
Lumpkin County is a county located in the north central portion of the U.S. state of Georgia. As of the 2010 census, the population was 29,966. Its county seat is Dahlonega.

Monroe is a city in Walton County, Georgia, United States. It is located both 1 hour east of Atlanta via US-78 and GA-138 to I-20 westbound and east of Hartsfield Jackson Int'l Airport and is part of the exurban cities in the Atlanta metropolitan area. Monroe is also a city known for its accessibility to Conyers just 20 minutes away and Lawrenceville 35 minutes away. The population was 13,234 at the 2010 census and 13,858 at the 2016 census.

Athens, officially Athens–Clarke County, is a consolidated city–county and college town in the U.S. state of Georgia. Athens lies about 70 mi (113 km) northeast of downtown Atlanta, a Global City and the cultural and economic center of the Atlanta metropolitan area, being in the top ten of the largest metropolitan areas in the nation. It is a component of the larger Atlanta–Athens–Clarke County–Sandy Springs Combined Statistical Area, a trading area. The University of Georgia, the state's flagship public university and a R1 research institution, is in the city and contributed to its initial growth. In 1991, after a vote the preceding year, the original City of Athens abandoned its charter to form a unified government with Clarke County, referred to jointly as Athens–Clarke County. As of 2017, the U.S. Census Bureau's estimated population of the consolidated city-county was 125,691; the entire county including Winterville and Bogart had a population of 127,064. Athens is the sixth-largest city in Georgia, and the principal city of the Athens metropolitan area, which had a 2017 estimated population of 209,271, according to the U.S. Census Bureau. The city is dominated by a pervasive student culture and music scene centered on downtown Athens, next to the University of Georgia's North Campus. Major music acts associated with Athens include numerous alternative rock bands such as R.E.M., the B-52's, Widespread Panic, and Neutral Milk Hotel. The city is also known as a recording site for such groups as the Atlanta-based Indigo Girls.

The history of Atlanta dates back to 1836, when Georgia decided to build a railroad to the U.S. Midwest and a location was chosen to be the line's terminus. The stake marking the founding of "Terminus" was driven into the ground in 1837. In 1839, homes and a store were built there and the settlement grew. Between 1845 and 1854, rail lines arrived from four different directions, and the rapidly growing town quickly became the rail hub for the entire Southern United States. During the American Civil War, Atlanta, as a distribution hub, became the target of a major Union campaign, and in 1864, Union William Sherman's troops set on fire and destroyed the city's assets and buildings, save churches and hospitals. After the war, the population grew rapidly, as did manufacturing, while the city retained its role as a rail hub. Coca-Cola was launched here in 1886 and grew into an Atlanta-based world empire. Electric streetcars arrived in 1889, and the city added new "streetcar suburbs".

The Western & Atlantic Railroad of the State of Georgia (W&A) is a government-owned railroad and is currently leased by CSX, which CSX operates in the Southeastern United States from Atlanta, Georgia, to Chattanooga, Tennessee.

Jonathan Norcross, was the fourth Mayor of Atlanta, Georgia. He was dubbed the "Father of Atlanta" and "hard fighter of everything." - Henry W. Grady

Oakland Cemetery is one of the largest cemetery green spaces, in Atlanta, Georgia, U.S. Founded as Atlanta Cemetery in 1850 on six acres (2.4 hectares) of land southeast of the city, it was renamed in 1872 to reflect the large number of oak and magnolia trees growing in the area. By that time, the city had grown and the cemetery had enlarged correspondingly to the current 48 acres (190,000 m2). Since then, Atlanta has continued to expand so that the cemetery is now located in the center of the city. Oakland is an excellent example of a Victorian-style cemetery, and reflects the "garden cemetery" movement started and exemplified by Mount Auburn Cemetery in Massachusetts.

Lemuel Pratt Grant (1817–1893) was an American engineer and businessman. He was Atlanta's quintessential railroad man as well as a major landowner and civic leader. In railroads he served as a laborer, chief engineer, speculator and executive all over the South. As part of his speculation, he owned enormous tracts of land in strategic areas. For example, at one point he owned more than 600 acres (240 ha) in what is now Atlanta. He designed and built Atlanta's defenses during the American Civil War and afterwards became an important civic leader: donating the land for Grant Park, Atlanta's first large park, and serving as councilman and on various boards and committees. His mansion is one of only four remaining original antebellum houses in the city of Atlanta.

Richard Peters was an American railroad man and a founder of Atlanta, Georgia, in the 1840s.

Dr. Joseph Thompson was an early settler of Atlanta, Georgia, hotelier, and real-estate investor.

Downtown Atlanta is the central business district of Atlanta, Georgia, United States. The largest of the city's three commercial districts, it is the location of many corporate or regional headquarters; city, county, state and federal government facilities; Georgia State University; sporting venues; and most of Atlanta's tourist attractions. It measures approximately four square miles, and had 26,700 residents as of 2010. Similar to other central business districts in the United States, it has recently undergone a transformation that included the construction of new condos and lofts, renovation of historic buildings, and arrival of new residents and businesses.

Rufus Brown Bullock was a Republican Party politician and businessman in Georgia. During the Reconstruction Era he served as the state's governor and called for equal economic opportunity and political rights for blacks and whites in Georgia. He also promoted public education for both, and encouraged railroads, banks, and industrial development. During his governorship he requested federal military help to ensure the rights of freedmen; this made him "the most hated man in the state", and he had to flee the state without completing his term. After returning to Georgia and being found "not guilty" of corruption charges, for three decades afterwards he was an esteemed private citizen.

State Route 29 (SR 29) is a 98.1-mile-long (157.9 km) state highway that travels southeast-to-northwest through portions of Toombs, Montgomery, Treutlen, Laurens, Wilkinson, and Baldwin counties in the central part of the U.S. state of Georgia. The highway connects the Vidalia area with the Milledgeville area, via the Dublin area.
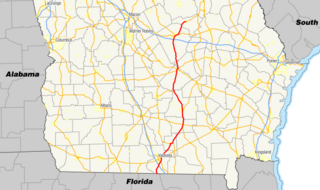
State Route 31 (SR 31) is a 166.9-mile-long (268.6 km) state highway that travels south-to-north through portions of Lowndes, Lanier, Clinch, Atkinson, Coffee, Telfair, Wheeler, Dodge, Laurens, and Johnson counties in the south-central part of the U.S. state of Georgia. The highway connects the Florida state line, south of Clyattville with Wrightsville, via Valdosta, Douglas, and Dublin.

State Route 60 (SR 60) is a 90.1-mile-long (145.0 km) state highway that travels southeast-to-northwest through portions of Jackson, Hall, Lumpkin, Union, and Fannin counties in the north-central part of the U.S. state of Georgia. The highway connects the Braselton area with McCaysville at the Tennessee state line, via Gainesville and Dahlonega.
There are at least thirteen current and three former special routes of U.S. Route 27.

The Big Bethel AME Church is the oldest African-American congregation in the Sweet Auburn neighborhood of Atlanta, Georgia, and according to AME historical documents, it is the mother church of AME in North Georgia. It is located at 220 Auburn Avenue NE in the Sweet Auburn neighborhood. It is the "first" church on the North Atlanta District, in the Atlanta-North Georgia Annual Conference of the African Methodist Episcopal Church.

Streetcars originally operated in Atlanta downtown and into the surrounding areas from 1871 until the final line's closure in 1949.























