROM, faster than common mass storage such as a disk drive. Acoustic sounds from brass, percussion, string and woodwind instruments as well as sounds created using waveforms from oscillators were utilized. Designed for professional musicians, it was invented by Raymond Kurzweil, founder of Kurzweil Computer Products, Inc., Kurzweil Music Systems and Kurzweil Educational Systems with consultation from Stevie Wonder; Lyle Mays, an American jazz pianist; Alan R. Pearlman, founder of ARP Instruments Inc.; and Robert Moog, inventor of the Moog synthesizer.

Logic Studio is a discontinued professional music production suite by Apple Inc. The first version of Logic Studio was unveiled on September 12, 2007. It claims to be the largest collection of modeled instruments, sampler instruments, effect plug-ins, and audio loops ever put in a single application.
Synthestration is the art of composing music in the form of a MIDI mockup. A mockup is an extensive demo of a musical recording, for playback by computers triggering virtual instrument software or hardware, to emulate an orchestral recording.

The B4 Organ II is a discontinued commercial, proprietary software synthesizer made by Native Instruments. The software runs as a stand-alone executable, or as a VST, DXi, or RTAS plugin in a Digital audio workstation. The software is an example of a "Clonewheel organ", an attempt at recreating the sound of a Hammond organ using software synthesis.













