
Malayalam, the lingua franca of the Indian state of Kerala and the union territories of Lakshadweep and Puduchery, is one of the six classical languages of India. Malayalam literature comprises those literary texts written in Malayalam, a South-Dravidian language spoken in the Indian state of Kerala. The first travelogue in any Indian language is the Malayalam Varthamanappusthakam, written by Paremmakkal Thoma Kathanar in 1785. Malayalam literature has been presented with 6 Jnanapith awards, the second-most for any Dravidian language and the third-highest for any Indian language.

The Malayali people are a Dravidian ethnolinguistic group originating from the present-day state of Kerala & Union Territory of Lakshadweep in India, occupying its southwestern Malabar coast. They form the majority of the population in Kerala and Lakshadweep. They are predominantly native speakers of the Malayalam language, one of the six classical languages of India. The state of Kerala was created in 1956 through the States Reorganisation Act. Prior to that, since the 1800s existed the Kingdom of Travancore, the Kingdom of Cochin, Malabar District, and South Canara of the British India. The Malabar District was annexed by the British through the Third Mysore War (1790–92) from Tipu Sultan. Before that, the Malabar District was under various kingdoms including the Zamorins of Calicut, Kingdom of Tanur, Arakkal kingdom, Kolathunadu, Valluvanad, and Palakkad Rajas.

Malabar Muslims or Malabar Mohammadens or Muslim Mappila or Muhammaden Mappila, generally in recent times, is a member of the Muslim community of same name found predominantly in Kerala and Lakshadweep Islands in Southern India, and historically used to identify Muslims from Northern Kerala. Muslims of Kerala make up 26.56% of the population of the state (2011), and as a religious group they are the second largest group after Hindus (54.73%). Mappilas share the common language of Malayalam with the other religious communities of Kerala.

The culture of Kerala has developed over the past millennia, influences from other parts of India and abroad. It is defined by its antiquity and the organic continuity sustained by the Malayali people. Modern Kerala society took shape owing to migrations from different parts of India and abroad throughout Classical Antiquity.
Mappila songs are a folklore Muslim song genre rendered to lyrics, within a melodic framework (Ishal), in Arabi Malayalam by the Mappilas of the Malabar region in Kerala, India. Mappila songs have a distinct cultural identity, while at the same time remain closely linked to the cultural practices of Kerala.

Islam arrived in Kerala, the Malayalam-speaking region in the south-western tip of India, through Middle Eastern merchants. The Indian coast has an ancient relation with West Asia and the Middle East, even during the pre-Islamic period.

Arabi Malayalam is the traditional Dravidian language of the Mappila Muslim community. It is spoken by several thousand people, predominantly in the Malabar Coast of Kerala state, southern India. The form can be classified as a regional dialect in northern Kerala, or as a class or occupational dialect of the Mappila community. It can also be called a vernacular in general, or as a provincial patois, with the latter label being increasingly applicable in Colonial times. All the forms of the Malayalam language, including Mappila, are mutually intelligible.
Arabi Malayalam script, also known as Ponnani script, is a writing system — a variant form of the Arabic script with special orthographic features — for writing Arabi Malayalam, a Dravidian language in southern India. Though the script originated and developed in Kerala, today it is predominantly used in Malaysia and Singapore by the migrant Muslim community.
Nellikuth is a town in Manjeri Municipality in Malappuram district of Kerala, India. It is situated 8 km west to Manjeri and 16 km north west to the Malappuram, the district headquarters. It is one of the major place in Payyanad Village, in Eranad Taluk.

Religion in Kerala is diverse. According to 2011 census of India figures, 54.73% of Kerala's population are Hindus, 26.56% are Muslims, 18.38% are Christians, and the remaining 0.33% follow other religions or have no religion. As of 2020, Hindus, Muslims, Christians and others account for 41.5%, 43.9%, 13.9% and 0.7% of the total child births in the state, respectively.
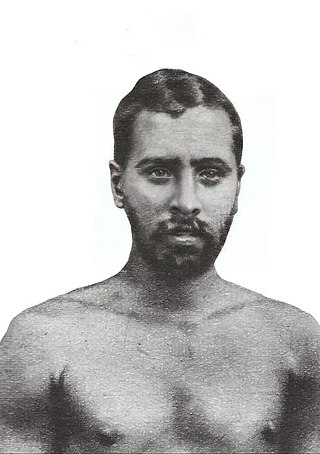
Variyankunnath Kunjahammad Haji sometimes called Variyamkunnan was a prominent leader during the war in Malabar against the British, during the Malabar rebellion, and the founder of a parallel government. He was an Indian freedom fighter, opposer of the Jenmi system, and an ordinary member of the Khilafat movement.

The Malabar rebellion of 1921 started as a resistance against the British colonial rule in certain places in the southern part of old Malabar district of present-day Kerala. The popular uprising was also against the prevailing feudal system controlled by elite Hindus.

Āli Musliyār was the leader of Malabar Rebellion, and a freedom fighter. Musliyār was the Imam of Tirurangadi Masjid from 1907 until his eventual execution at Coimbatore Prison for the allegation against him for calling to fight against British rule. He was an active orator of the Khilafat Movement in Malabar region.
Habib Fazl Bin Alawi Mouladvīla Al HusayniPashaaliasFazal Pookoya Thangal, also known as Sayyid Fadl and Fadl Pasha, was a Yemeni Islamic missionary and political activist who played a prominent role in the Mappila community of Kerala, India. He was the spiritual leader of Kerala Muslims as well as one of the pioneers of the Indian freedom movement. He belonged to a family of Sayyids who traced their lineage to Ali ibn Abi Talib through Mamburam Sayyid Alavi Mouladhavila. His father was Mamburam Sayyid Alavi Thangal, a Muslim mystic and political leader who had migrated from Hadramaut in Yemen to Malabar in 1798 CE to spread Islam. After his father's death in 1845 CE, he succeeded him as the spiritual leader of Kerala Muslims.
Malappuram is one of the 14 districts in the South Indian state of Kerala. The district has a unique and eventful history starting from pre-historic times. During the early medieval period, the district was the home to two of the four major kingdoms that ruled Kerala. Perumpadappu was the original hometown of the Kingdom of Cochin, which is also known as Perumbadappu Swaroopam, and Nediyiruppu was the original hometown of the Zamorin of Calicut, which is also known as Nediyiruppu Swaroopam. Besides, the original headquarters of the Palakkad Rajas were also at Athavanad in the district.

Kaathib Thayyil Mohammed Kutty Musliyar, popularly known as K. M. Moulavi or K. M. Maulavi, was an Indian religious Leader. He was a leader of the Muslim League and Islahi Movement from Malabar district. He was a religious scholar who promoted modern education, the Malayalam language, and Muslim women's education. He worked to uplift the Mappila community after the Malabar rebellion.

C. N. Ahmad Moulavi was an Indian writer of Malayalam literature, best known as the translator of the first complete publication of Quran in Malayalam. He was the author of a number of books on Islam and was reported to have contributed to the propagation of education among the Muslims of Malabar region. A member of the Kerala Sahitya Akademi during the period 1959–64, Moulavi was honoured by the academy with the distinguished fellowship in 1989.

The Battle of Pookkottur was a battle that the Mappilas of Malabar fought against the British army during anti-colonial struggles in Malabar province of Northern Kerala, India. The battle took place on 26 August 1921 at Pookkottur in Malappuram district. Indian forces were led by Vadakkuveettil Mohammed, the Secretary of the Khilafat Committee in the Malabar region. He led the force of Variyankunnath Kunjahammad Haji, while Cuthbert Buxton Lancaster and Captain P. McEnroy led the British force. The Battle played an important role in Malabar rebellion.

The Tirurangadi Taluk Office, also known as Hajur Kacheri, is a historic building located in Tirurangadi Talk of Malappuram District in the Indian state of Kerala. It houses the Tirurangadi Taluk Office since the post-independence Malabar District or British-era Madras Presidency. The Taluk office, which was once the Hajur Kacheri (Huzur Office) under the British, was one of the major administrative centers of the British government in Malabar region. The building also functioned as the headquarters of a short-lived Khilafat government during the rebellion.
Roland E. Miller is a Canadian historian and academic known for his studies on Muslims of Kerala, southern India. He is a Professor Emeritus of Islam and World Religions at Luther College, University of Regina (Saskatchewan), and Professor Emeritus at Luther Seminary, Minnesota.












