
A postmark is a postal marking made on an envelope, parcel, postcard or the like, indicating the place, date and time that the item was delivered into the care of a postal service, or sometimes indicating where and when received or in transit. Modern postmarks are often applied simultaneously with the cancellation or killer that marks postage stamps as having been used. Sometimes a postmark alone is used to cancel stamps, and the two terms are often used interchangeably. Postmarks may be applied by handstamp or machine, using methods such as rollers or inkjets, while digital postmarks are a recent innovation.
A first day of issue cover or first day cover (FDC) is a postage stamp on a cover, postal card or stamped envelope franked on the first day the issue is authorized for use within the country or territory of the stamp-issuing authority. Sometimes the issue is made from a temporary or permanent foreign or overseas office. Covers that are postmarked at sea or their next port of call will carry a Paquebot postmark. There will usually be a first day of issue postmark, frequently a pictorial cancellation, indicating the city and date where the item was first issued, and "first day of issue" is often used to refer to this postmark. Depending on the policy of the nation issuing the stamp, official first day postmarks may sometimes be applied to covers weeks or months after the date indicated.

A cancellation is a postal marking applied on a postage stamp or postal stationery to deface the stamp and to prevent its reuse. Cancellations come in a huge variety of designs, shapes, sizes, and colors. Modern cancellations commonly include the date and post office location where the stamps were mailed, in addition to lines or bars designed to cover the stamp itself. The term "postal marking" sometimes is used to refer specifically to the part that contains the date and posting location, but the term is often used interchangeably with "cancellation." The portion of a cancellation that is designed to deface the stamp and does not contain writing is also called the "obliteration" or killer. Some stamps are issued pre-cancelled with a printed or stamped cancellation and do not need to have a cancellation added. Cancellations can affect the value of stamps to collectors, positively or negatively. Cancellations of some countries have been extensively studied by philatelists, and many stamp collectors and postal history collectors collect cancellations in addition to the stamps themselves.

Postal service in the United States began with the delivery of stampless letters whose cost was borne by the receiving person, later encompassed pre-paid letters carried by private mail carriers and provisional post offices, and culminated in a system of universal prepayment that required all letters to bear nationally issued adhesive postage stamps.

Postal history is the study of postal systems and how they operate and, or, the study of the use of postage stamps and covers and associated postal artifacts illustrating historical episodes in the development of postal systems. The term is attributed to Robson Lowe, a professional philatelist, stamp dealer and stamp auctioneer, who made the first organised study of the subject in the 1930s and described philatelists as "students of science", but postal historians as "students of humanity". More precisely, philatelists describe postal history as the study of rates, routes, markings, and means.

In philately, a pen cancel is a cancellation of a postage or revenue stamp by the use of a pen, marker or crayon.

A fancy cancel is a postal cancellation that includes an artistic design. Although the term may be used of modern machine cancellations that include artwork, it primarily refers to the designs carved in cork and used in 19th century post offices of the United States.

A postal marking is any kind of annotation applied to a letter by a postal service. The most common types are postmarks and cancellations; almost every letter will have those. Less common types include forwarding addresses, routing annotations, warnings, postage due notices and explanations, such as for damaged or delayed mail and censored or inspected mail. A key part of postal history is the identification of postal markings, their purpose, and period of use.

Bullseye, in philately, also called Socked on the nose (SON), refers to a cancellation of a postage stamp in which the postmark, typically a circle with the date and town name where mailed, has been applied centered on the stamp. The ideal bullseye has the entire postmark inside the margins, although this is not always possible, because the stamp may be too small or the postmark too large. The colloquial expression "Socked on the nose" does not seem to be used in Europe: the terms Oblitération centrale in French or luxus in German are in common usage.

The postage stamps and postal system of the Confederate States of America carried the mail of the Confederacy for a brief period in American history. Early in 1861 when South Carolina no longer considered itself part of the Union and demanded that the U.S. Army abandon Fort Sumter, plans for a Confederate postal system were already underway. Indeed, the Confederate Post office was established on February 21, 1861; and it was not until April 12 that the American Civil War officially began, when the Confederate Army fired upon US soldiers who had refused to abandon the fort. However, the United States Post Office Department continued to handle the mail of the seceded states as usual during the first weeks of the war. It was not until June 1 that the Confederate Post office took over collection and delivery, now faced with the task of providing postage stamps and mail services for its citizens.

A cancelled to order postage stamp is a stamp the issuing postal service has cancelled, but has not traveled through the post, but instead gets handed back to a stamp collector or dealer. They can come from withdrawn stocks of stamps cancelled in sheets and sold as remainders or from new sheets for sale at reduced rates to the stamp trade. Postal services of various countries do this in response to collector demand, or to preclude stamps issued for the collector market being used on mail. Some of the history of CTOs is from stamps being given to collectors on an approval basis, in person or through mailings; the first CTOs began in the late 19th century.
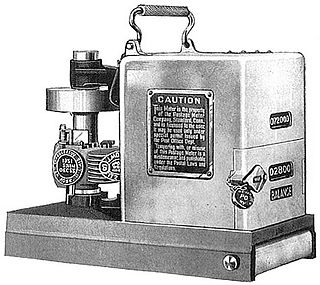
A postage meter or franking machine is a mechanical device used to create and apply physical evidence of postage to mailed items. Postage meters are regulated by a country's postal authority. A postage meter imprints an amount of postage, functioning as a postage stamp, a cancellation and a dated postmark all in one. The meter stamp serves as proof of payment and eliminates the need for adhesive stamps.

The postal history of the Bahamas begins in the 18th century, with the first post office operating since 1733. The earliest known letters date from 1802. In 1804 a straight-line "BAHAMAS" handstamp came into use. The Royal Mail Line initiated a regular mail service in 1841, and from 1846 used a "Crown Paid" handstamp along with a dated postmark for New Providence.

The Mexican postal system has its roots in the Aztec system of messengers which the Spanish adopted after the Conquest. A postal service was established in 1580, mainly to communicate between the viceroyalty of New Spain with the motherland Spain. During the 18th century, Spain established a formal postal system with regular routes. In 1856, Mexico issued its first adhesive postage stamps, with "district overprints", a unique feature among postal systems worldwide, employed to protect from theft of postage stamps.

The Daguin machine was one of the first cancelling machines used by the French postal administration. It was created by Eugène Daguin (1849-1888). Its first official use took place in June 1884 in Paris. It could cancel three thousand covers per hour.

Thomas Leavitt (1827–1899) patented, along with his brother Martin Leavitt, the first machine in the U.S. that made machine-cancelled postal letters practicable, enabling the United States Post Office to increase the volume of mail it handled, quickening the pace of delivery and allowing customers to more easily send letters of various sizes.

Colombia is a country in north-western South America. Colombia is bordered by Venezuela, Brazil, Ecuador, Peru, Panama and the Caribbean Sea and the Pacific Ocean. With a population of over 45 million people, Colombia has the second largest population in South America, after Brazil. The capital is Bogotá.

Poczta Polska, the Polish postal service, was founded in 1558 and postal markings were first introduced in 1764. The three partitions of Poland in 1772, 1793 and 1795 saw the independent nation of Poland disappear. The postal services in the areas occupied by Germany and Austria were absorbed into those countries' postal services. In 1772 the area occupied by Austria was created into the Kingdom of Galicia, a part of the Austrian Empire. This lasted till 1918. The Duchy of Warsaw was created briefly, between 1807 and 1813, by Napoleon I of France, from Polish lands ceded by the Kingdom of Prussia under the terms of the Treaties of Tilsit. In 1815, following Napoleons' defeat in 1813, the Congress of Vienna, created Congress Poland out of the Duchy of Warsaw and also established the Free City of Kraków. Congress Poland was placed under the control of Russia and the postal service was given autonomy in 1815. In 1851 the postal service was put under the control of the Russian post office department regional office in St Petersburg. In 1855 control was restored for a while to the Congress Kingdom but following the uprising in 1863 again came under Russian control from 1866 and continued until World War I. In November 1918 the Second Polish Republic was created.

In philately a fiscal cancel is a cancellation on a stamp that indicates that the stamp has been used for fiscal (taxation) purposes.

The J.B. Catalogue of Malta Stamps and Postal History is Malta's leading stamp catalogue. It was first published in 1984 and is published bi-annually by Joseph Buttigieg of Sliema Stamp Shop. It is currently in its twenty-second edition (2014). The catalogue originally used the SG numbering system, but from the early 1990s it had separate numbering. It is in English and the pricing was in Maltese pounds until 2006, and euros from 2008.




















