
The Advanced Gas-cooled Reactor (AGR) is a type of nuclear reactor designed and operated in the United Kingdom. These are the second generation of British gas-cooled reactors, using graphite as the neutron moderator and carbon dioxide as coolant. They have been the backbone of the UK's nuclear power generation fleet since the 1980s.

Magnox is a type of nuclear power/production reactor that was designed to run on natural uranium with graphite as the moderator and carbon dioxide gas as the heat exchange coolant. It belongs to the wider class of gas-cooled reactors. The name comes from the magnesium-aluminium alloy used to clad the fuel rods inside the reactor. Like most other "Generation I nuclear reactors", the Magnox was designed with the dual purpose of producing electrical power and plutonium-239 for the nascent nuclear weapons program in Britain. The name refers specifically to the United Kingdom design but is sometimes used generically to refer to any similar reactor.

The Nyongbyon Nuclear Scientific Research Center is North Korea's major nuclear facility, operating its first nuclear reactors. It is located in Nyongbyon County in North Pyongan Province, about 100 km north of Pyongyang. The center produced the fissile material for North Korea's six nuclear weapon tests from 2006 to 2017, and since 2009 is developing indigenous light water reactor nuclear power station technology.

Dungeness nuclear power station comprises a pair of non-operational nuclear power stations located on the Dungeness headland in the south of Kent, England. Dungeness A is a legacy Magnox power station that was connected to the National Grid in 1965 and has reached the end of its life. Dungeness B is an advanced gas-cooled reactor (AGR) power station consisting of two 1,496 MWt reactors, which began operation in 1983 and 1985 respectively, and have been non-operational since 2018 with decommissioning beginning in 2021.

Chapelcross nuclear power station is a decommissioned and partly demolished Magnox nuclear power station near Annan in Dumfries and Galloway in southwest Scotland, which was in operation from 1959 to 2004. It was the sister plant to the Calder Hall plant in Cumbria, England; both were commissioned and originally operated by the United Kingdom Atomic Energy Authority. The primary purpose of both plants was to produce weapons-grade plutonium for the UK's nuclear weapons programme, but they also generated electrical power for the National Grid.

Wylfa nuclear power station is a decommissioned Magnox nuclear power station situated west of Cemaes Bay on the island of Anglesey, off the northwestern coast of Wales. Construction of the two 490 MW nuclear reactors, known as "Reactor 1" and "Reactor 2", began in 1963. They became operational in 1971. Wylfa was located on the coast because seawater was used as a coolant.
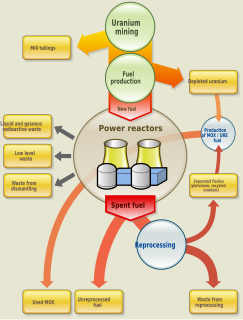
Nuclear fuel is material used in nuclear power stations to produce heat to power turbines. Heat is created when nuclear fuel undergoes nuclear fission.

A reactor pressure vessel (RPV) in a nuclear power plant is the pressure vessel containing the nuclear reactor coolant, core shroud, and the reactor core.
The Steam Generating Heavy Water Reactor (SGHWR) is a United Kingdom design for commercial nuclear reactors. It uses heavy water as the neutron moderator and normal "light" water as the coolant. The coolant boils in the reactor, like a boiling water reactor, and drives the power-extraction steam turbines.
Magnox is an alloy—mainly of magnesium with small amounts of aluminium and other metals—used in cladding unenriched uranium metal fuel with a non-oxidising covering to contain fission products in nuclear reactors. Magnox is short for Magnesium non-oxidising. This material has the advantage of a low neutron capture cross section, but has two major disadvantages:

Scottish Nuclear was formed as a precursor to the privatisation of the electricity supply industry in Scotland on 1 April 1990. A purpose-built headquarters was built in 1992 in the new town of East Kilbride.

Hinkley Point A nuclear power station is a decommissioned Magnox nuclear power station located on a 19.4-hectare (48-acre) site in Somerset on the Bristol Channel coast, 5 miles (8 km) west of the River Parrett estuary. The ongoing decommissioning process is being managed by Nuclear Decommissioning Authority licensee Magnox Ltd.

Latina Nuclear Power Plant is a former nuclear power plant at Latina, Lazio, Italy. Consisting of one 153 MWe Magnox reactor, it operated from 1963 until 1987. A second reactor, the experimental CIRENE design, began construction at Latina in 1972 but it was not completed until 1988 and never operated.

Oldbury nuclear power station is decommissioned Magnox nuclear power station located on the south bank of the River Severn close to the village of Oldbury-on-Severn in South Gloucestershire, England. The ongoing decommissioning process is managed by Magnox Ltd, a subsidiary of the Nuclear Decommissioning Authority (NDA). Oldbury is one of four stations located close to the mouth of the River Severn and the Bristol Channel, the others being Berkeley, Hinkley Point A, and Hinkley Point B.
A gas-cooled reactor (GCR) is a nuclear reactor that uses graphite as a neutron moderator and a gas as coolant. Although there are many other types of reactor cooled by gas, the terms GCR and to a lesser extent gas cooled reactor are particularly used to refer to this type of reactor.

The UNGG is an obsolete nuclear power reactor design developed in France. It was graphite moderated, cooled by carbon dioxide, and fueled with natural uranium metal. The first generation of French nuclear power stations were UNGGs, as was Vandellos unit 1 in Spain. Of ten units built, all were shut down by end 1994, most for economic reasons due to staffing costs.
Reactor-grade plutonium (RGPu) is the isotopic grade of plutonium that is found in spent nuclear fuel after the uranium-235 primary fuel that a nuclear power reactor uses has burnt up. The uranium-238 from which most of the plutonium isotopes derive by neutron capture is found along with the U-235 in the low enriched uranium fuel of civilian reactors.

Hunterston A nuclear power station is a decommissioned Magnox nuclear power station located at Hunterston in Ayrshire, Scotland, adjacent to Hunterston B. The ongoing decommissioning process is being managed by Nuclear Decommissioning Authority (NDA) subsidiary Magnox Ltd.

Trawsfynydd nuclear power station is a decommissioned Magnox nuclear power station situated in Snowdonia National Park in Gwynedd, Wales. The plant, which became operational in 1965, was the only nuclear power station in the UK to be built inland, with cooling water that was taken from the man-made Llyn Trawsfynydd reservoir which also supplies the hydro-electric Maentwrog power station. It was closed in 1991. Its planned decommissioning by Magnox Ltd was expected to take almost 100 years, but in 2021, the Welsh government arranged for the power station to be redeveloped using small-scale reactors.

Magnox Ltd is a nuclear decommissioning Site Licence Company (SLC) under the Nuclear Decommissioning Authority (NDA), a government body set up specifically to deal with the nuclear legacy under the Energy Act 2004. In September 2019, it became a direct subsidiary of the NDA.















