Related Research Articles
In Māori mythology, the Ponaturi are a group of hostile creatures (goblins) who live in a land beneath the sea by day, returning to shore each evening to sleep. They dread daylight, which is fatal to them. They appear in a number of stories, including:
In the Tahitian story of Rata 'Aremata-Popoto and 'Aremata-Roroa are two ocean-dwelling monsters that Rata must overcome.

In Hawaiian mythology, Laka is the name of two different popular heroes from Polynesian mythology.. Lengthy legends of their exploits extend throughout the islands, and the kings of Tahiti and Hawaiʻi claimed them as their ancestors.
Kaha'i is a handsome Polynesian demigod whose exploits were popular in many Polynesian mythologies.

In Māori mythology, Matuku-tangotango (Matuku) is an ogre who kills Wahieroa the son of Tāwhaki. In some versions, Matuku lives in a cave called Putawarenuku. Rātā, the son of Wahieroa, sets off to avenge his murdered father, and arrives at last at Matuku's village. He hears from Matuku's servant that at the new moon his master can be killed at the pool where he washes his face and hair. When the new moon has come, Rātā waits until the ogre comes out of his cave and is leaning over with his head in the pool. He grabs him by the hair and kills him. Rātā then sets off to rescue his father's bones from the Ponaturi. A South Island version names the islands where Matuku lives as Puorunuku and Puororangi and also states that Rātā nooses Matuku as he comes out of his lair to perform certain rituals.
In the mythology of Tahiti, Pua Tu Tahi was one of the giant monster clam of the deep in the legend of Rata.
In the mythology of the Tuamotu archipelago, Kiho-tumu represents the supreme god.
Tuamotuan, Paʻumotu or Paumotu is a Polynesian language spoken by 4,000 people in the Tuamotu archipelago, with an additional 2,000 speakers in Tahiti.
In Māori mythology, Arawa was one of the great ocean-going, voyaging canoes that was used in the migrations that settled Aotearoa.
In Tuamotu mythology, Vahieroa marries Matamata-taua or Tahiti-to'erau, and on the night of the birth of their son, the great Tuamotuan hero, Rata, the parents go fishing and are snatched away by the demon bird belonging to Puna, king of Hiti-marama, "an island north of Pitcairn and Elizabeth but long since swallowed in the sea."
In the Tuamotu Rata cycle, Tahiti-tokerau was a water-nymph whom Vahi-vero marries. She was abducted by Puna, king of the underworld and rescued by her husband. They then become parents of Rata.
Karihi-nui was the brother of Tahaki in Tuamotuan legend. In Samoa, Karihi Alise accompanied his brother Tafa'i to heaven to woo the goddess Sina.
In Māori tradition, Tainui was one of the great ocean-going canoes in which Polynesians migrated to New Zealand approximately 800 years ago. The Tainui waka was named for an infant who did not survive childbirth. At the burial site of this child, at a place in Hawaiki known then as Maungaroa, a great tree grew; this was the tree that was used to build the ocean canoe.

In Māori mythology, Tiki is the first man created by either Tūmatauenga or Tāne. He found the first woman, Marikoriko, in a pond; she seduced him and he became the father of Hine-kau-ataata. By extension, a tiki is a large or small wooden or stone carving in humanoid form, although this is a somewhat archaic usage in the Māori language. Carvings similar to tikis and coming to represent deified ancestors are found in most Polynesian cultures. They often serve to mark the boundaries of sacred or significant sites.

In Māori mythology, accounts vary somewhat as to the ancestry of Rātā. Usually he is a grandson of Tāwhaki and son of Wahieroa. Wahieroa is treacherously killed by Matuku-tangotango, an ogre. Rātā sets out to avenge the murder, travelling to the home of Matuku, where a servant of the ogre tells him that Matuku comes out to devour people each new moon, and that he can be killed at the pool where he washes his face and hair. Rātā waits till the ogre comes out and is leaning over with his head in the pool. He grabs him by the hair and kills him. Matuku's bones are used to make spears for hunting birds.
In the Tuamotu islands, the telling of the full cycle of the legend of Rata takes several evenings to tell.
Rata, in Tahitian mythology, is said to have become king of Tahiti when his uncle, king Tumu-nui, and his father Vahieroa are swallowed by a great clam while they are on their way to Pitcairn. When he reaches adulthood, Rata plans to avenge his father. As in the Tuamotuan version, Rata identifies a tree to build his canoe, but it is protected by forest elves. After he captures them they build it for him in a single night. While en route for Pitcairn, Rata and his crew are sucked down into the same clam, but they use their spears to cut the monster open. They rescue the remains of Rata's father and uncle and bury them back in Tahiti. After recovering from their adventure, Rata sets out for further adventures. See also Aremata-Popoa and Aremata-Rorua.
In Tuamotu mythology, Vahi-vero is the son of the demigod Kui and a goblin woman named Rima-roa.
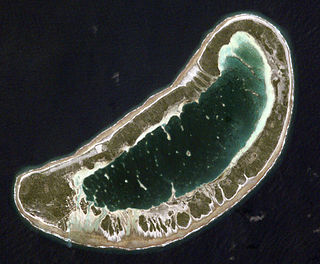
Fangatau, or Nakai-erua, is a small atoll in the Tuamotu group in French Polynesia. The nearest land is Fakahina Atoll, located 72 km to the ESE. This small atoll has an elongated shape. Its length is 8 kilometres, maximum width 3.5 kilometres. It has a total area of 22.2 square kilometres, land area 5.9 km2. Its reef encloses its lagoon completely. Anchorage is difficult. Fangatau Atoll has 135 inhabitants. Teana is the main village.

Tahiti and Society Islands mythology comprises the legends, historical tales, and sayings of the ancient people of the Society Islands, consisting of Tahiti, Bora Bora, Raiatea, Huahine, Moorea and other islands. It is considered a variant of a more general Polynesian mythology, developing its own unique character for several centuries. The religion was officially suppressed in the 19th century, and ultimately abandoned by the natives in favor of Christianity.
References
- R.D. Craig, Dictionary of Polynesian Mythology (Greenwood Press: New York, 1989), 156;
- J.F. Stimson, Tuamotuan Legends: Island of Anaa (Honolulu: Bernice P. Bishop Museum Press, 1937), 126–129.
| This article relating to a myth or legend from Oceania is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |