Related Research Articles

Upper Peru is a name for the land that was governed by the Real Audiencia of Charcas. The name originated in Buenos Aires towards the end of the 18th century after the Audiencia of Charcas was transferred from the Viceroyalty of Peru to the Viceroyalty of the Río de la Plata in 1776. It comprised the governorships of Potosí, La Paz, Cochabamba, Chiquitos, Moxos and Charcas.

Mato Grosso is one of the states of Brazil, the third-largest by area, located in the western part of the country.

Mato Grosso do Sul is one of the Midwestern states of Brazil. Its total area of 357,125 square kilometers, or 137,891 square miles, is roughly the same size as Germany.

Rondônia is a state in Brazil, located in the northern part of the country. To the west is a short border with the state of Acre, to the north is the state of Amazonas, in the east is Mato Grosso, and in the south and southwest is Bolivia. Its capital is Porto Velho. The state was named after Cândido Rondon.

Classification of indigenous peoples of the Americas is based upon cultural regions, geography, and linguistics. Anthropologists have named various cultural regions, with fluid boundaries, that are generally agreed upon with some variation. These cultural regions are broadly based upon the locations of indigenous peoples of the Americas from early European and African contact beginning in the late 15th century. When indigenous peoples have been forcibly removed by nation-states, they retain their original geographic classification. Some groups span multiple cultural regions.
Matos or Mattos may refer to:

Bauru is a Brazilian municipality in midwestern region of the state of São Paulo. It is the main city of the mesoregion and microregion of Bauru. The population is 366,992 in an area of 667.68 km². Established in 1896, its boundaries are Reginópolis to the north, Arealva to the northeast, Pederneiras to the east, Agudos and Piratininga to the south and Avaí to the west.

The Paraguay River is a major river in south-central South America, running through Brazil, Bolivia, Paraguay and Argentina. It flows about 2,621 kilometres (1,629 mi) from its headwaters in the Brazilian state of Mato Grosso to its confluence with the Paraná River north of Corrientes and Resistencia.

The Gran Chaco or Dry Chaco is a sparsely populated, hot and semi-arid lowland natural region of the Río de la Plata basin, divided among eastern Bolivia, western Paraguay, northern Argentina and a portion of the Brazilian states of Mato Grosso and Mato Grosso do Sul, where it is connected with the Pantanal region. This land is sometimes called the Chaco Plain.

The Pantanal is a natural region encompassing the world's largest tropical wetland area. It is located mostly within the Brazilian state of Mato Grosso do Sul, but it extends into Mato Grosso and portions of Bolivia and Paraguay. It sprawls over an area estimated at between 140,000 and 195,000 square kilometres. Various subregional ecosystems exist, each with distinct hydrological, geological and ecological characteristics; up to 12 of them have been defined.

CorumbáPortuguese pronunciation: [koɾũˈba] is a municipality in the Brazilian state of Mato Grosso do Sul, 425 km northwest of Campo Grande, the state's capital. It has a population of approximately 111,000 inhabitants, and its economy is based mainly on agriculture, animal husbandry, mineral extraction, and tourism, being the gateway to the biggest wetlands of the world, the Pantanal.

Guaporé River is a river in western Brazil and northeastern Bolivia. It is 1,530 km (950 mi) long; 970 km (600 mi) of the river forms the border between Brazil and Bolivia.
The Mbayá or Mbyá are an ethnic group, commonly called "Indians", which formerly ranged on both sides of the Paraguay River, on the north and northwestern Paraguay frontier, eastern Bolivia, and in the adjacent province of Mato Grosso do Sul, Brazil. They have also been called Caduveo. In the 16th century the Mbayá were called Guaycuru, a name later used generically for all the nomadic and semi-nomadic Indians of the Gran Chaco. The Kadiwéu people of Brazil are the surviving branch of the Mbayá.
The flammulated bamboo tyrant, also called flammulated pygmy tyrant is a species of bird in the family Tyrannidae, the tyrant flycatchers. It is found in Amazonian Peru and Bolivia, and the bordering states of Brazil's northwest, the North Region. Its natural habitat is subtropical or tropical moist lowland forests.
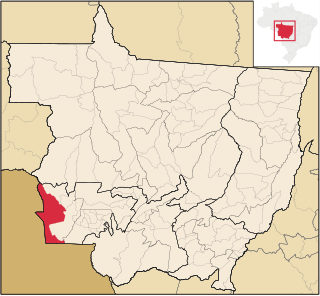
Vila Bela da Santíssima Trindade is a Brazilian municipality in Mato Grosso with 14,523 (2009) inhabitants. It is located at upper Guaporé River close to the border with Bolivia. It served as the capital of the Captaincy of Mato Grosso from 1752 to 1820.
The Curiche Grande River is a river of Mato Grosso state in western Brazil. It forms a portion of the international border between Brazil and Bolivia.

The São Lourenço River is a tributary of the Paraguay River within the Pantanal, an alluvial plain that spans portions of Brazil, Bolivia and Paraguay. The São Lourenço river basin lies in the Mato Grosso state of Brazil.
The Verde River (Bolivia) is a river of Mato Grosso state in western Brazil.

The Bolivia–Brazil border is the international border between the territories of Bolivia and Brazil. It extends from Corumbá, Mato Grosso do Sul, to Assis Brasil, in Acre.
References
- Rand McNally, The New International Atlas, 1993.
| This Beni Department location article is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |
| This article related to a river in Bolivia is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |
- ↑ "Río Matos". Ramsar Sites Information Service. Retrieved 25 April 2018.