The government of the U.S. state of Missouri is organized into the state government and local government, including county government, and city and municipal government.

The federal government of the United States is the national government of the United States, a federal republic located primarily in North America, composed of 50 states, five major self-governing territories, several island possessions, and the federal district of Washington, D.C., where most of the federal government is based.

The United States Court of Appeals for the Eighth Circuit is a United States federal court with appellate jurisdiction over the following United States district courts:
The Missouri Plan is a method for the selection of judges. It originated in Missouri in 1940 and has been adopted by many states of the United States. Similar methods are used in some other countries.

The government of Maryland is conducted according to the Maryland Constitution. The United States is a federation; consequently, the government of Maryland, like the other 49 state governments, has exclusive authority over matters that lie entirely within the state's borders, except as limited by the Constitution of the United States.

The Supreme Court of Missouri is the highest court in the state of Missouri. It was established in 1820 and is located at 207 West High Street in Jefferson City, Missouri. Missouri voters have approved changes in the state's constitution to give the Supreme Court exclusive jurisdiction – the sole legal power to hear – over five types of cases on appeal. Pursuant to Article V, Section 3 of the Missouri Constitution, these cases involve:

The government of Florida is established and operated according to the Constitution of Florida and is composed of three branches of government: the executive branch consisting of the governor of Florida and the other elected and appointed constitutional officers; the legislative branch, the Florida Legislature, consisting of the Senate and House; and the judicial branch consisting of the Supreme Court of Florida and lower courts. The state also allows direct participation of the electorate by initiative, referendum, and ratification.
The Superior Court is the state court in the U.S. state of New Jersey, with statewide trial and appellate jurisdiction. The New Jersey Constitution of 1947 establishes the power of the New Jersey courts: under Article Six of the State Constitution, "judicial power shall be vested in a Supreme Court, a Superior Court, and other courts of limited jurisdiction." The Superior Court has three divisions: the Law Division which is the main trial court for cases of civil or criminal law, the Chancery Division, which tries equity law cases, and the Appellate Division, which is the intermediate appellate court in New Jersey. "Appeals may be taken to the Appellate Division of the Superior Court from the law and chancery divisions of the Superior Court and in such other causes as may be provided by law." Each division of the Superior Court is divided into various Parts."

The Oklahoma Court on the Judiciary is one of the two independent courts in the Oklahoma judiciary and has exclusive jurisdiction in adjudicating discipline and hearing cases involving the removal of a judge from office, excluding the Oklahoma Supreme Court, exercising judicial power under the Oklahoma Constitution.

The United States District Court for the Eastern District of Missouri is a trial level federal district court based in St. Louis, Missouri, with jurisdiction over fifty counties in the eastern half of Missouri. The court is one of ninety-four district-level courts which make up the first tier of the U.S. federal judicial system. Judges of this court preside over civil and criminal trials on federal matters that originate within the borders of its jurisdiction. It is organized into three divisions, with court held in St. Louis, Hannibal, and Cape Girardeau.

The government of the U.S. State of Oklahoma, established by the Oklahoma Constitution, is a republican democracy modeled after the federal government of the United States. The state government has three branches: the executive, legislative, and judicial. Through a system of separation of powers or "checks and balances," each of these branches has some authority to act on its own, some authority to regulate the other two branches, and has some of its own authority, in turn, regulated by the other branches.
The government of Virginia combines the executive, legislative and judicial branches of authority in the Commonwealth of Virginia. The current governor of Virginia is Glenn Youngkin. The State Capitol building in Richmond was designed by Thomas Jefferson, and the cornerstone was laid by Governor Patrick Henry in 1785. Virginia currently functions under the 1971 Constitution of Virginia. It is Virginia's seventh constitution. Under the Constitution, the government is composed of three branches: the legislative, the executive and the judicial.
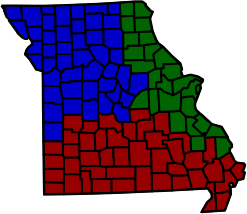
The Missouri Court of Appeals is the intermediate appellate court for the state of Missouri. The court handles most of the appeals from the Missouri Circuit Courts. The court is divided into three geographic districts: Eastern, Western, and Southern. For example, appeals taken from trials in St. Louis County will go to the Eastern District, and appeals taken from trials in Jackson County will go to the Western District.
The term county judge is applied as a descriptor, sometimes as a title, for a person who presides over a county court. In most cases, such as in Northern Ireland and the Victorian County Courts, a county judge is a judicial officer with civil or criminal jurisdiction. In the United States, however, there are some "County Courts" which exercise primarily administrative functions, in which case the County Judge may exercise largely or solely executive authority and be equivalent to the county executive in other local government areas.
The Government of Guam (GovGuam) is a presidential representative democratic system, whereby the president is the head of state and the governor is head of government, and of a multi-party system. Guam is an organized, unincorporated territory of the United States with policy relations between Guam and the US under the jurisdiction of the Office of Insular Affairs.
The Judiciary of Vermont is the state court system of Vermont, charged with Vermont law.

The Judiciary of New York is the judicial branch of the Government of New York, comprising all the courts of the State of New York.

The Missouri Circuit Courts are the state trial courts of original jurisdiction and general jurisdiction of the state of Missouri.
Theodore Hoskins, also referred to as Ted Hoskins, is an American politician with the Democratic Party. He was a member of the Missouri House of Representatives and has been mayor of Berkeley, Missouri since his election in 2012. Hoskins was born in St. Louis, Missouri, and raised in Berkeley, Missouri. He served in the United States Air Force from 1956 to 1961, and left with an honorable discharge. He received education in business administration at Florissant Valley Community College, where he obtained an associate's degree, and at the University of Missouri-St. Louis. He is married with three children, and resides in Berkeley, Missouri. Hoskins has worked in a financial capacity with Bi-State Development Agency, and is owner and CEO of T & L Automated Accounting Services.

The Supreme Court of Mauritius is the highest court of Mauritius and the final court of appeal in the Mauritian judicial system. It was established in its current form in 1850, replacing the Cour d'Appel established in 1808 during the French administration and has a permanent seat in Port Louis. There is a right of appeal from the Supreme Court of Mauritius directly to the Judicial Committee of the Privy Council in London. The Judicial Committee of the Privy Council (JCPC) is the court of final appeal for Mauritius.