
Fortified wine is a wine to which a distilled spirit, usually brandy, has been added. In the course of some centuries, winemakers have developed many different styles of fortified wine, including port, sherry, madeira, Marsala, Commandaria wine, and the aromatised wine vermouth.

Sicilian cuisine is the style of cooking on the island of Sicily. It shows traces of all cultures that have existed on the island of Sicily over the last two millennia. Although its cuisine has much in common with Italian cuisine, Sicilian food also has Greek, Spanish, French and Arab influences.

Marsala is an Italian town located in the Province of Trapani in the westernmost part of Sicily. Marsala is the most populated town in its province and the fifth in Sicily.

Marsala is a fortified wine, dry or sweet, produced in the region surrounding the Italian city of Marsala in Sicily. Marsala first received Denominazione di Origine Controllata (DOC) status in 1969. The European Union grants Protected Designation of Origin (PDO) status to Marsala, and most other countries limit the use of the term Marsala to products from the Marsala area.
The term Lombard refers to people or things related to Lombardy, a region in northern Italy.

The Province of Agrigento is a province in the autonomous island region of Sicily in Italy, situated on its south-western coast. Following the suppression of the Sicilian provinces, it was replaced in 2015 by the Free municipal consortium of Agrigento. It has an area of 3,041.90 square kilometres (1,174.48 sq mi), and a total population of 474,493. There are 43 comunes in the province.

Trapani is a province in the autonomous island region of Sicily, southern Italy. Following the suppression of the Sicilian provinces, it was replaced in 2015 by the Free municipal consortium of Trapani. Its capital is the city of Trapani. It has an area of 2,469.62 square kilometres (953.53 sq mi) and a total population of 433,826 (2017). There are 25 comunes in the province.

Nero d'Avola is "the most important red wine grape in Sicily" and is one of Italy's most important indigenous varieties. It is named after Avola in the far south of Sicily, and its wines are compared to New World Shirazes, with sweet tannins and plum or peppery flavours. It also contributes to Marsala Rubino blends.
The Florio family is a prominent entrepreneurial Italian family who started many lucrative activities in Sicily involving above all the exportation of Sicilian products in the nineteenth century, in some ways redeeming Sicily from feudal immobility. The family extended its interests to shipping, shipbuilding, fisheries, mining, metallurgy and ceramics.

Grillo, also known as Riddu and Rossese bianco, is a white Italian wine grape variety that withstands high temperatures and is widely used in Sicilian winemaking and, in particular, for making Marsala. Its origins are uncertain, but it may have been introduced into the island of Sicily from Apulia. It was already widely planted in the Province of Trapani by 1897; today it may be grown throughout Sicily and also in the Aeolian Islands.
Balestrate is a comune (municipality) in the Metropolitan City of Palermo in the Italian region Sicily, located about 25 kilometres (16 mi) southwest of Palermo. As of 31 July 2015, it had a population of 6,505 and an area of 3.9 square kilometres (1.5 sq mi).

Chicken marsala is an Italian-American dish of chicken escalopes in a Marsala wine sauce. It is a variation of traditional Italian scaloppina dishes, of which there are many varieties throughout Italy. The dish dates to the 19th century, when it may have originated with English families who lived in western Sicily, where Marsala wine is produced.

The Marsala Ship is the oldest known warship wreck in existence and it was found in a harbor at Sicily, Italy. The discovery came about accidentally by a commercial dredging operation. A four-year excavation took place for historical reasons to save what was left of the ruins of the 2000 year old Punic warship. There were ancient artifacts found with the wreckage. The remains of the ship are displayed at the Archaeological Museum Baglio Anselmi specially built for it.
Ansonica or Inzolia is a white Italian wine grape planted primarily in western Sicily where it can be used to produce Marsala wine. The grape is noted for its nutty aroma. In Tuscany, the grape is known as Ansonica. It is the chief component of the Tuscan D.O.C. Ansonica Costa dell'Argentario, which is located on the extreme southern coast of Tuscany and on the island of Giglio.
Perricone is a red Italian wine grape variety that is grown in Sicily. In the late 20th century there was around 1000 hectares/2,500 acres of the grape planted throughout the island. According to wine expert Oz Clarke in Sicily Perricone is used to make full bodied, deeply colored, highly alcoholic wines.
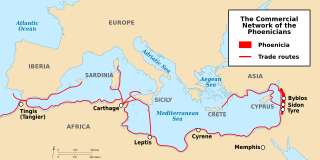
The culture of the ancient Phoenicians was one of the first to have had a significant effect on the history of wine. Phoenicia was a civilization centered in current day Lebanon. Between 1550 BC and 300 BC, the Phoenicians developed a maritime trading culture that expanded their influence from the Levant to North Africa, the Greek Isles, Sicily, and the Iberian Peninsula. Through contact and trade, they spread not only their alphabet but also their knowledge of viticulture and winemaking, including the propagation of several ancestral varieties of the Vitis vinifera species of wine grapes.
Albanello bianco is a white Italian wine grape variety grown primarily in Sicily where it has a long tradition producing sweet dessert-style wines from grapes that have been dried in the sun on mats for several days after harvest. In the eighteenth century, the grape was an important component in the rare and expensive Marsala-style wine Ambrato di Comiso.

Vincenzo Florio Sr. was an Italian entrepreneur and politician, member of the rich Florio economic dynasty, one of the wealthiest Sicilian families during the late 19th century.
Marsala is an Italian surname, originated from the city of Marsala, in Sicily. Notable people with the surname include:
The Whitaker family is an US-American family notable for its involvement in the life of Sicily. Benjamin Ingham set up a wine business in Marsala and his relative Joseph Whitaker expanded and diversified the business. Their story is told in Raleigh Trevelyan's 1972 Princes Under the Volcano: Two Hundred Years of a British Dynasty in Sicily.











